Showing results 1 - 250 of 559
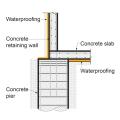
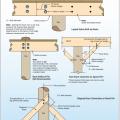
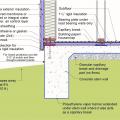
A method for preventing waterproofing issues at the intersection of a concrete pier, concrete retaining wall, and concrete slab.
Impervious surfaces like patio slabs, sidewalks, and driveways that are within 10 feet of the home should slope away from the house.
Place plants at least 18 inches from the building's walls and foundation and direct irrigation water to spray away from the structure.
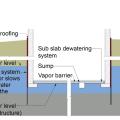
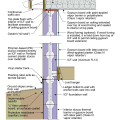
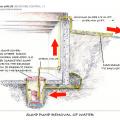
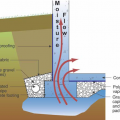
The “perimeter cutoff and dewatering” approach can be used to control groundwater in cases where the building foundation is below the groundwater table.
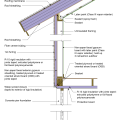
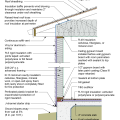
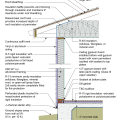
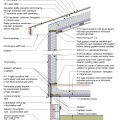
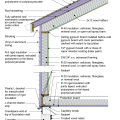
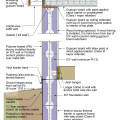
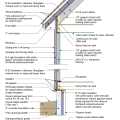
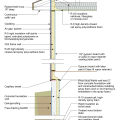
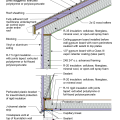
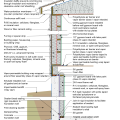
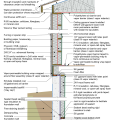
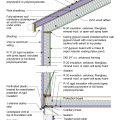
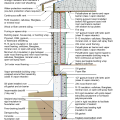
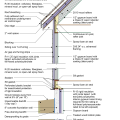
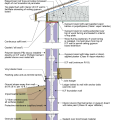
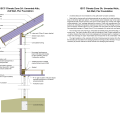
2021 IECC Climate Zone 1A: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade
2021 IECC Climate Zone 1A: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade (with notes)
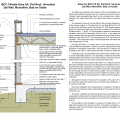
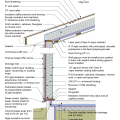
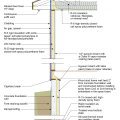
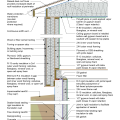
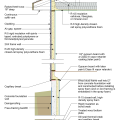
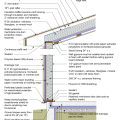
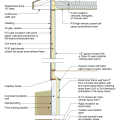
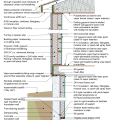
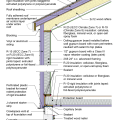
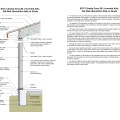
2021 IECC Climate Zone 2A: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade
2021 IECC Climate Zone 2A: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade (with notes)
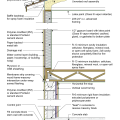
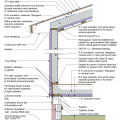
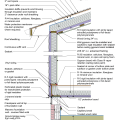
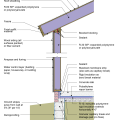
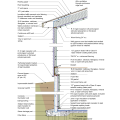
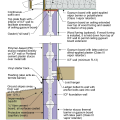
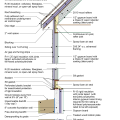
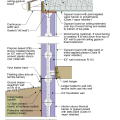
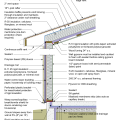
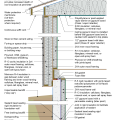
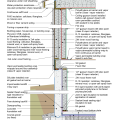
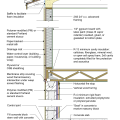
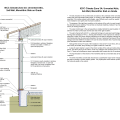
2021 IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall-CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
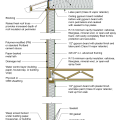
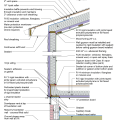
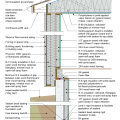
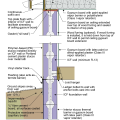
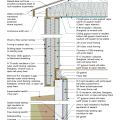
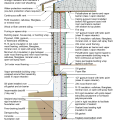
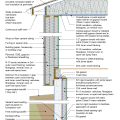
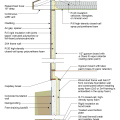
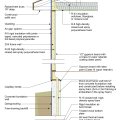
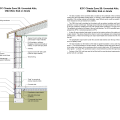
2021 IECC Climate Zone 2B: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade
2021 IECC Climate Zone 2B: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade (with notes)
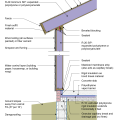
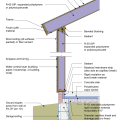
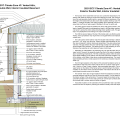
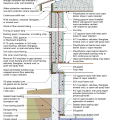
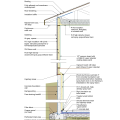
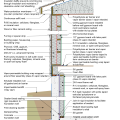
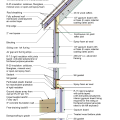
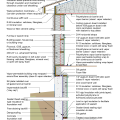
2021 IECC Climate Zone 3A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space
2021 IECC Climate Zone 3A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 3B: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space
2021 IECC Climate Zone 3C: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space
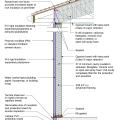
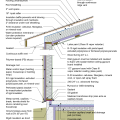
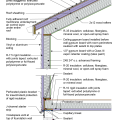
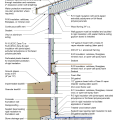
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Slab on Grade (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4B: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Slab on Grade (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4B: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space
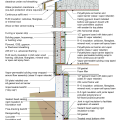
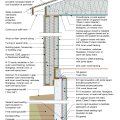
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, 2x4 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, ICF Wall, ICF Basement Foundation (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Slab on grade (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Over-Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5: Vented Attic, 2x4 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5A: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5A: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5A: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5A: Vented Over Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5B: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5B: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5B: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5B: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5B: Vented Over Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5C: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5C: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5C: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5C: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5C: Vented Over Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6: Vented Cathedral ceiling, 2x6 Wall, interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6: Vented Cathedral ceiling, 2x6 Wall, interior Insulated Basement (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6A: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6A: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6A: Vented Over-Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6A:Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6B: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6B: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6B: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6B: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6B: Vented Over-Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
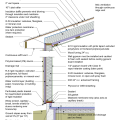
2021 IECC Climate Zone 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, 2x4 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, ICF Wall, ICF Basement Foundation
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Slab on Grade
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Over-Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
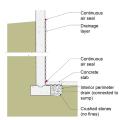
A common method of addressing significant groundwater leakage in the foundation is to line the entire foundation assembly, including the slab, with a drainage layer.
A common method of addressing significant groundwater leakage in the foundation is to line the interior perimeter of the foundation with a drainage layer.
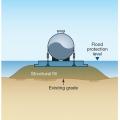
A concrete slab floor can be elevated above local grade as a strategy to prevent flood damage.
A concrete slab-on-grade foundation with exterior insulation, which can be elevated above the local grade as a flood-prevention strategy.
A dimpled rain mat and perforated drain pipe provide drainage around the basement foundation.
A drywell, shown here used for downspout catchment, can also be used to receive water from a French drain.
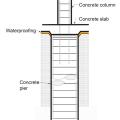
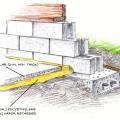
A method for preventing waterproofing issues at the intersection of a concrete column, concrete slab, and concrete pier.
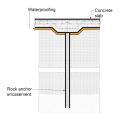
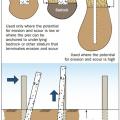
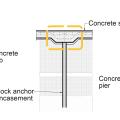
A method for preventing waterproofing issues at the intersection of a concrete slab and a rock anchor.
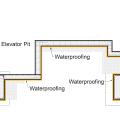
A method to ensure waterproofing continuity across the elevator pit of a multistory multifamily building.
A paint-on waterproofing covers the exterior and tops of the concrete block foundation walls and piers to block moisture moving up through the concrete, while foil-faced R-13 insulation lines the inside surface of the exterior walls.
A raised wood pier foundation can raise the subfloor above the design flood elevation.
A sprayer-applied waterproofing covers the grout-filled top course of concrete foundation blocks to prevent moisture migration from the ground into the framing.
A vapor barrier was installed on the floor of this crawlspace and extended up the walls then the foundation walls were covered with rigid foam.
Advanced framing techniques include constructing on a 2-foot grid where wall studs are placed 24 inches on center and aligned with roof and floor trusses for a continuous load path from roof to foundation.
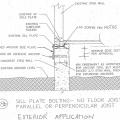
An anchor side plate is used to connect the concrete foundation to the sill plate from the exterior as part of a seismic retrofit when the sill plate is not accessible from the interior of the home
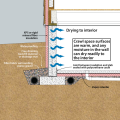
An exhaust fan pulls damp air out of a retrofitted sealed crawlspace while drawing in dry air from the living space
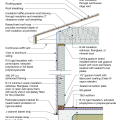
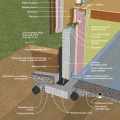
An externally insulated slab-on-grade is pest-protected by a metal termite shield under sill plate, metal-flashing-wrapped foam under siding, a removable inspection strip of PVC-covered foam, and 2 feet of gravel next to the foundation.
An ultra-efficient layer of R-20 rigid foam foundation insulation covers the ground underneath the vapor barrier and radiant floor loops, which will circulate water heated by an ultra-efficient geo heat pump.
An uninsulated (or existing insulated) basement slab is retrofitted to reduce moisture transmission by sealing with epoxy paint.
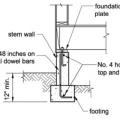
Anchor bolts should be at least 1/2-inch diameter and should be embedded at least 7 inches into the foundation, spaced not more than 6 feet apart, and between 3.5 and 12 inches from each end of the sill plates.
Any holes through the vapor barrier installed over the basement floor slab are thoroughly sealed as part of the foundation water barrier system.
Assembly can be used in IECC CZ 3 and above to thermally isolate garages in multifamily row houses with slab foundations. For unheated garages, it is unnecessary to insulate wall between garage and exterior of slab or slab underneath garage.
Basic foundation types: deep basement, submerged crawl space, flush crawl space, and slab-on-grade
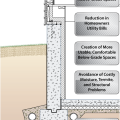
Because the above-grade potions of the wall lack exterior insulation, condensation and even ice form during cold winter conditions
Before sealing and insulating the crawlspace, the windows were sealed, the window wells backfilled, and sumps pumps were installed that discharged to the gutter downspouts
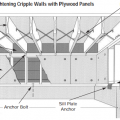
Braced cripple wall construction in crawlspace anchored to framing and foundation
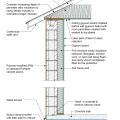
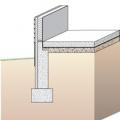
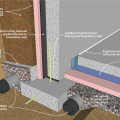
Brick veneer framed wall supported by a concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Brick veneer is supported by a concrete stem wall thermally separated from the slab-on-grade foundation with turn-down footing which is also insulated on top; anchorage for seismic resistance is also shown
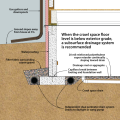
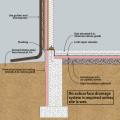
Building perimeter detail view of the recommended approach for groundwater management in cases where the foundation is entirely above the groundwater table.
Building siding extended down and over the breakaway wall so the upper wall was damaged when the lower wall broke away.
Buildings damaged by a hurricane storm surge: upper homes on gulf shoreline were hit by large waves above the lowest floor, lower left home on bay and right school 1.3 miles from gulf shoreline were hit by surge and small waves.
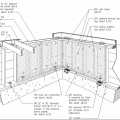
Built-up beam connections, knee brace connections, and diagonal brace connections for wood piles.
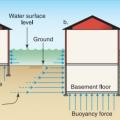
Buoyancy force on dry floodproofed homes with deep basements leads to possible foundation damage
Closed-cell spray foam insulates the floor above a vented crawlspace; a protection board made of fiber cement is screwed in place under the floor joists to keep out pests
Closed-cell spray foam insulates the floor above an open foundation; a protection board made of fiber cement is screwed in place under the floor joists to keep out pests
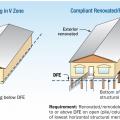
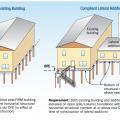
Comparison of a building that sits below the Design Flood Elevation and renovated to be above the DFE and to add a second story.
Comparison of a building that sits below the Design Flood Elevation and renovated to be above the DFE.
Comparison of a building that sits below the Design Flood Elevation and renovated to be above the DFE.
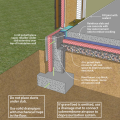
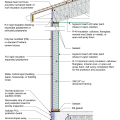
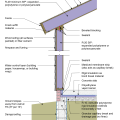
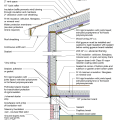
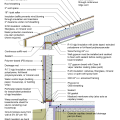
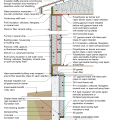
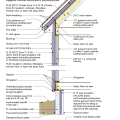
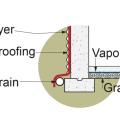
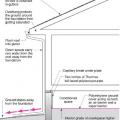
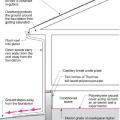
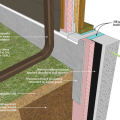
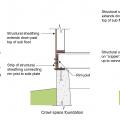
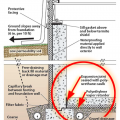
Comprehensive above-grade water management details for a crawlspace foundation include a capillary break over the crawlspace floor, slope the surface grade away, installing gutters that slope away, and capillary break under sill plate.
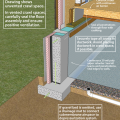
Comprehensive water management features include a capillary break (≥ 6-mil polyethylene sheeting) at all crawlspace floors
Concrete (4 inches thick at 5% slope) provides a pest-resistant perimeter around the foundation
Concrete pavers set in 4 inches of sand provide a pest-resistant ground break at the building perimeter.
Concrete pier foundations can be used in place of wood piles in coastal areas where risk of erosion and scour is low.
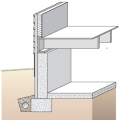
Concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
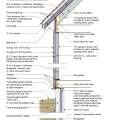
Connecting hardware helps tie the roof to the walls to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
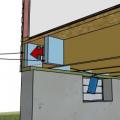
Connecting hardware helps tie the walls to the top plates and rim joists to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
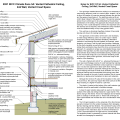
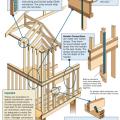
Correct seismic retrofit hardware for securing the sill plate to foundation wall
Crawl space interior insulation with EPS or XPS semi-permeable insulation on inside wall
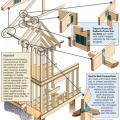
Critical connections for providing a continuous load path in buildings and storm shelters
Design the roof, walls, foundation, and site to drain water away from the structure on all sides.
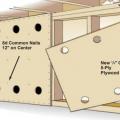
Detail for reinforcing a cripple wall to resist earthquake movement by installing anchor bolts and plywood reinforcement.
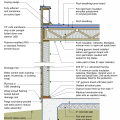
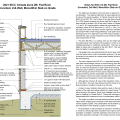
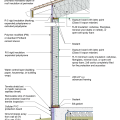
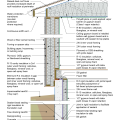
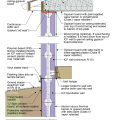
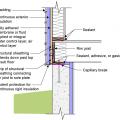
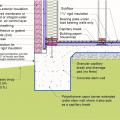
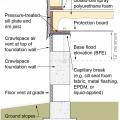
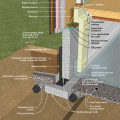
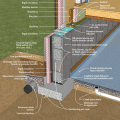
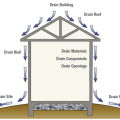
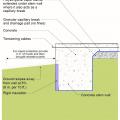
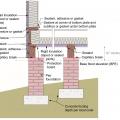
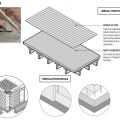
Drainage and waterproofing system components in a basement, single perimeter drain system, footing detail
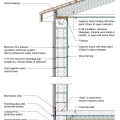
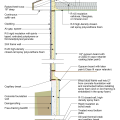
Effectively manage below-grade water in urban sites to prevent moisture issues in new and existing buildings. This foundation wall has been waterproofed to prevent water infiltration.
Epoxy paint is installed to provide a moisture control layer on the surface of an existing basement slab
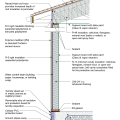
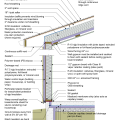
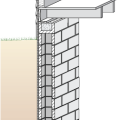
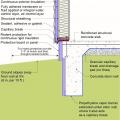
Exterior fiberglass insulation on this new home was (incorrectly) cut to terminate below-grade after backfill, which will expose the above-grade portions of the foundation wall to cold temperatures
Exterior XPS basement insulation is correctly installed to completely cover the foundation wall
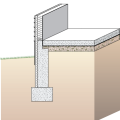
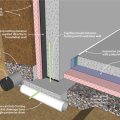
Externally insulated concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
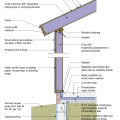
Flashing is installed above the foundation wall before installing the siding. Seams in sheathing are sealed with tape and caulk, while nail holes are sealed with caulk.
Foil-faced rigid foam and spray foam can be used to insulate a basement on the interior; use good moisture management techniques to keep the basement dry
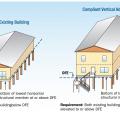
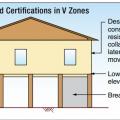
For homes built in V Zones a registered professional engineer or architect must certify that the lowest floor elevation is above the BFE and piles and structure are anchored to resist flotation, collapse, or lateral movement due to combined wind and water
For homes built on an open foundation, provide a continuous air barrier by sealing all joints between the rigid insulation, floor support beams, rim joist, and bottom wall plate
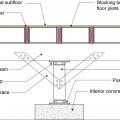
For seismic resistance in basement, crawlspace, and crawlspace “cripple” wall foundations, connect the plywood or OSB sheathing to the wall framing, rim joist, and sill plate and anchor bolt the sill plate to the foundation
For seismic retrofit of crawlspace with posts and piers, add cross bracing to posts; add cross bracing and solid blocking between floor joists
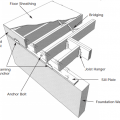
Framing anchors, anchor bolts, joist hangers, and bridging pieces all help to tie the components of the floor system together and to the foundation to increase resistance against seismic forces.
Fuel tank is elevated above flood waters on a base of structural fill and anchored to the concrete pad
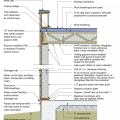
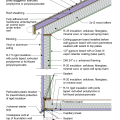
Good water management practices like sloping grade away from house, and installing gutters, perimeter drain pipe, a capillary break, and free-draining soils or drainage mat protect the foundation from water saturation.
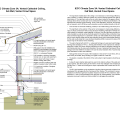
Green Coast Enterprises built this New Orleans home on piers so that the floor is 1 foot above the base flood level; borate treated framing and closed-cell spray foam insulation add to the home's moisture resistance.
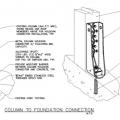
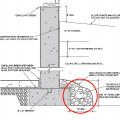
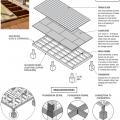
How to properly anchor a new home to its foundation with foundation sill plate, stem wall, and footing
Hurricane straps, hold-down connectors, and bolts help to transfer loads from the building’s walls to its foundation, increasing resistance to vertical and horizontal pressures acting on the building from wind, waves, or ground movement.
ICF bricks are stacked to form hollow walls that are reinforced with steel rebar before the concrete is poured in
ICF foundation walls wrap the floor slab in R-22 of insulation while the entire space under the slab is covered with 4.3 inches of closed-cell spray foam.
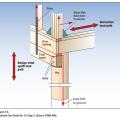
IECC Climate Zone 1A: Unvented Attic with Spray foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall-CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
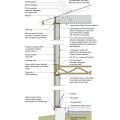
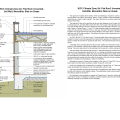
IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall/CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall/CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
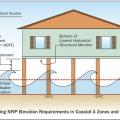
In Coastal A Zones and V Zones best practice is to construct the home so the bottom support of the lowest floor is above the 100-year wave crest elevation.