Showing results 251 - 500 of 1165
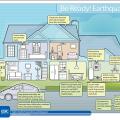
Earthquake-ready home actions include securing water heaters, shelves, and heavy furniture to walls and preparing utilities for emergency shut-off.
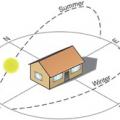
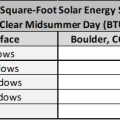
East- and west-facing walls receive significantly more sun than north- and south-facing walls in the summertime
Encourage dune formation by installing sand fences or pallets and planting dune grasses.
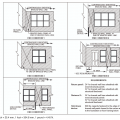
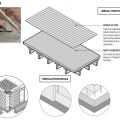
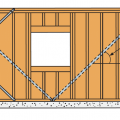
End conditions for braced wall lines with continuous sheathing, Figure R602.10.7 in the IRC
End wall failure under hurricane force winds due to inadequate bracing of the gable end wall.
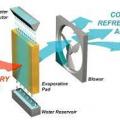
Evaporative coolers use a fan to draw outside air through a wetted pad which cools and humidifies it
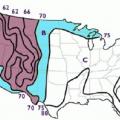
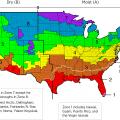
Evaporative cooling is most appropriate in areas where the summer design mean coincident wet bulb temperature is less than 70°F, shown in purple here and labeled as region “A”
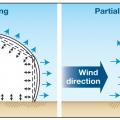
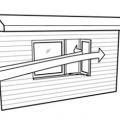
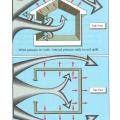
Even when wind is blowing parallel to a wall, an open casement window can create a zone of higher pressure near the window opening, driving airflow into the house
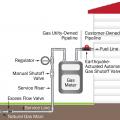
Every natural gas appliance has a shutoff valve in the gas line to the appliance that can be manually shut off if a leak happens at a specific appliance or in preparation for an impending natural disaster.
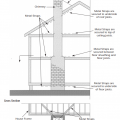
Example A of a gable truss and gable end wall bracing for a home in a hurricane region
Example B of a gable truss and gable end wall bracing for a home in a hurricane region
Example of a portable gasoline powered electric backup generator to be used during power outages.
Example of a truss bracing requirement tag that some truss manufactures place strategically onto the truss to remind installers
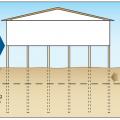
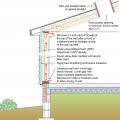
Example of an earth-sheltered home in hot climate Tempe, AZ uses the cooling properties of the ground to decrease cooling costs
Example of masonry construction. Wall separated from building envelope due to inadequate vertical wall reinforcing in connection to horizontal tie-beam.
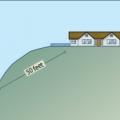
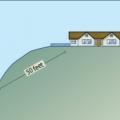
Example of setback from wildland vegetation Image title: Homes sited on hills in wildfire prone areas should be set back at least 50 feet from downslope wildland vegetation.
Example sketch of porch for calculations showing tributary areas for column uplift loads
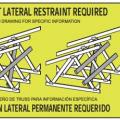
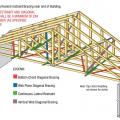
Example truss bracing for resisting wind loads as determined by design software used by truss manufactures
Examples of many common ceiling penetrations that will be difficult to insulate and air seal in this cathedral ceiling.
Excess Flow Valves and Earthquake-Actuated Gas Shutoff Valves are two different types of valves that automatically stop the flow of gas into the house: excess flow valves stop gas flow if there is a break in the line, earthquake valves stop gas flow if th
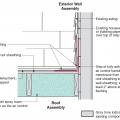
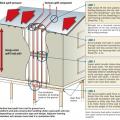
Existing wall-to-lower roof transition retrofitted with a new strip of fully adhered air control transition membrane, new step flashing, new roof underlayment, and new cladding
Existing wall-to-lower roof transition with a new strip of fully adhered air control transition membrane, new step flashing, new roof underlayment, and new cladding – view from eave
Existing wall-to-lower roof with attic transition with a new strip of fully adhered air control transition membrane, new step flashing, new roof underlayment, and new cladding – view from eave
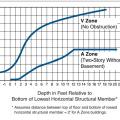
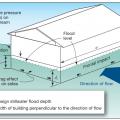
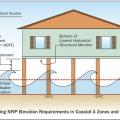
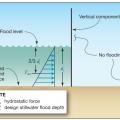
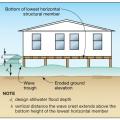
Expected flood damage (as a percent of building’s pre-damage market value) at flood depths above the bottom of the floor beam), for a building in the coastal V Zone and riverine A Zone.
Exterior electrical service components are raised and clearances are provided around components to minimize contact with flood waters and people
Exterior low-e storm windows were added to historic Halligan Hall on the U.S. Naval Academy campus in Annapolis, Maryland; frames were custom colored to match the existing seafoam green window trim
Exterior shading devices such as awnings or overhangs can significantly reduce cooling loads
External solar screens are an effective way to reduce solar heat gains through windows while maintaining view.
Externally insulated concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
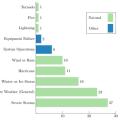
Extreme weather, such as wind, fire, flood, or extreme heat (included in the Severe Weather category above) causes most large electric disturbance events in the U.S (defined as affecting at least 50,000 customers) (data from 2000-2016)
Failure at a gable end of a home under hurricane force wind conditions due to improper continuous load path design.
Failure in brick veneer connection under high wind conditions due to anchor corrosion, tie fastener pull-out, failure to embed ties into the mortar, poor bonding between ties and mortar, and poor-quality mortar; on left - five ties not embedded.
Failure of "S" tile roofing in high winds due to bond failure between mortar and tiles.
Failure of a freestanding concrete masonry end wall due to discontinuous tie-beam when exposed to hurricane force winds.
Failure of barrel tile roofing due to bond failure between underlayment, mortar, and tiles during a hurricane.
Failure of extruded concrete flat tile roofing due to bond failure between tile, mortar, and underlayment resulting from hurricane force winds.
Failure of Roof Structure from Pressurization Due to Window Failure During a Hurricane.
Failure of the wall to roof connection resulted in loss of roof under hurricane force winds.
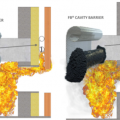
Fire barriers for ventilated wall cavities use thermally activated expansive materials to close off the ventilation space between the wall cladding and the sheathing during a fire while allowing air flow through the metal mesh during normal conditions
Fire barriers for ventilated walls use heat activated intumescent expansive materials to close off the ventilation space between the wall cladding and the sheathing during a fire while allowing air flow through the metal mesh during normal conditions
Fire resistance plans for a community include creating defensible space for each home and for the whole community, constructing with fire-resistant materials, and providing turn-around space for emergency response vehicles.
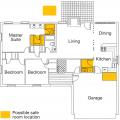
Fire suppression sprinklers can be set to activate only in the room where a fire is sensed.
Firewall separation. Results from building corners being discontinuous with tie-beams.
Flame Spread Classification and Ratings for Common Building Materials (adapted from Louisiana Office of State Fire Marshall 2021)
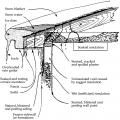
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.
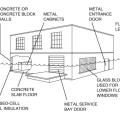
Flood damage-resistant materials include concrete and tile flooring, metal cabinets and doors, and glass-block windows.
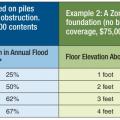
Flood Insurance Premiums Can be Reduced Significantly by Building above the BFE.
Flood vents allow floodwaters to enter and exit the crawlspace without causing hydrostatic pressure differences
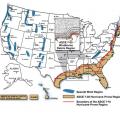
Florida Wind-Borne Debris Region, Category II and III Buildings and Structures except health care facilities.
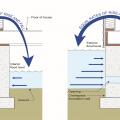
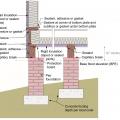
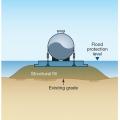
For homes built in high probability flood zones, move all possible plumbing equipment above the Base Flood Elevation (BFE), shown here as “Flood Protection Level;” equipment that cannot be moved should be watertight to resist floodwater
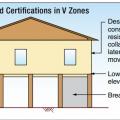
For homes built in V Zones a registered professional engineer or architect must certify that the lowest floor elevation is above the BFE and piles and structure are anchored to resist flotation, collapse, or lateral movement due to combined wind and water
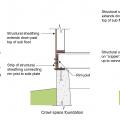
For homes built on an open foundation, provide a continuous air barrier by sealing all joints between the rigid insulation, floor support beams, rim joist, and bottom wall plate
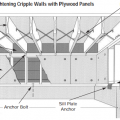
For seismic resistance in basement, crawlspace, and crawlspace “cripple” wall foundations, connect the plywood or OSB sheathing to the wall framing, rim joist, and sill plate and anchor bolt the sill plate to the foundation
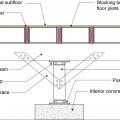
For seismic retrofit of crawlspace with posts and piers, add cross bracing to posts; add cross bracing and solid blocking between floor joists
Four types of residential fire sprinkler heads: pendent, concealed, sidewall, and concealed sidewall.
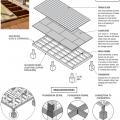
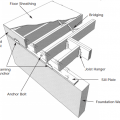
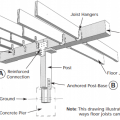
Framing anchors, anchor bolts, joist hangers, and bridging pieces all help to tie the components of the floor system together and to the foundation to increase resistance against seismic forces.
Fuel storage tanks are at risk of displacement during floods and should be securely anchored to the ground or base
Fuel tank anchored below ground in a flood-prone area anchored to a counterweight to counteract the buoyancy force.
Fuel tank is elevated above flood waters and anchored to supporting frame
Fuel tank is elevated above flood waters on a base of structural fill and anchored to the concrete pad
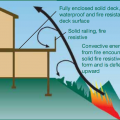
Fully enclosing the area under the deck increases its resistance to wildfire by minimizing the space where embers can lodge.
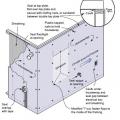
Furniture and heavy household items should be anchored to prevent tipping over during an earthquake and for everyday use if small children are in the home
Gable end vents allow in wind-driven rain because pressures that develop between the outside surface of the wall and the inside of the attic are sufficient to drive water uphill several inches.
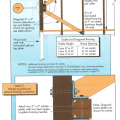
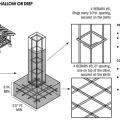
Gable-end bracing detail; nailing schedule, strap specification, brace spacing, and overhang limits should be adapted for the applicable basic wind speed.
Glass blocks allow in daylight while maintaining privacy and also provide protection against high winds and floods.
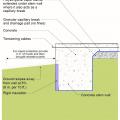
Good water management practices like sloping grade away from house, and installing gutters, perimeter drain pipe, a capillary break, and free-draining soils or drainage mat protect the foundation from water saturation.
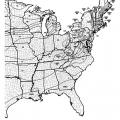
Ground Snow Loads for the United States (eastern), from 2021 IRC, Figure R301.2 (4)
Ground Snow Loads for the United States (western), from 2021 IRC, Figure R301.2 (3)
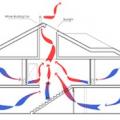
Having both low and high ventilation openings is necessary to promote airflow from the stack effect
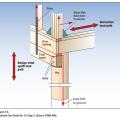
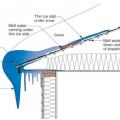
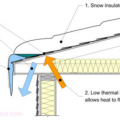
Heat loss through the roof of a home in a cold climate zone leads to snow melting to form ice dams.
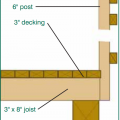
Heavy metal flashing protects the deck timbers and separates them from the wall at the wall-deck connection which is vulnerable to both ember entrapment and water damage.
Heavy timber deck construction uses slow burning thick timbers to reduce the flammability of the deck.
Heavy timber deck construction uses slow burning thick timbers to reduce the flammability of the deck.
Heavy-gauge metal strapping can be used to secure water heaters and other appliances
High winds pulled the asphalt shingles and sheathing panels off this coastal home, although storm shutters protected the windows
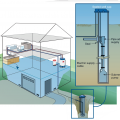
Homeowners in remote areas may choose to install their own cisterns to provide water for fire suppression in case of wildfires.
Homes located in the Wildland Urban Interface should be designed and constructed with fire resistance in mind.
Homes sited on hills in wildfire prone areas should be set back at least 50 feet from downslope wildland vegetation.
House wrap is sealed at all seams and overlaps flashing to serve as a continuous drainage plane over the exterior walls.
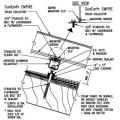
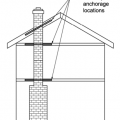
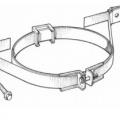
How to reinforce a chimney to resist earthquakes and high winds – side and top views.
Hurricane force winds that breach external windows and doors can then cause failure of the entire building due to internal pressures on walls and roof.
Hurricane shutter styles include colonial, Bahama, roll-up, and accordion shutters.
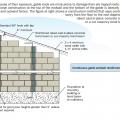
Hurricane straps, hold-down connectors, and bolts help to transfer loads from the building’s walls to its foundation, increasing resistance to vertical and horizontal pressures acting on the building from wind, waves, or ground movement.
Ice dams form when warmth from the attic causes roof snow to melt and flow to roof eaves where it refreezes at the colder overhang and forms a buildup of ice causing more snowmelt to puddle where it can wick back through shingles and leak into the attic
Ice dams formed by melting of snow on roofs can affect roofs, walls, ceilings, siding, and insulation.
If a cool room is directly under an attic or roof, having lighter colored roofing (home on left) will reduce heat gain to the space as compared to darker roofing (home on right) because the temperature of the roof will be lower (see thermal image)
If both the shingles and the underlayment blow off the roof is more susceptible to water intrusion; sealed seams or a self-adhering underlayment provide greater protection.
If snow level is estimated to exceed roof load limits, snow removal may be needed; hire professionals
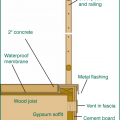
If water rises above the foundation and enters the wall cavity it will not damage the moisture-resistant closed-cell foam or exterior extruded polystyrene, while gaps in the paperless drywall allow airflow of easy removal of panels for drying and cleaning
Improper continuous load path design lacking bracing results in the failure of gable end walls under high wind conditions.
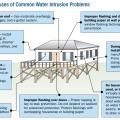
Improper flashing can allow rain water into walls, causing significant damage
Improperly installed fuel tanks can break free from attachments under the force of flood waters, risking broken fuel lines which could cause fire or explosion. Here, the tank is tethered only by the gas piping, which is not designed to perform this functi
In areas prone to high winds and hurricanes, double vertical “jack trim” and horizontal “header” and “sill” studs are recommended on all sides of window and door openings.
In Coastal A Zones and V Zones best practice is to construct the home so the bottom support of the lowest floor is above the 100-year wave crest elevation.
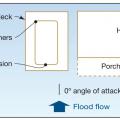
In coastal flood zones, in-ground pools should located as far landward on the lot as possible and be oriented perpendicular to the shoreline with rounded corners.
In high wind areas, provide lateral support to masonry end walls to resist high winds.
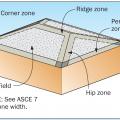
In high wind zones, if roof tiles are fastened with screws or nails, consider using clips on tiles at the corners, ridges, hips, and perimeters.
In high-flood-risk areas, install a roof hatch or openable skylight, min. 20x24 inches or 821 in.2 to serve as a means to access the roof for refuge
In high-wind regions, special hardware is used for most framing connections; toe-nailing is not acceptable.
In hot climate zones, shade building surface with vegetation for passive cooling.
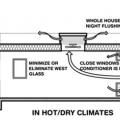
In hot, dry climates, passive cooling should focus on shading, night flush through cross ventilation and whole-house fans, potentially using high-mass construction
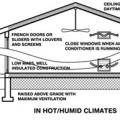
In hot, humid climates, passive cooling should focus on shading, airflow through cross ventilation and ceiling fans, and low-mass construction
In midsummer, the roof and skylights will receive much more solar radiation per square foot than an unshaded east- or west-facing wall, which in turn will receive more solar energy than north- or south-facing walls
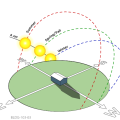
In the middle of summer, the sun shines most directly on the east and west sides of a house, while in winter it shines mostly from the south.
In this IBHS Research Center test of two homes exposed to flying embers and high winds, the home with wood siding and a wood door went up in flames, the home with fiber cement siding and a metal door suffered little damage.
In tropical climates such as Puerto Rico, some houses have metal jalousie louvers instead of glass windows; metal jalousies look like shutters, but typically offer little debris resistance.
Inadequate connections between the foundation columns and footings or grade beams can lead to column connection failures during flooding.
Incandescent lights such as these are a wasteful consumer of generator or battery energy, producing much more unwanted heat than light
Incorrectly done seismic retrofit, the plywood sheathing is not nailed to the mud sill and therefore it is not providing any shear strength
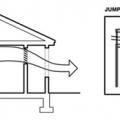
Inducing airflow through the stack effect requires low inlets and high outlets such as a ridge hood or crown monitor
Infrared photometry shows the impact of a roof overhang on the south façade of a home, where the unshaded patio stonework is significantly hotter than the shaded portions of the patio and wall surfaces (temperature scale shown is in Celsius).
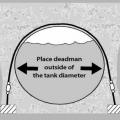
Install “deadmen” anchors and straps over an underground storage tank to offset the buoyancy of flood waters.
Install a concrete collar over an underground storage tank to offset the buoyancy of flood waters.
Install all layers of the drainage plane to overlap, not underlap, to direct bulk water down and out of the wall.
Install an ENERGY STAR labeled insulated door with an automatic closer. Weather strip the door frame
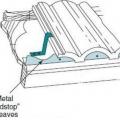
Install birdstop at the eave in tile roofs to minimize the accumulation of debris, a fire hazard, at the roof edge.
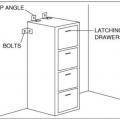
Install cabinets with latching drawers or add latches; secure file cabinets to the wall with heavy L brackets to prevent damage during seismic events.
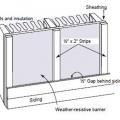
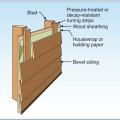
Install furring strips over house wrap to provide a rainscreen behind wood siding.
Install hold-down straps to securely attach the tank to the bottom hold-down pad to offset the buoyancy of flood waters.
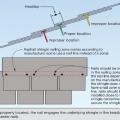
Install shingle starter strip then kick-out diverter; attach to roof deck but not sidewall
Install the house wrap. Cut house wrap to fit over diverter and tape top of cut wrap
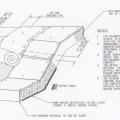
Installation of an erosion control blanket to minimize soil loss on sloped ground that has no established vegetation
Installation of permanent exterior low-E storm windows is simple and easy, requiring a few basic tools and about 20 minutes of labor
Installing an ENERGY STAR ceiling fan is a low-energy way to improve comfort in a designated cool room
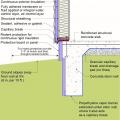
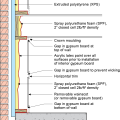
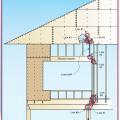
Insulating a crawlspace foundation with “cripple wall” in warm climates; in Climate Zones 5+ replace the foil- or plastic-faced fiberglass batt/roll insulation with impermeable rigid insulation or closed-cell spray polyurethane foam
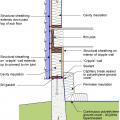
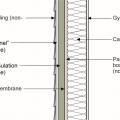
Insulating sheathing is installed on exterior of an existing framed wall with water control between existing sheathing and insulating sheathing
Integrate pre-formed vent pipe flashing, shingle-fashion, with roofing underlayment and shingles
Interior storm windows have very little impact on the appearance of the window, although the window frame may appear slightly wider
Interior window attachments such as these light-filtering roller shades can reduce heat gains while providing pleasant, diffuse natural light.
Jalousie windows use shutters rather than glass over the window openings to allow for maximum ventilation. Screens may be installed to keep out insects.
Joist straps or hangers and metal connector plates can reinforce a post-and-pier foundation against seismic movement
Keep mulch away from trunk of the tree to allow air circulation at the root collar.
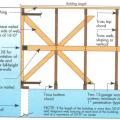
Key connection points for a continuous load path for earthquake and high wind disaster resistance
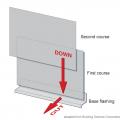
Kickout diverter flashing keeps bulk water from the roof from overflowing the gutter and continuously wetting the siding material.
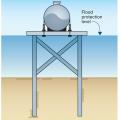
Knee braces do not stiffen a pile foundation as much as diagonal bracing, but they present less obstruction to waves and debris, are less prone to compression buckling, and may be designed for both tension and compression loads.
Lack of insulation over the top plate can lead to ice dam formation on a low sloped roof.
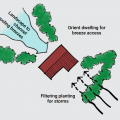
Landscape trees and shrubs to funnel cooling breeze towards a home in hot climate zones.
Landscaping and Bahama shutters can provide important shade for a designated cool room
Large deciduous trees provide heat-blocking shade to the walls and windows of this house.
Leave the soil level around an existing trunk as is (left); do not increase soil height (center) or remove soil in the root zone (right).
Light colors have been used on exterior walls and roofs to keep buildings cooler in hot climates for centuries, as shown by this traditional building in Morocco, built in the early 1800s
Likely amount of time and radiant heat exposure at which different types of window glass would break at 30 feet from the edge of a wildfire.
Locating windows on adjacent and opposite sides of the house will allow cross ventilation regardless of wind direction
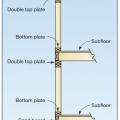
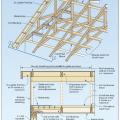
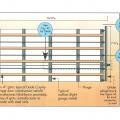
Location of Braced Wall Panels and Braced Wall Lines, Figure R602.10.2.2 in the IRC
Loss of the fascia cover in high winds exposes the vinyl soffit to entry by wind-driven rain.
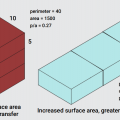
Low perimeter to area (P/A) ratio home designs reduce heat transfer and perform better in hot climate zones than high P/A ratio homes.
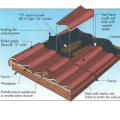
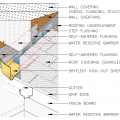
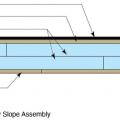
Low-slope roof assemblies constructed of two deck sheathing layers sandwiching rigid foam, and topped with mechanically fastened membrane
Lower-story wall anchorage to masonry (or concrete) base. Straps properly nailed at wall studs.
Many hardware stores sell appliance bracing kits to secure the water heater to wall framing with metal straps
Metal birdstop is installed at the eaves of a tile roof to keep out birds, bats, rodents, and flying insects
Metal connectors help resist wind uplift at the wall to roof framing connection.
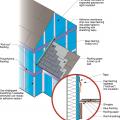
Metal hat channel provides a drainage gap of 1 inch between fiber-cement siding and mineral wool continuous insulation.
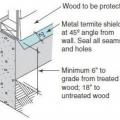
Metal termite shields make it easier to see termite tunnels and may discourage termite access to wood framing
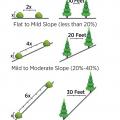
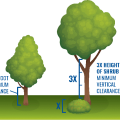
Minimum horizontal clearance between trees and plants on various slopes for wildfire resistance
Modern interior storm windows include new technology and sleek design features that offer an easy-to-install, cost-effective method for upgrading the energy efficiency of existing windows
Modern Low-E storm windows are typically kept up year-round but can be removed without damage to the existing window frame, an important consideration for historic preservation projects
Modern low-E storm windows can significantly improve the energy performance of the home by reducing both air infiltration and thermal conductance through the window assemblies
Moisture-resistant plastic and fiber cement exterior trim and cladding are indistinguishable from wood building elements.
Multi-layer honeycomb cellular shades such as these can provide summertime energy savings by blocking and reflecting solar heat, as well as wintertime energy savings by providing added insulation.
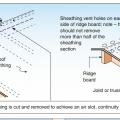
Nailing and ridge ventilation for roof sheathing used as a structural diaphragm in high-wind and seismic hazard areas.
Natural ventilation can be wind-driven (cross ventilation) or buoyancy-driven (stack ventilation)
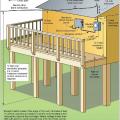
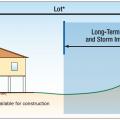
New Charleston, SC home's first level used as parking, storage, and access space
Newer home damaged from internal pressurization and inadequate connections, Hurricane Katrina.
On ocean-front lots set the home as far back on the lot as possible, preferably with a protective dune between structures and shoreline.
Passive cooling techniques can reduce or eliminate the use of air conditioning and can be used for backup cooling during emergencies.
Permanent options for keeping sun off windows to minimize solar heat gain include permanent overhangs and awnings, frames, and louvers.
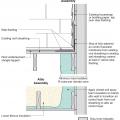
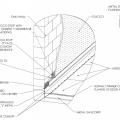
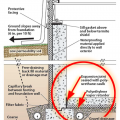
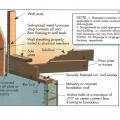
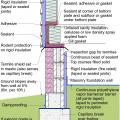
Pest proofing of this unvented crawlspace includes a metal termite shield that extends out from the sill plate, metal flashing wrapping the bottom of exterior rigid foam, and a termite inspection gap above interior rigid foam.
Pest protection measures include a termite shield under the rim joist and extending out on either side of the stem wall, insect screening under the furring air gap, and brick veneer to protect slab-edge insulation.