Showing results 1 - 100 of 483
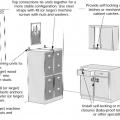
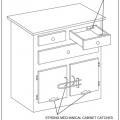
A combination of brackets and self-locking drawers. Drawer closures should be used to protect the home during seismic events.
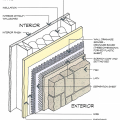
A continuous drainage mat rainscreen made from vacuum-molded plastic provides uniform support for the siding and allows moisture to flow horizontally and diagonally in addition to vertically.
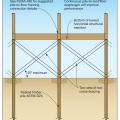
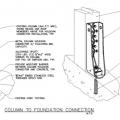
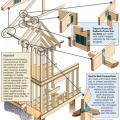
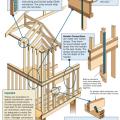
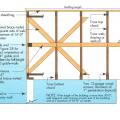
A continuous load path uses structural connections to transfer horizontal and vertical loads from the roof to the foundation to help keep the building intact in high-wind and seismic events
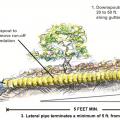
A drywell, shown here used for downspout catchment, can also be used to receive water from a French drain.
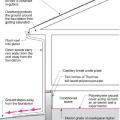
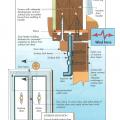
A flat plate solar hot water system heat potable water in a glass covered collector that sits on the roof.
A French drain contains a perforated drain pipe wrapped in rock and landscape fabric.
A gable end failure due to improper bracing caused collapse of most of the trusses on this roof under hurricane force wind conditions.
A masonry chimney is reconstructed to withstand seismic forces by adding an insert to the existing firebox
A masonry chimney is reconstructed to withstand seismic forces by completely retrofitting the firebox and chimney using light-frame construction on the top of the foundation
A masonry chimney is reconstructed to withstand seismic forces by maintaining the current firebox but replacing the chimney section with a metal flue and light-weight chimney enclosure.
A masonry chimney is shortened and capped at roof level to reduce its chances of detaching in high winds or earthquakes; the fireplace can no longer be used.
A metal storm panel is installed in a track permanently mounted above and below the window frame and secured with wing nuts to studs mounted on the track.
A molded plastic drainage board rainscreen allows vertical drainage while providing uniform support for the siding and resisting compression from screws and nails.
A plastic fiber drainage mat rainscreen provides uniform support for the siding and allows moisture to flow horizontally and diagonally in addition to vertically.
A raised wood pier foundation can raise the subfloor above the design flood elevation.
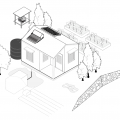
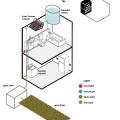
A resilient home with storm shutters, a sump pump that drains to a french drain, rainwater collection, solar thermal and PV, and raised garden beds.
A resilient multifamily building in Puerto Rico constructed of concrete on a raised slab foundation with a hip roof design for wind resistance and deep overhangs and permanent awnings to keep sun and rain off windows.
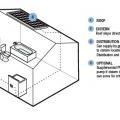
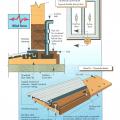
A self-sufficient water system for a home could include a rooftop cistern and solar thermal water heater.
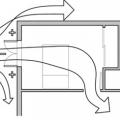
A shallow, open floor plan allows free flow of cross ventilation through the house
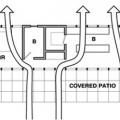
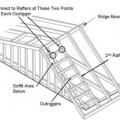
A single-story house floor plan showing braced wall line locations at A through E and 1 through 5
A swale and berm can be installed together across a slope to slow the downhill flow of water.
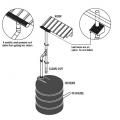
A thermosiphon solar hot water system heats a fluid in the solar collector; the heated fluid heats potable water in a roof top tank.
Accordion-type hurricane shutters protect sliding glass doors from high winds and wind-borne debris.
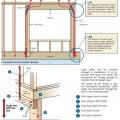
Add metal connectors to strengthen framing connections in an existing wall from inside the home by removing drywall.
Adding planted terraces to a sloped yard can slow down runoff and reduce erosion
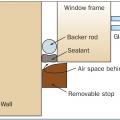
Air seal door and window rough openings with backer rod, caulk, or nonexpanding foam
Airflow can be directed across thermal mass in the ceiling, floor, or elsewhere inside the home through various window and louver configurations
An engineered bioswale uses perforated pipe laid in rock and landscape fabric at the bottom of a vegetated trench to direct water away from a site.
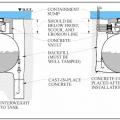
An underground fuel tank is anchored onto poured-in-place concrete counterweights.
Anchorage failure in sliding glass doors due to negative pressures from hurricane force winds.
Anchoring hardware is used to tie down equipment and components of the home to resist high winds and hurricanes.
Backup generators usually run on gas, propane, or diesel-powered and typical sizes for homes generate 2,500 to 7,500 watts.
Berms are compacted earth or gravel ridges that slow the flow of water from rain, riverine flooding, or storm surges in coastal areas.
Berms, swales, bioswales, ridges, and vegetation all help to control rainwater runoff on residential sites.
Bioswales or rain gardens filter storm water through vegetation and rock and sand substrate layers.
Building America worked with Mercedes Homes in east Florida to design homes using cast-in-place concrete walls capable of withstanding wind-blown debris impacts of up to 200 mph (Source: Mercedes Homes).
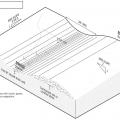
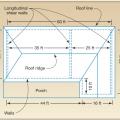
Building elevation and plan view of roof showing longitudinal shear walls; dimensions are wall-to-wall and do not include the 2-ft roof overhang.
Building siding extended down and over the breakaway wall so the upper wall was damaged when the lower wall broke away.
Buildings damaged by a hurricane storm surge: upper homes on gulf shoreline were hit by large waves above the lowest floor, lower left home on bay and right school 1.3 miles from gulf shoreline were hit by surge and small waves.
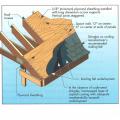
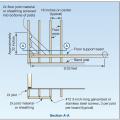
Built-up beam connections, knee brace connections, and diagonal brace connections for wood piles.
Casement windows or wing walls can create zones of higher pressure (right) and lower pressure (left) to encourage cross ventilation when wind is flowing parallel to window openings
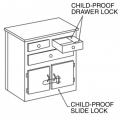
Child-proof slide locks can be used on drawers and cabinets to prevent their accidental, unintended use.
Coastal flooding washed away most of the first floor of this home; however, the piers and roof are still standing.
Coastal flooding washed away this home but left the masonry piers, which are set in concrete bases.
Comfort ventilation focuses on airflow over occupants; in this example of wind-driven cross ventilation, the air is directed through the main occupied areas of the bedroom
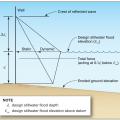
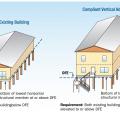
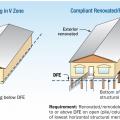
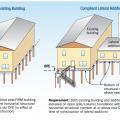
Comparison of a building that sits below the Design Flood Elevation and renovated to be above the DFE and to add a second story.
Comparison of a building that sits below the Design Flood Elevation and renovated to be above the DFE.
Comparison of a building that sits below the Design Flood Elevation and renovated to be above the DFE.
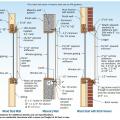
Composition shingle roofing system showing sheathing and hot-mopped underlayment
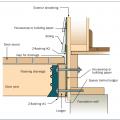
Comprehensive water management features include a capillary break (≥ 6-mil polyethylene sheeting) at all crawlspace floors
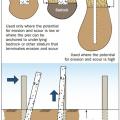
Concrete pier foundations can be used in place of wood piles in coastal areas where risk of erosion and scour is low.
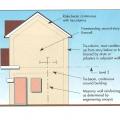
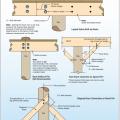
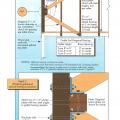
Connecting hardware helps tie the roof to the walls to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
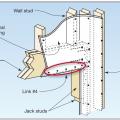
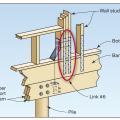
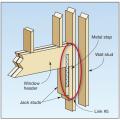
Connecting hardware helps tie the walls to the top plates and rim joists to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
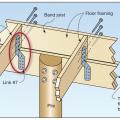
Connection of floor framing to support beam for a coastal home built on piles (band joist nailing to the floor joist is adequate to resist uplift forces).
Continuous load path failure due to improper connections between a home and its foundation allowed this building to be overturned in hurricane force winds.
Continuous load path failure due to improper connections between the roof decking and roof framing resulting from hurricane force winds.
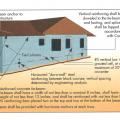
Correct seismic retrofit hardware for securing the sill plate to foundation wall
Covering old asphalt shingles with new shingles can cause substrate irregularities that can interfere with the bonding of the self-seal adhesives in the new shingles.
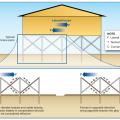
Diaphragm stiffening and corner pile bracing to reduce pile cap rotation for homes built on pile foundations.
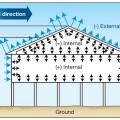
Distribution of roof, wall, and internal pressures on one-story, pile-supported building.