The Building Science Tools of Choice
The stand-alone RED Calc tools are intended for one-off situations for a quick calculation when you do not need to save or print a report. No login is required. For a more modern and professional experience, check out the RED Calc Pro web app.
RED Calc Tools are used daily by home performance analysts; WAP energy auditors, inspectors, and monitors; HERS raters; design professionals; building inspectors; engineers; and building science researchers.
Getting Started with RED Calc
Supported Browsers
The advanced features of RED Calc will run on most versions of these web browsers:
- Chrome
- Safari
- Opera
- Firefox
- Edge
- Internet Explorer (version 8 or higher)
Using the Buttons at the Top of RED Calc Tools
- The Reset button:
 is used to reset the input values of the current tool to the “factory” values, usually blank.
is used to reset the input values of the current tool to the “factory” values, usually blank. - The Print button:
 is used to print the tool without the surrounding web page content.
is used to print the tool without the surrounding web page content.
Warning/Error Icons
The three icons explained below are indications of different types of errors and a warning. These errors will not be detected until you click outside of the input box.

A warning icon to the right of an input indicates the entered value is outside the normal range for the input. You may continue with your use of the tool without an error. Clicking on this icon will bring up a dialogue box showing what the normal range is. This is merely a heads-up to you to check your entered value.
An error icon indicates that the entered value is outside the allowed range for the input. Clicking on this icon will bring up a dialogue box showing what the allowed range is. If you see this icon, you will NOT be able to proceed without entering an allowed value.
A syntax error icon indicates the RED Calculation Engine could not make sense of what you entered. Clicking on this icon will bring up a dialogue box explaining what type of entry is expected.
Using Context-Sensitive Pop-Up Help
If you have a question about an input or a result, just click on the label for an explanation. Simply click on the “x” in the upper right of the dialogue box to close the box. You may open more than one dialogue box at a time.
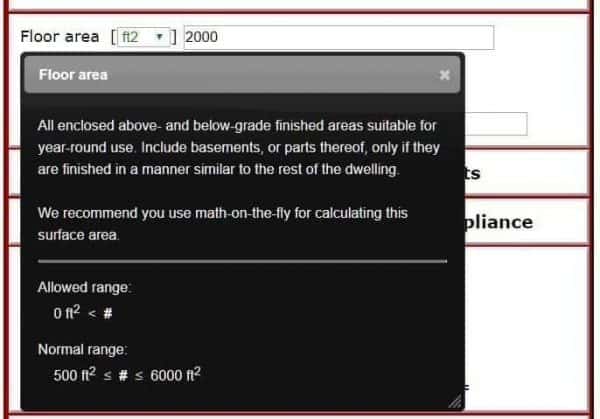
Math On-The-Fly
Math on-the-fly gives you the ability to enter mathematical equations in an input box, such as![]()
When you tab or click away from the input, your equation is replaced with the result, 1980 for this example. To edit your inputs, just click back in the input box and your entered values and mathematical operators are visible. This feature provides a powerful calculator in each tool input box. The available mathematical operations include +, -, *, /, and “( )”; or addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and parentheses.
White space (blanks in your created equation) are ignored, so enter blank spaces if you wish.
Tool categories
Ventilation Sizing
Airflow Measurement
Insulation and R-Value
Moisture
Domestic Hot Water
Electrical Usage
Weather Data
Ventilation Sizing

These RED Calc tools calculate dwelling-unit ventilation based on the ASHRAE 62.2 Standard, Ventilation and Acceptable Indoor Air Quality in Residential Buildings, which is updated by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) every three years. When used correctly, these RED tools comply in all instances with the 62.2 Standard.
ASHRAE 62.2-2016
Calculates the required minimum flow rate of dwelling-unit ventilation. Complies with ASHRAE 62.2-2016, including Alternative Compliance Path, fan run-time, and leakage-rate solver. Scope includes detached dwellings and dwelling units in multifamily buildings of any height.
ASHRAE 62.2-2013
Calculates the required minimum flow rate of dwelling-unit ventilation. Complies with ASHRAE 62.2-2013, including Alternative Compliance Path, fan run-time, and leakage-rate solver. Scope includes detached dwellings and dwelling units in multifamily buildings of three stories or less.
ASHRAE 62.2-2010
Calculates the required minimum flow rate of dwelling-unit ventilation. Complies with ASHRAE 62.2-2010, including Alternative Compliance Path, and fan run-time. Scope includes detached dwellings and dwelling units in multifamily buildings of three stories or less.
ASHRAE 62.2-2010 California
Calculates the required minimum flow rate of dwelling-unit ventilation. Specifically for the state of California and in compliance with 2013 Title 24, Chapter 6, The tool includes Alternative Compliance Path and fan run-time. A hybrid version of ASHRAE 62.2-2010 and ASHRAE 62.2-2013. Scope includes detached dwellings and dwelling units in multifamily buildings of three stories or less.
Airflow Measurement
This group of RED Calc tools calculates two important and broad categories of building science: Air measurement, including air flow in a duct, and air leakage, including ACH50 and Equivalent Leakage Area. As our residential buildings become tighter as a result of efforts to save energy and curb global climate change, this data becomes more important.
Advanced Infiltration (AIM-2)
Calculates hourly (low, average, and high) stack, wind, and total infiltration; the effect of combining whole-building ventilation and natural infiltration; and the load on heating and/or cooling systems due to ventilation and infiltration. Additionally, three separate charts provide graphical representations of these results. All calculations are based on TMY3 weather data and may be set to a specific date range (one day to one year).
Air Leakage Metrics
Calculates all the useful air leakage metrics. Enter one of eight Air Leakage Metrics to solve for seven others. You choose which to solve with this “solve-all” tool. Includes leakage at 50Pa, ACH50, Equivalent Leakage Area (ELA), Effective Leakage Area (EqLA), Specific leakage area, Leakage at 50Pa/floor area, Leakage at 50Pa /surface area, and Leakage coefficient.
Box Airflow Measurement
Calculates required exhaust airflow rate with your custom-made box and a digital manometer. The size of the box may vary.
Depressurization Analysis
Calculates Depressurization Tightness Limit (DTL) CFM50, the maximum exhaust appliance airflow rate for a given DTL or house pressure, and the negative pressure threshold for a given DTL and appliance airflow rate. This is a “solve-all” tool, meaning you can solve for all or most of the tool variables by checking the radio button to the left of the variable name.
Design Infiltration
Calculates stack-induced, wind-induced, and the combined infiltration, as well as the resulting sensible heat loss or gain, for a given indoor/outdoor temperature and wind speed. The primary use case is determining the design infiltration rate used in a heating or cooling load calculation for system sizing.
Pitot Tube Airflow Measurement
Calculates airflow rate in supply or return duct. With a pitot tube and a digital manometer (pressure gauge), you can calculate duct airflow by inserting your pitot tube through the side of the duct into the air stream. This tool allows for adjustment to altitude, duct air temperature, and pitot tube K-factor. The tool includes a calculator for the cross-sectional area of the duct, whether rectangular, round, or oval.
Zone Pressure Diagnostics (ZPD)
Calculates air leakage through and leakage area in the interior and exterior pressure boundaries of a zone. Find the zone’s contribution to whole-house leakage. Appraise the effectiveness of your air sealing work, and much more. Simply the best ZPD tool ever! No need to measure openings, hole and door methods combined and accuracy is reported.
Insulation and R-Value

This bundle of RED Calc includes tools for determining R-Value, the number of bags of insulation, the density of insulation, and more.
Dense-Pack Insulation
Calculates installed density or the number of bags of insulation. This tool will work of any dense-pack insulation and accommodates hidden or exposed framing in ceiling, walls, and floors.
Infrared R-Value
This tool calculates R-value or interior surface temperature with your infrared measurement device (infrared camera or thermometer). This is a great tool for determining if a wall is insulated or not and, if it is, what the effective R-value is.
Loose-Fill Insulation
Calculates installed depth, settled depth, settled R-value, or the number of bags of insulation when installing loose-fill cellulose or fiberglass. This tool works best for open-joist attic insulation.
Parallel Path R-Value
Calculates overall R-value, U-factor, or total UA value of a building section made up of up to 10 distinct R-values. For example, the framed area and the insulated area of a wall (2 distinct R-values).
Surface Heat Transfer
Used for determining surface heat transfer. This solve-all tool also allows you to solve for temperature difference, time, R-value, and area.
Moisture
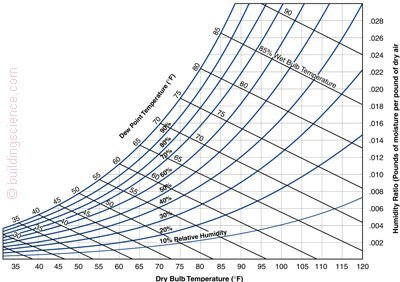
This group of RED Calc tools includes all you need for analyzing moisture issues in buildings, including dew point temperatures, vapor pressure, humidity ratios, and much more.
Moisture Metrics
Calculates dry-bulb temperature, saturation (equilibrium) vapor pressure, relative humidity, dew point temperature, water vapor density, vapor pressure, wet-bulb temperature, and humidity ratio.
Wood Moisture
Calculates relative humidity or wood Equilibrium Moisure Content (EMC). Enter the air temperature and equilibrium moisture content of a sample piece of wood that has been in the space. The RED tool will calculate the average relative humidity for you. Or enter the air temperature and the EMC to find the average relative humidity.
Domestic Hot Water (DHW)
These tools help you analyze hot water use, allow you to compare hot water systems, and guide you through the procedure of determining flow rate from a fixture.
DHW Average Daily Usage
Calculates average daily hot water use based on the amount of hot water used by various appliances and use incidents. Default usage values are included.
DHW First Hour Rating
Calculates the First Hour Rating for the purpose of properly sizing a storage water heater. This method is based on guidance from the Air-Conditioning, Heating and Refrigeration Institute (AHRI), the industry standard for sizing storage water heaters.
DHW Instantaneous Sizing
A “solve-all” tool used for sizing an instantaneous (tankless) hot water heater. It can also be used to determine the maximum hot water flow rate for a given system and temperature rise.
DHW Systems Comparison
Used for comparing up to three DHW systems with a base-case system. You can use this tool for any hot water system for which you have an Energy Factor (EF) or Uniform Energy Factor (UEF) and a fuel price per unit. This tool can also be used to determine the savings from lowering the hot water supply temperature.
DHW Volume per Use
Calculates the volume of hot water used given an amount of mixed (hot + cold) water used and the temperatures of the hot, cold, and mixed water. The amount of mixed water can be specified by volume directly, or from a flow rate and duration.
Water Flow Rate
This is a “solve-all” tool that relates the volume of water drawn, the duration of the water draw, and the flow rate. The primary expected use-case is determining flow rate using a test container with a known volume and a stopwatch. The tool was developed as an aid in using the DHW Volume per Use tool when the flow rate is used and must be determined, but may also be used for more general purposes.
Electrical Usage
If you need to determine the cost of operating an electrical device, this tool will help you.
Electrical Usage
Calculates the electrical cost of operating a ventilation fan (or another electrical device) for a year (or another period). This tool will work for continuous or intermittent operation of a fan.
Weather Data
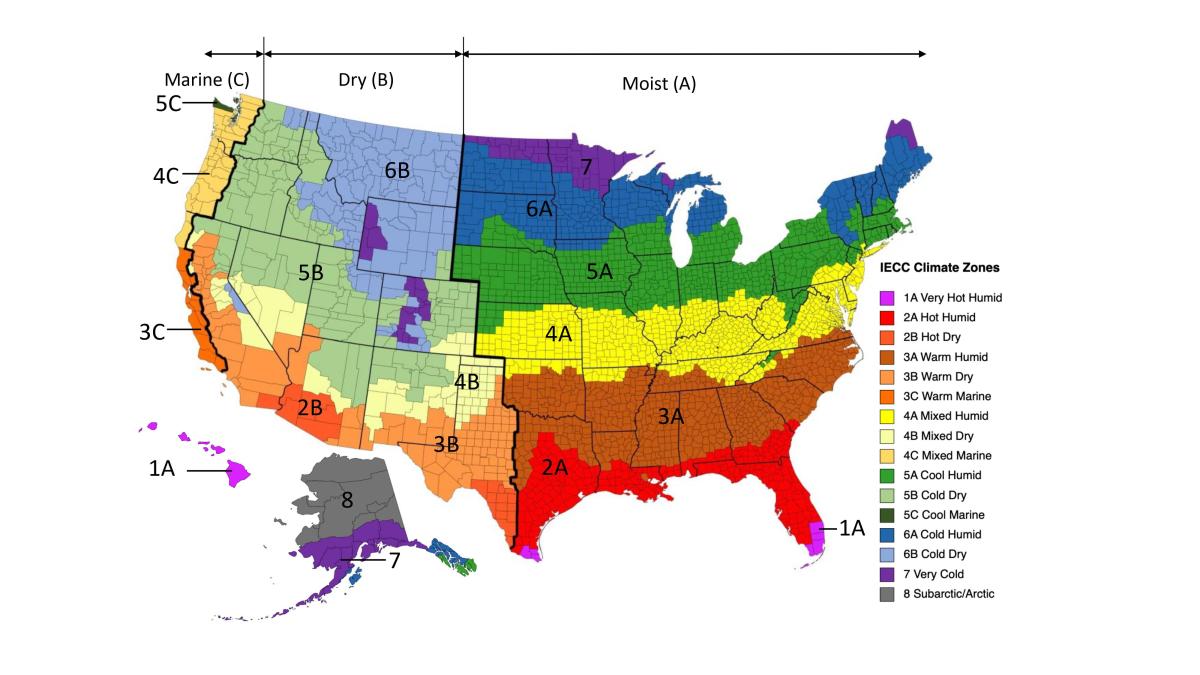
These tools report and analyze weather data. Often it is useful to use these tools with other RED Calc tools. For example, it is useful to use the Weather Station Data (TMY) tool to find your closest weather station before using one of the ASHRAE 62.2 ventilation tools.
Weather Station Data (TMY)
Calculates the Typical Meteorological Year (TMY) weather data for 1100 weather stations in North America. Weather station latitude, longitude, and altitude (elevation) are displayed. Additionally, dry bulb and dew point temperatures and wind speed are displayed in a table for the selected date range. An embedded Google map helps in locating the nearest weather station location and an interactive charting feature allows you to analyze weather data.