There are two levels of insulation: high-efficiency insulation, which meets the 2015 International Energy Conservation Code, and ultra-efficient insulation, which is 25% more efficient than this national code. Using high-efficiency and ultra-efficient insulation along with professional installation...
Showing results 1 - 44 of 44
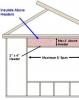
Solid wood headers above windows and doors are often oversized for the load they need to carry. And the solid wood creates a cold spot because there is no insulation. On a non-load-bearing wall (a gable-end wall), the header space can often be left open so it can be insulated like the rest of the...
There are two levels of floor insulation: high-efficiency insulation, which meets the 2015 International Energy Conservation Code, and ultra-efficient insulation, which is 25% more efficient than this national code. Using high-efficiency and ultra-efficient insulation along with professional...
There are two levels of attic insulation: high-efficiency insulation, which meets the 2015 International Energy Conservation Code, and ultra-efficient insulation, which is 25% more efficient than this national code. Using high-efficiency and ultra-efficient insulation along with professional...
There are two levels of foundation insulation: high-efficiency insulation, which meets the 2015 International Energy Conservation Code, and ultra-efficient insulation, which is 25% more efficient than this national code. Using high-efficiency and ultra-efficient insulation, along with professional...
There are two levels of wall insulation: high-efficiency insulation, which meets the 2015 International Energy Conservation Code, and ultra-efficient insulation, which is 25% more efficient than this national code. Using high-efficiency and ultra-efficient insulation along with professional...
Poorly installed insulation can result in higher heating and cooling costs, comfort problems, mold and other moisture problems. Professionally-installed insulation meets industry best practices as specified for Grade 1 installation by the Residential Energy Services Network (RESNET). This includes...
Without adequate duct insulation, there can be significant heat loss or heat gain as conditioned air travels through the comfort delivery system. This is especially true where ducts are located in an uninsulated attic or crawlspace. Insulation significantly reduces this energy loss and helps ensure...
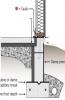
Foundation slab edges that are not insulated can have excessive heat loss and gain, along with comfort challenges due to cold and hot floors. Rigid foam insulation along the outside or inside edge of the foundation should be used to prevent this heat loss or gain.
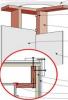
Wood framing accounts for 24% of conventionally framed walls and 14% of advanced-framed walls. This represents a large thermal hole since wood has about one-fourth the thermal resistance of most insulation materials. This problem is effectively addressed with a continuous thermal blanket of rigid...
Poorly installed insulation and inadequate amounts of insulation can result in rooms that are too hot in the summer, too cold in the winter, temperatures that vary from room to room, and homes with unnecessarily high utility bills. High-performance insulation systems include generous amounts of...
Insulated concrete forms use hollow rigid foam insulation blocks that are stacked like bricks to form walls that are then reinforced with steel rebar and filled with poured concrete. These systems greatly reduce the amount of wood framing in exterior walls. The foam insulation creates a thermal...
Structural insulated panels (SIPs) are a sandwich made up of foam insulation glued between two layers of sheathing (e.g., oriented strand board, magnesium oxide board, or drywall). SIP wall and roof panels are produced in a factory and come to the job site clean, dry, straight, and precisely made to...
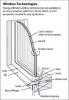
Homes with high-performance window systems are more comfortable and consume less energy than homes with traditional windows. High-efficiency ENERGY STAR-rated windows perform at least 15% better than a standard window and have an insulating value of R-3 or higher. Ultra-efficient windows perform at...
Power outages, freezing water pipes, and ice dams are among the risks that accompany severe winter weather. A thoroughly air sealed and insulated house can stay warm for hours or even days if the power goes out. Water pipes should be protected from freezing conditions by not locating them in...
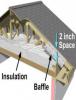
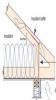
Attics are insulated to reduce the amount of heat loss or gain through the ceiling. However, sloped attic framing or trusses are inherently shallow at the roof eaves, leaving inadequate space for full insulation. As a result, there can be excessive thermal losses and gains along the roof edge...
Traditional wall framing uses more studs than necessary to structurally support a wall. Using more studs not only increases the amount of lumber used, it decreases the amount of available space for insulation, and increases the surface area of lumber. Framing materials are not good insulators; heat...
In termite-prone areas, rigid foam insulation should not be used on the exterior of the foundations below grade because they can provide a pathway for infestation. Termite detection systems discourage termites and allow for inspection. This includes adherence to local codes that require at least a...
Traditional wall framing uses more lumber than is necessary and limits a builder’s ability to insulate walls. Wood and other framing materials are not good insulators. Heat can move through them from one side of the wall to the other. High-efficiency advanced framing uses techniques like thicker...
Even when insulated, homes can still have unnecessary heat loss due to the ability of heat to transfer through the wood framing. Because framing can comprise up to one-fourth of the wall in stud-framed walls, the studs can significantly contribute to heat loss. To address this, a continuous thermal...
Comfort systems installed in vented attics work much better when they are buried in insulation. Vented attics can reach extreme temperatures. Deeply burying the ducts in the attic's insulation provides significant protection from these harsh conditions. The ducts need to be tightly sealed to ensure...
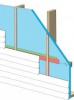
One way to achieve very high levels of insulation in walls is to build two stud walls separated by an air space. The inner wall provides framing for attaching gypsum board; the outer wall does the same for sheathing, a weather barrier, and siding. Two 2x4 framed walls spaced three inches apart will...
Traditionally built homes use three or more studs in exterior wall corners leaving minimal space for insulation, resulting in thermal losses. By only using two studs and a clip to help hold the drywall, high-efficiency corner framing allows for insulation in the corners of a home and reduces heat...
Heat loss often occurs where interior walls intersect with exterior walls in traditionally built homes because the additional studs required for nailing drywall leave minimal space for insulation. In contrast, high-efficiency wall intersections use techniques that require less wood, provide required...
Poorly air-sealed homes are less comfortable and cost more to maintain because they provide a pathway for drafts, cold spots, moisture, and insects into the home. Comprehensive draft protection includes a continuous air barrier around the whole house along with caulking and sealing in all holes and...
Hurricanes pose a serious threat along the Gulf and Atlantic coasts. Designers and builders can choose from a variety of features to help minimize losses from high winds and the impact of flying debris. Measures are available to fortify all typical construction types, including concrete, masonry...
In termite-prone areas, rigid foam insulation should not be used on the exterior of foundations below grade. To discourage termites and allow for inspection, some codes require that rigid foam insulation on the exterior of the foundation be held at least six inches above the ground. Wood siding...
There are two levels of window efficiency relative to standard windows: high-efficiency (e.g., ENERGY STAR Certified windows), which perform at least 15% better than standard windows, and ultra-efficient (e.g., most triple-glazed windows) which perform at least 50% better. These windows use a...
Designers and builders can choose from a variety of features to help minimize losses from high winds. The choice of features will depend on the severity and type of local wind events, but the entire continental United States is exposed to high winds. This is especially true for tornado and hurricane...
A whole-house draft barrier is a continuous layer of air-tight materials that block air leaks. This barrier can be integrated with other materials to also function as a water barrier, thermal barrier, and vapor barrier. For example, rigid foam insulation can be used to block thermal flow as well as...
Tornados pose a serious threat in the midsection and southern parts of the nation, but many other regions are also at risk. Designers and builders can choose from a variety of features to help minimize losses from high winds and the impact of flying debris. Measures are available to fortify all...
Air needs to flow from the central heating and cooling comfort system to living spaces and back again. Comfort crossover vents allow air to flow from each bedroom to the central return ducts, often located in hallways. The vents are typically built into the ceiling on either side of the adjoining...
Traditional vented attics can reach extreme temperatures compared to living spaces and are inhospitable to heating and cooling equipment and ducts. Comfort systems work much better when they are inside conditioned space. That’s why unvented attics that are fully insulated provide a more efficient...
A home energy rater will conduct an in-depth energy performance assessment of a home using diagnostic testing equipment, such as a blower door test, a duct leakage tester, a combustion analyzer, and infrared camera to determine the amount and location of air leaks in the building envelope, the...
As conditioned air flows through the ducts from heating and cooling equipment to the spaces where people live, excessive length, sharp bends, crimps, and crushed or disconnected ducts can compromise air flow, reducing comfort and causing the HVAC system to work harder than necessary. Professionally...
Draft tests are usually performed by a home energy performance professional with a device called a blower door. This test determines how much air is leaking through cracks and holes in the home’s walls, ceilings, and floors. The blower door equipment uses a strong fan to pressurize or depressurize a...
Because heating and cooling costs are the largest contributors to utility bills, inefficient comfort equipment creates significant costs for homeowners. Not installing high- or ultra-efficient comfort equipment is a missed opportunity, especially if the proper steps have been taken to insulate and...
A thermal x-ray uses an infrared camera that senses radiative surface temperatures rather than visible light. As a result, it takes photographs or videos that expose surface temperature anomalies. When looking at an infrared image, darker areas are cooler and lighter areas are warmer. For example...
A wall water barrier blocks the penetration of moisture that gets past the siding and provides a path for it to safely drain down and away from the wall. The water-resistant surface could be house wrap that is lapped shingle style, water-resistant rigid foam insulation that is taped or sealed at all...
Porous concrete foundations should be treated to avoid water seepage into the home. Builders treat below-grade walls with a damp-proof coating such as an asphalt emulsion. For more reiorous protection, a plastic drainage plane may be used instead of, or in addition to, the damp proof coating. This...
In addition to the savings that come with being an efficient heat pump, ductless heat pumps save energy and money by avoiding the use of ducts or using much more compact duct layouts inside the conditioned space. That’s because ducts are often sources of heat loss where not properly insulated and...
Conditioned air is often lost in transition from comfort equipment to living spaces because of poorly designed duct layouts and poor installation practices, which cause homeowners to pay for conditioned air that never reaches the living spaces of their home. Poor duct layouts with overly long duct...
Radon is an odorless, colorless radioactive gas naturally occurring in the earth that can cause lung cancer in humans. It can enter homes through foundations and basements unless steps are taken to prevent it. Radon-resistant homes help minimize this risk by including a radon barrier with a fully...
The roof is the home's primary defense against water intrusion from rain, snow, and ice. Water that seeps into the house through the roof can quickly ruin insulation, create conditions for mold growth and pest invasion, and even set into motion structural rot. Valleys and penetrations through the...