Scope
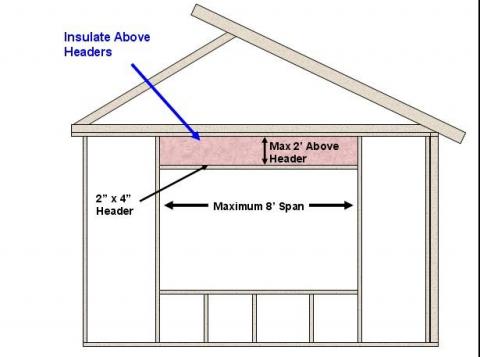
Construct framed walls using advanced framing details like insulated headers over windows and doors that reduce framing and thermal bridging and allow more space for insulation.
- Use pertinent code requirements to determine minimum header lumber requirements.
- Eliminate jack studs (also known as shoulder studs) on non-load-bearing walls and replace with metal hangers on load-bearing walls. Add 2x2 nailers as needed for siding attachment.
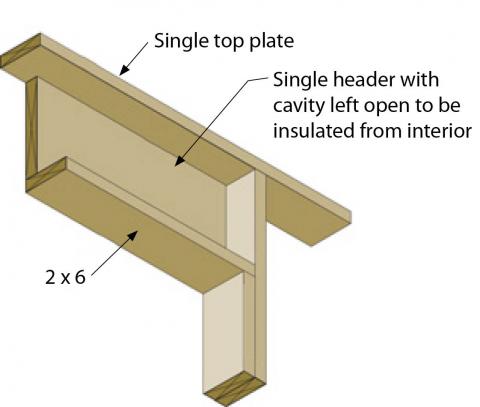
- On non-load-bearing walls, install open headers and insulate like wall cavities.
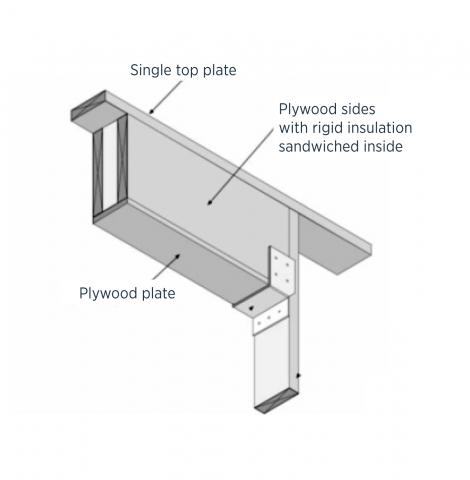
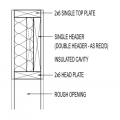
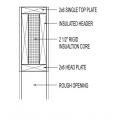
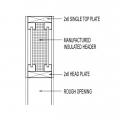
- On load-bearing walls, install an insulated header that meets minimum header strength requirements. Options include a prefabricated insulated header, a SIP header, or a header made of one piece of plywood plus rigid foam, or two pieces of plywood sandwiching rigid foam.
- ENERGY STAR requires that the header be insulated to at least R-3 in 2x4 framed wall assemblies or at least R-5 in thicker wall assemblies (e.g., 2x6 framing). (ENERGY STAR).
See the Compliance Tab for links to related codes and standards and voluntary federal energy-efficiency program requirements.
Description
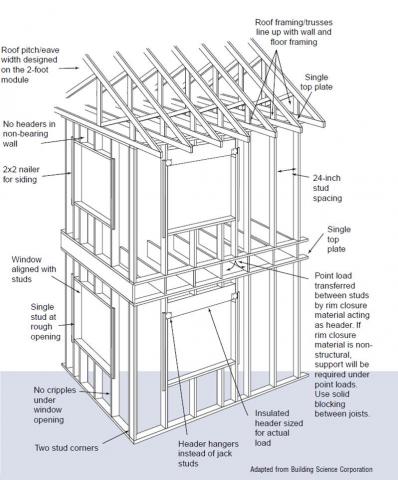
In load-bearing exterior walls, structural headers are placed over windows and doors to pick up the load from the building above and transfer it to the posts on both sides of the window or door opening. Structural headers are a point of increased heat loss because they are made from solid or laminated framing timbers with no insulation. Proper sizing of headers allows better insulation and saves wood. Insulated headers reduce heat transfer to keep the home warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer.
In many cases, headers are overdesigned, consisting of solid wood layers that add up to the full 4- or 6-inch wall thickness. (For example, a header made of two 2x12s sandwiching a ½-inch layer of plywood is installed when a header comprised of thinner layers of plywood or OSB would provide enough structural strength and allow room for a layer of rigid foam.) In some cases, no solid wood layer is needed; in nonbearing walls, the header space can be left open and filled with insulation instead. Structural headers are not required in most interior walls or in gable-end walls with only non-bearing trusses directly above. A single flat 2x4 or 2x6 can be used as a header in interior or exterior non-bearing walls for openings up to 8 feet in width if the vertical distance to the parallel nailing surface above (usually the top plate) is not more than 24 inches. For such non-bearing headers, no cripples or blocking are required above the header (2009 IRC R602.7.2). Insulated or open headers should be used except where a framing plan provided by the builder, architect, designer, or engineer indicates that full-depth solid headers are the only acceptable option. [See 2009 IRC Tables R502.5(1) and R502.5(2) for header span requirements.]
Insulated headers can be made of rigid foam sandwiched between two layers of plywood or OSB or one layer of foam and one layer of plywood, or structural insulated panels. These can be built onsite, or pre-fabricated insulated headers can be purchased.
Headers are installed by the framers using plans provided by the designer or architect. This task should be included in the contract for the appropriate trade depending on the workflow at the specific job site. High-performance branding programs and the IECC code require that builders meet specified insulation levels. See the Compliance tab for these specified insulation levels.
How to Install an Insulated Header on a Bearing Wall
1. Use pertinent code requirements to determine minimum header lumber requirements. [See for example, 2009 IRC R602.7 and Tables R502.5 (1) and (2).] Install a properly sized prefabricated header or fabricate the header onsite from one piece of rigid foam and one or two pieces of plywood; see Figures 2 and 3.
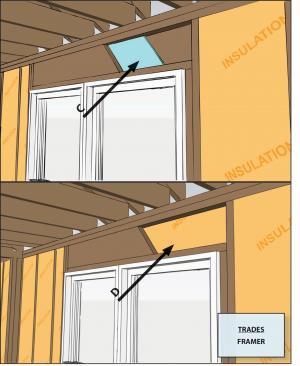
2. Eliminate jack studs (also known as shoulder studs) on load-bearing walls by hanging structural headers with metal hangers instead. Note that jack studs are not needed on non-bearing walls. Eliminating jack studs will reduce the available nailing area for siding and trim if nailable sheathing (e.g., plywood or OSB) is not used. If needed, attach a 2x2 wood nailer to the outside edge of the stud for siding attachment.
How to Insulate a Header on a Non-Bearing Wall
Install a single flat 2x4 or 2x6 at the top of the door or window rough opening as the header in interior or exterior non-bearing walls for openings up to 8 feet in width if the vertical distance to the parallel nailing surface above (usually the top plate) is not more than 24 inches. For such non-bearing headers, no cripples or blocking are required above the header (2009 IRC R602.7.2). Insulate the cavity above the header in the same manner as the rest of the wall.
Structural headers are not needed on nonbearing walls; the open space above the window can be filled with the same insulation as the other wall cavities.
Success
It may be possible to detect heat loss at the headers with an infrared camera, if a sufficient temperature difference exists between the outside and the conditioned space of the house. The quality of installation of the insulation should be visually inspected by the site supervisor before the drywall is installed.
Climate
No climate specific information applies.
Training
CAD
Compliance
More
More Info.
Access to some references may require purchase from the publisher. While we continually update our database, links may have changed since posting. Please contact our webmaster if you find broken links.
The following authors and organizations contributed to the content in this Guide.
Sales
Insulated Headers = High-Efficiency Window Framing
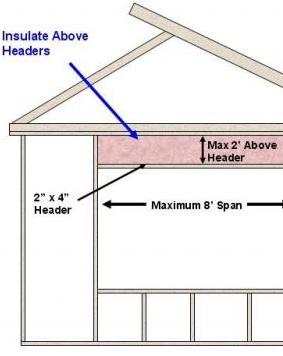
Solid wood headers above windows and doors are often oversized for the load they need to carry. And the solid wood creates a cold spot because there is no insulation. On a non-load-bearing wall (a gable-end wall), the header space can often be left open so it can be insulated like the rest of the wall. On load-bearing walls, the builder can install headers with rigid insulation sandwiched between structural framing. By sizing and locating windows to align with wall framing, the builder can avoid having to put extra studs in the walls to support the windows, which also allows more room for insulation.