Scope
Treat bulk water drainage issues and provide additional moisture control measures as needed to address site moisture issues before retrofitting a vented crawlspace to an unvented, insulated crawlspace.
See the Compliance Tab for links to related codes and standards and voluntary federal energy-efficiency program requirements.
Description
When looking for opportunities to improve the energy efficiency of older single-family and multi-family residential buildings, sealing and insulating of vented crawlspaces is one retrofit measure that can improve the energy efficiency, comfort, and durability of the structure, particularly in climates with cold winters and/or hot humid summers. However, before any sealing and insulating of the crawlspace walls can take place, water drainage and moisture management issues in and around the crawlspace must be dealt with to ensure that the crawlspace will be dry and remain dry once enclosed.
See the guide Unvented Insulated Crawlspaces for more information on constructing sealed, insulated crawlspaces.
How to Address Water Management Issues in a Crawlspace
Several steps can be taken to address moisture issues in the crawlspace depending on the initial conditions at the site and the project budget:
- Reduce the chances of bulk intrusion of water into the crawlspace by re-grading the ground around the building to slope away from the structure, installing drainage pipes around exterior footings that drain to daylight or a drywell, and installing or modifying gutters and downspouts to ensure that they carry rainwater away from the foundation. Ensure that any existing concrete patios, sidewalks, or driveways slope away from the house. If they slope toward the house, consider replacing with pervious pavers or correctly sloped concrete, or install drains, for example at the base of a down-sloping driveway, to carry water away from the foundation.
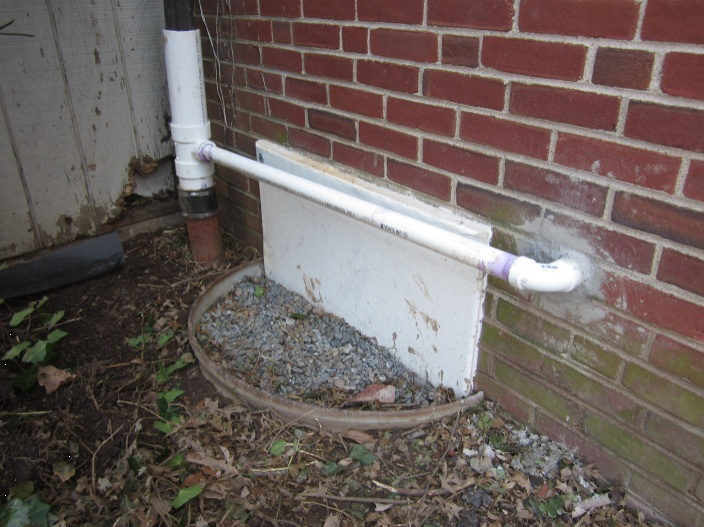
- Block off and thoroughly seal crawlspace windows and vents with durable, waterproof materials that will prevent air and water leakage. Completely fill crawlspace window wells to above-grade levels.
- Install exhaust fans that will pull damp air out of the crawlspace, while indirectly pulling drier air from the dwelling unit into the crawlspace. This infusion of conditioned air will help to dry out the crawlspace.
- Install sump pumps in low-lying areas of the crawlspace floor that can be activated to carry away any water that accumulates at the crawlspace floor from seepage under the foundation walls or rising water table from periodic storm events. The sump pump should have a plastic pit that is 2-ft to 3-ft deep and perforated with holes drilled in the bottom so that if the water table rises (for example due to storm events), the water will be removed before it reaches the floor of the crawlspace. Use sump pumps that are equipped with gasketed, tight-fitting lids. For more on sump pumps, see the guide Drain or Sump Pump Installed in Basements or Crawlspaces.
- Install a vapor barrier of 6-mil or thicker polyethylene sheeting that completely covers the crawlspace floor and extends up the foundation walls and any piers by 8 to 12 inches, or preferably up to the exterior ground level. The plastic should be secured with pressure-treated wood furring strips, mechanical fasteners, or fiberglass mesh tape and duct mastic. Seams in the vapor barrier sheeting should be overlapped 6 to 12 inches and taped. This vapor barrier can be covered with a concrete slab for additional durability. For more information, see the guides Capillary Break at Crawlspace Floors - Polyethylene Lapped Walls and Piers and Secured in the Ground and Capillary Break Beneath Slab - Polyethylene Sheeting or Rigid Insulation.
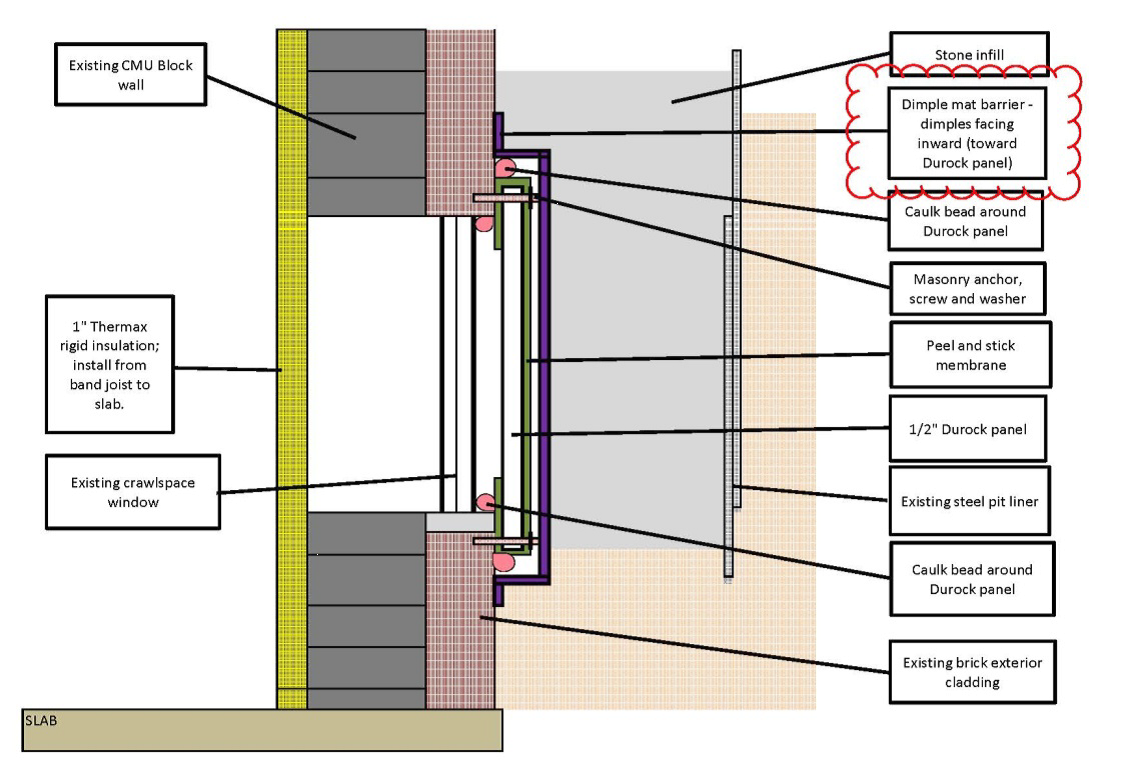
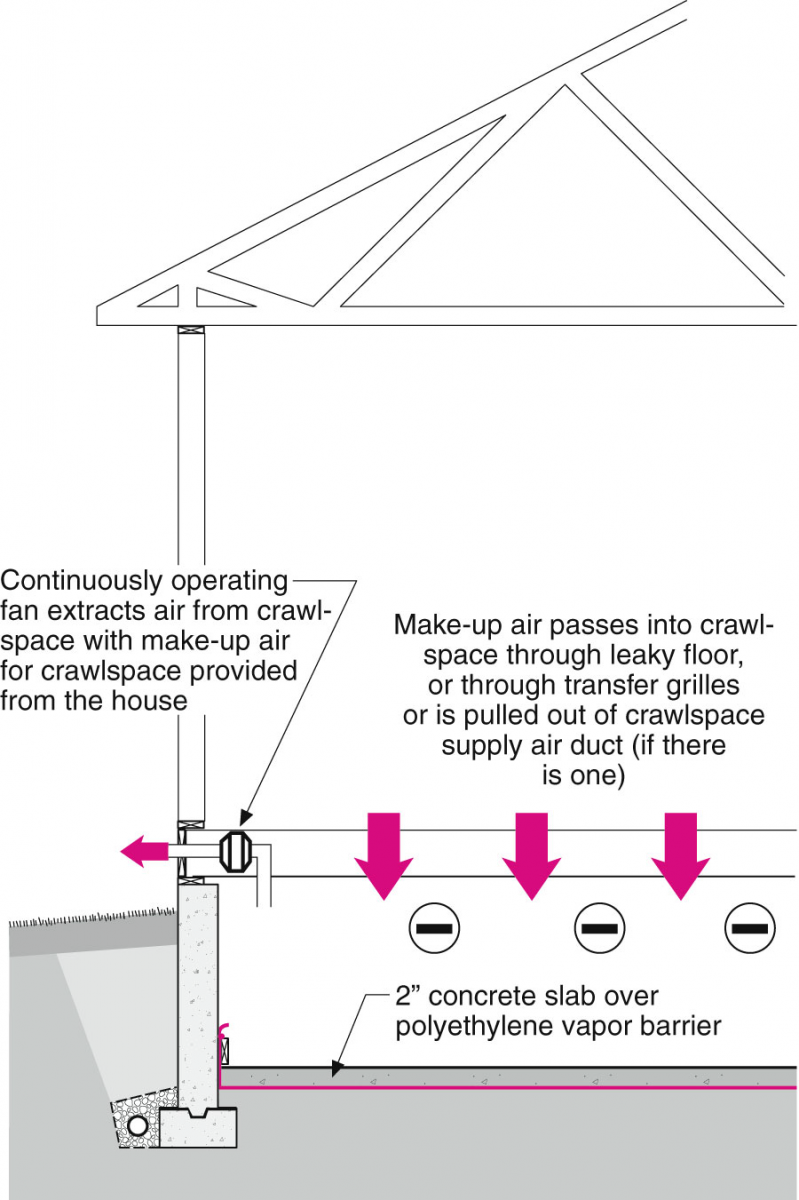

Success
A period of post-retrofit monitoring should be conducted, preferably for one year, to track the crawlspace temperature and relative humidity conditions, and to test the moisture content of the rim and floor joists. If moisture accumulation is detected in the wood of the rim joists, mitigate by allowing air to reach the joists if necessary. For example if rigid foam has been installed in the rim joists and then moisture accumulation is detected in the wood, one-half inch of foam could be trimmed away around the joists to allow air to circulate around the wood (Rudd, 2014).
Climate
These recommendations for retrofitting a vented crawlspace to a sealed, insulated crawlspace apply primarily to climate zones 3 through 8. Crawlspaces are uncommon in climate zones 1 and 2, and the likelihood of termites in climate zones 1 and 2 discourages the use of below-grade foam insulation for unvented crawlspaces.
The map in Figure 1 shows the climate zones for states that have adopted energy codes equivalent to the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) 2009, 12, 15, and 18. The map in Figure 2 shows the climate zones for states that have adopted energy codes equivalent to the IECC 2021. Climate zone-specific requirements specified in the IECC are shown in the Compliance Tab of this guide.
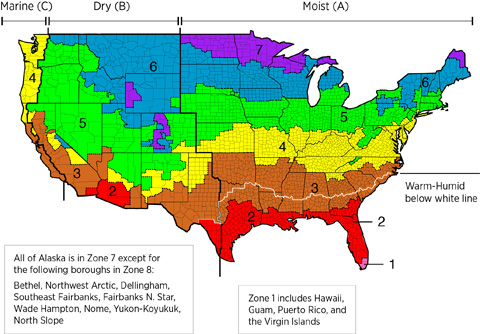
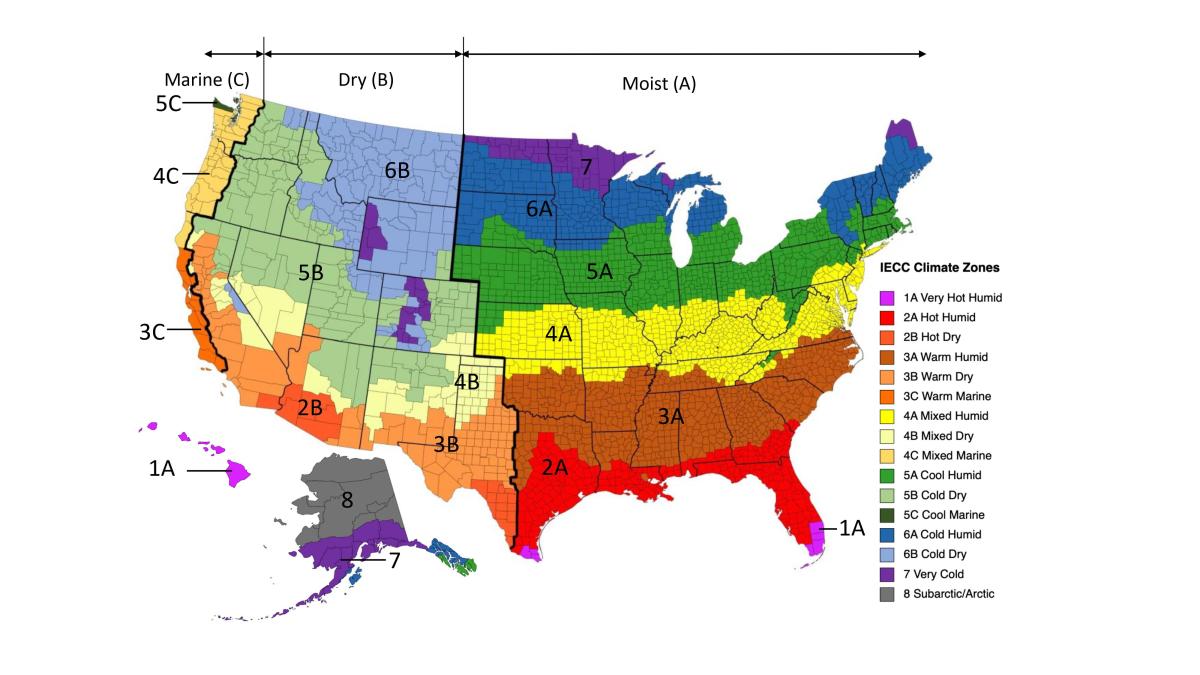
Training
Compliance
More
More Info.
Access to some references may require purchase from the publisher. While we continually update our database, links may have changed since posting. Please contact our webmaster if you find broken links.
The following authors and organizations contributed to the content in this Guide.
Building Science Corporation, lead for the Building Science Consortium (BSC), a DOE Building America Research Team
Sales
Water Managed Foundation = Foundation Water Barrier System
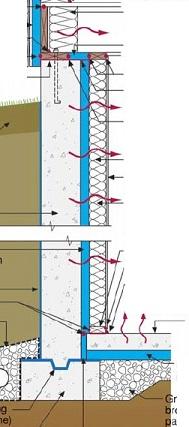
Ground water and rainwater can cause a lot of damage to a home. Building materials that are allowed to remain damp or saturated for long periods of time will eventually fail. Builders can take several steps to protect the home’s foundation. For example they can properly grade the site so water drains away from the home on all sides, install footing drains at the footing of the foundation walls that drain to daylight or to a French drain away from the home, build the foundation on a bed of aggregate rock, use a vapor barrier under slabs and on crawlspace floors, and damp-proof the exterior of foundation walls.


















