Showing results 1 - 248 of 248
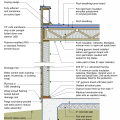
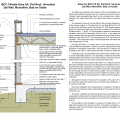
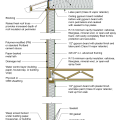
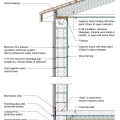
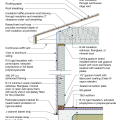
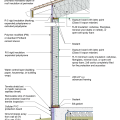
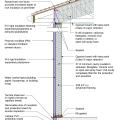
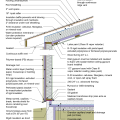
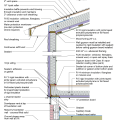
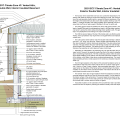
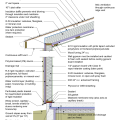
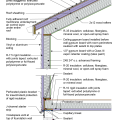
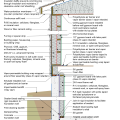
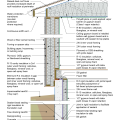
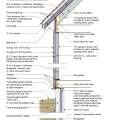
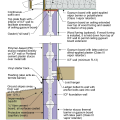
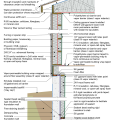
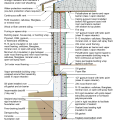
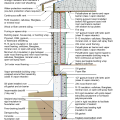
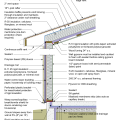
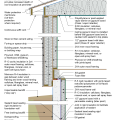
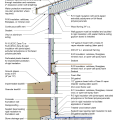
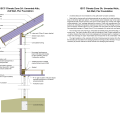
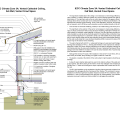
2021 IECC Climate Zone 1A: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade
2021 IECC Climate Zone 1A: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade (with notes)
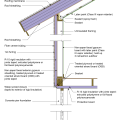
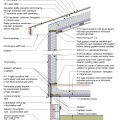
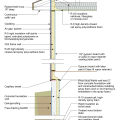
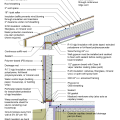
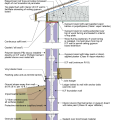
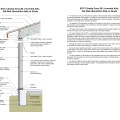
2021 IECC Climate Zone 2A: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade
2021 IECC Climate Zone 2A: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade (with notes)
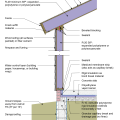
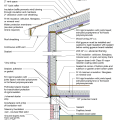
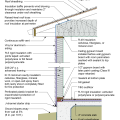
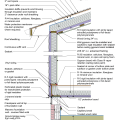
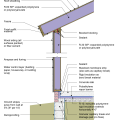
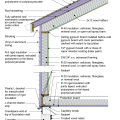
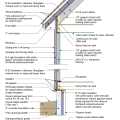
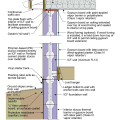
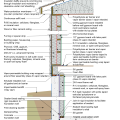
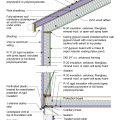
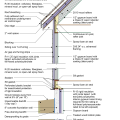
2021 IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall-CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
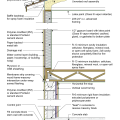
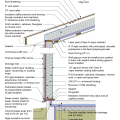
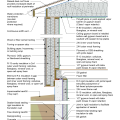
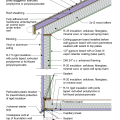
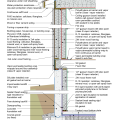
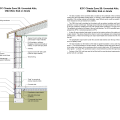
2021 IECC Climate Zone 2B: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade
2021 IECC Climate Zone 2B: Flat Roof, Unvented, 2x6 Wall, Monolithic Slab on Grade (with notes)
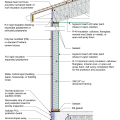
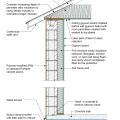
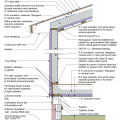
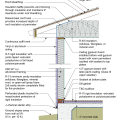
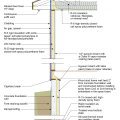
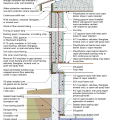
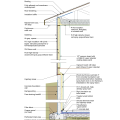
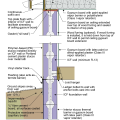
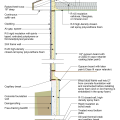
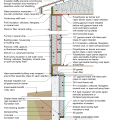
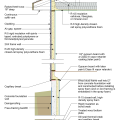
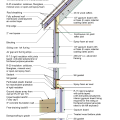
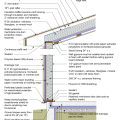
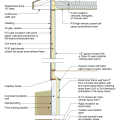
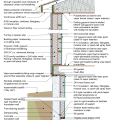
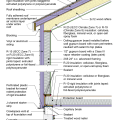
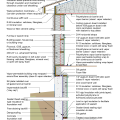
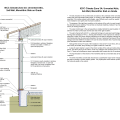
2021 IECC Climate Zone 3A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space
2021 IECC Climate Zone 3A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 3B: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space
2021 IECC Climate Zone 3C: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space
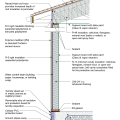
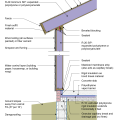
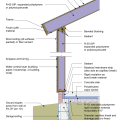
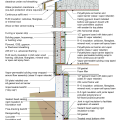
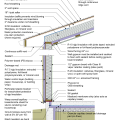
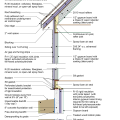
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Slab on Grade (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4B: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Slab on Grade (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4B: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Vented Crawl Space
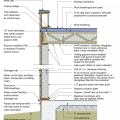
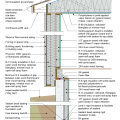
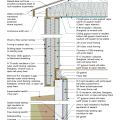
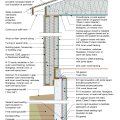
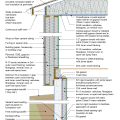
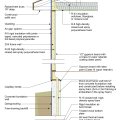
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, 2x4 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, ICF Wall, ICF Basement Foundation (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Slab on grade (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 4C: Vented Over-Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5: Vented Attic, 2x4 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5A: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5A: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5A: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5A: Vented Over Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5B: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5B: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5B: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5B: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5B: Vented Over Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5C: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5C: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5C: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5C: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 5C: Vented Over Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6: Vented Cathedral ceiling, 2x6 Wall, interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6: Vented Cathedral ceiling, 2x6 Wall, interior Insulated Basement (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6A: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6A: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6A: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6A: Vented Over-Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6A:Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6B: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6B: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6B: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6B: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 6B: Vented Over-Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zone 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement (with notes)
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, 2x4 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, ICF Wall, ICF Basement Foundation
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Slab on Grade
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Over-Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
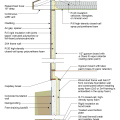
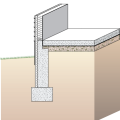
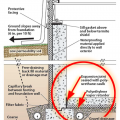
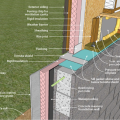
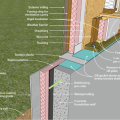
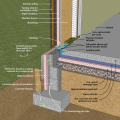
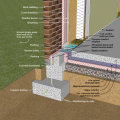
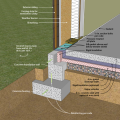
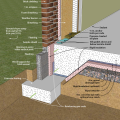
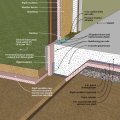
A concrete slab-on-grade foundation with exterior insulation, which can be elevated above the local grade as a flood-prevention strategy.
A paint-on waterproofing covers the exterior and tops of the concrete block foundation walls and piers to block moisture moving up through the concrete, while foil-faced R-13 insulation lines the inside surface of the exterior walls.
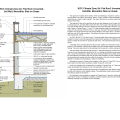
Assembly can be used in IECC CZ 3 and above to thermally isolate garages in multifamily row houses with slab foundations. For unheated garages, it is unnecessary to insulate wall between garage and exterior of slab or slab underneath garage.
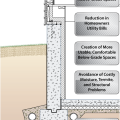
Because the above-grade potions of the wall lack exterior insulation, condensation and even ice form during cold winter conditions
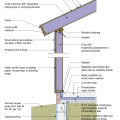
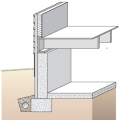
Brick veneer framed wall supported by a concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
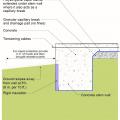
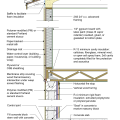
Crawl space interior insulation with EPS or XPS semi-permeable insulation on inside wall
Exterior fiberglass insulation on this new home was (incorrectly) cut to terminate below-grade after backfill, which will expose the above-grade portions of the foundation wall to cold temperatures
Exterior XPS basement insulation is correctly installed to completely cover the foundation wall
Externally insulated concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
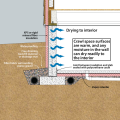
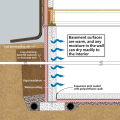
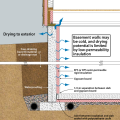
Foil-faced rigid foam and spray foam can be used to insulate a basement on the interior; use good moisture management techniques to keep the basement dry
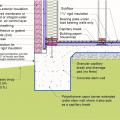
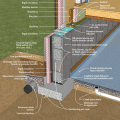
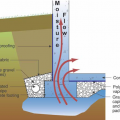
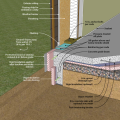
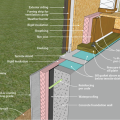
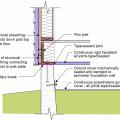
Good water management practices like sloping grade away from house, and installing gutters, perimeter drain pipe, a capillary break, and free-draining soils or drainage mat protect the foundation from water saturation.
ICF bricks are stacked to form hollow walls that are reinforced with steel rebar before the concrete is poured in
ICF foundation walls wrap the floor slab in R-22 of insulation while the entire space under the slab is covered with 4.3 inches of closed-cell spray foam.
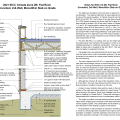
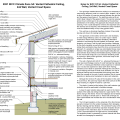
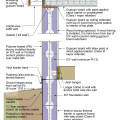
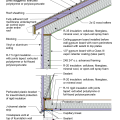
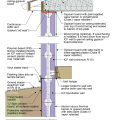
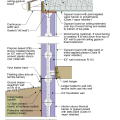
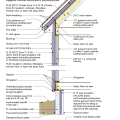
IECC Climate Zone 1A: Unvented Attic with Spray foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall-CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
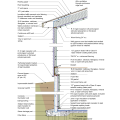
IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall/CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall/CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
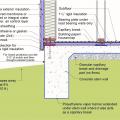
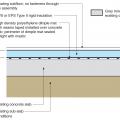
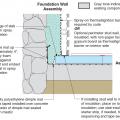
In cold climates, install slab edge insulation when pouring slab on grade foundations.
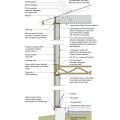
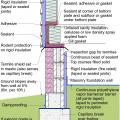
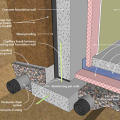
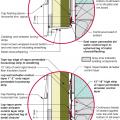
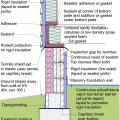
Pest proofing of this unvented crawlspace includes a metal termite shield that extends out from the sill plate, metal flashing wrapping the bottom of exterior rigid foam, and a termite inspection gap above interior rigid foam.
Right - A corrugated metal closure conceals the exterior rigid insulation at the slab edge
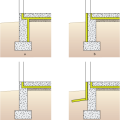
Right - Additional potential locations for slab-on-grade insulation include (a) under the slab and outside the perimeter with optional underground moisture block, (b) under the whole foundation, or (c) on top of the slab.
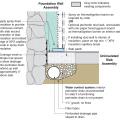
Right - Basement slab with a capillary break of either gravel or a drainage mat.
Right - Basement with exterior XPS or EPS insulation and insulation under the basement slab.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam covers the interior of the foundation wall and wall framing is placed to the inside of the spray foam.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam is used to retrofit an existing rubble basement foundation wall.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam was applied to the interior of a foundation wall.
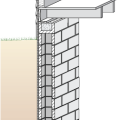
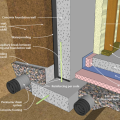
Right - Concrete masonry unit (CMU) basement wall showing exterior insulation and sill detail; above-grade wall has sheathing to the inside of the rigid foam.
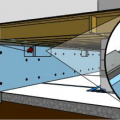
Right - Foil-faced polyisocyanurate insulating rigid foam sheathing is installed below the floor framing of this house built on piers; however, the seams should be sealed with metal taped and the plumbing elevated and protected.
Right - Foil-faced polyisocyanurate rigid foam board is tightly installed and sealed against a concrete foundation wall prior to installing fibrous blanket insulation.
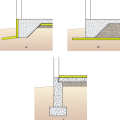
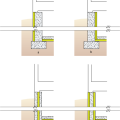
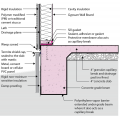
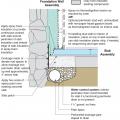
Right - Potential locations for basement insulation in new construction, slab insulation should always be underneath, with walls insulated (a) inside, (b) outside, (c) sandwiched inside, or (d) inside and outside of walls.
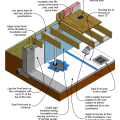
Right - Potential locations for crawlspace insulation: vapor sheeting should always cover the floor with insulation (a) outside walls, (b) inside walls, (c) both sides of walls, (d) sandwiched inside walls, or (e) under the first floor.
Right - Potential locations for slab-on-grade stem insulation in new construction: slab insulation should always be underneath, with stem walls insulated (a) inside, (b) outside, (c) not at all, or (d) outside with underground extension to repel moisture.
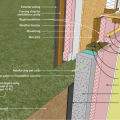
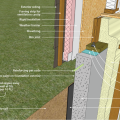
Right - Poured concrete basement wall showing exterior insulation and sill detail; above-grade wall has sheathing to the inside of the rigid foam.
Right - Poured concrete basement wall showing exterior insulation and sill detail; above-grade wall has sheathing to the outside of the rigid foam.
Right - Retrofit of an existing basement slab by adding dimple plastic mat, rigid foam insulation, and a floating subfloor.
Right - Rigid foam insulation is installed along the exterior edge of an existing foundation slab.
Right - Rigid foam is installed over a waterproofing membrane that has been applied to the basement foundation walls.
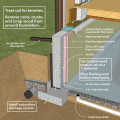
Right - The basement foundation is insulated on the exterior and termite shield extends out past the top of the insulation.
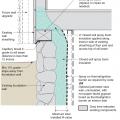
Right - The concrete basement wall is insulated on the interior with rigid foam; the footing detail is shown.
Right - The concrete masonry unit (CMU) basement wall has exterior insulation; the footing details include interior and exterior footing drain pipe.
Right - The existing basement slab is retrofitted by installing a dimple plastic drainage mat, rigid foam insulation, and a floating subfloor.
Right - The slab-on-grade foundation is insulated with two layers (R-20) of XPS foam under the-slab and R-10 on the exterior of the stem walls.
Right - This concrete basement wall is insulated on the interior basement walls with spray foam and under the slab with rigid foam; footing details are shown.
Right - This concrete basement wall is insulated on the interior with rigid insulation; sill details are shown.
Right - This concrete basement wall is insulated on the interior with spray foam insulation; sill detail are shown.
Right - This poured concrete basement wall is insulated on the exterior and under the slab with rigid insulation; footing details include interior and exterior footing drain pipe.
Right - This rigid insulation is correctly installed in a level layer over aggregate; the seams will be taped
Right - XPS rigid foam board is tightly installed against a concrete foundation wall and seams are sealed with tape prior to installing fibrous blanket insulation.
Right – 11-inch ICFs provide R-50 of wall insulation from the footing to the roof on this cold-climate home.
Right – After installing the insulated concrete foundation wall panels, the builder installed underslab rigid foam, which was topped by 4 inches of crushed rock then the poured slab.
Right – Insulated concrete forms (ICFs) provide the insulated stem wall for the slab-on-grade foundation for this SIP house.
Right – Polyethylene sheeting vapor barrier is installed and sealed to the crawlspace walls with mastic
Right – Prepoured foundation panels with integrated insulation and vapor barrier are installed in place.
Right – R-20 of XPS and polyiso rigid foam were added on the slab shelf that is part of this precast foundation wall system.
Right – Rigid foam was attached to the tops of the precast foundation walls to form an insulated edge for the floor slab.
Right – Spray foam insulation was sprayed onto the ground and along the sides of the foundation walls and piers of this insulated crawl space.
Right – The raised slab foundation has a 3-ft stem wall of filled concrete block, then is back-filled with compacted dirt and crushed rock, then insulated with 1” rigid foam covered with taped vapor barrier, under a floor slab.
Right – This wall is constructed with the sill plate overhanging the top of the foundation wall so that when rigid foam is installed on the exterior of the foundation wall, its surface will align with the surface of the wall sheathing.
Right – Two inches of rigid foam was installed on the ground before pouring the basement floor slab while precast, pre-insulated concrete panels comprise the basement walls.
Right-Polyethylene sheeting is correctly installed over aggregate and taped to pillars and foundation wall
Rigid foam extends under the full slab and lines the inside edges of the foundation walls.
Rigid foam insulation and a thin slab were installed over the dirt and gravel of this sealed crawlspace
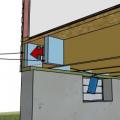
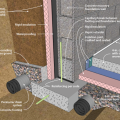
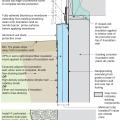
Rigid insulation and water control layers are installed on the exterior of a flat foundation wall; spray foam insulates the rim joist
Spray foam and rigid foam were used under the slab while rigid foam wraps the exterior of the foundation walls.
Spray foam extends down the foundation wall to the slab, which has been retrofitted by adding dimple plastic drainage mat and rigid foam insulation.
Spray foam extends down the inside of the foundation wall to the uninsulated slab; because the wall lacked exterior perimeter drainage, the slab was cut and an interior footing drain was installed.
Spray foam insulation extends down the foundation wall to the slab, which has been retrofitted by cutting the slab to install drainage mat against the wall and a new perimeter footing drain, along with rigid foam plastic above the slab.
Stucco is installed over rigid insulation, which is installed over a drainage plane consisting of a drainage gap and building wrap layer over the sheathing
The basement slab is wrapped in a blanket of insulation including R-27 of closed-cell spray foam under the slab and R-22 ICF blocks wrapping the slab edges.
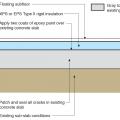
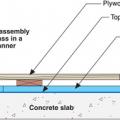
The existing slab is retrofitted by coating with epoxy paint, then installing rigid foam insulation and a floating subfloor.
The existing slab is retrofitted with epoxy paint, rigid foam insulation, sleepers (furring strips), and subfloor.
The home’s slab-on-grade foundation is wrapped in a blanket of rigid foam extending completely under the slab and along the edges.
These below-grade walls are insulated along the exterior with R-5 of bug-resistant high-density rigid fiberglass insulation installed over damproofing.
This 4-inch layer of rigid foam insulation (R-20) will be sandwiched between two layers of concrete poured on site for a highly insulated foundation wall.
This assembly can be used to thermally isolate heated or partially heated garages with slab foundations from the exterior in multifamily row houses/townhouses in IECC Climate Zones 3 and higher.
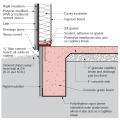
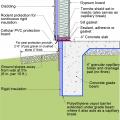
This basement is insulated on the exterior with rigid foam over dampproofing, with granular backfill and footing drains to facilitate drainage away from the foundation, a termite shield to protect from pests, and cellular PVC to protect the rigid foam.
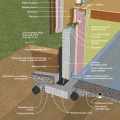
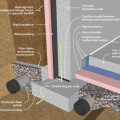
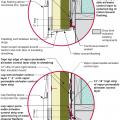
This exterior insulated slab-on-grade monolithic grade beam foundation is protected from pests by termite shield at the sill plate, borate-treated framing, flashing at end of wall insulation, brick veneer over slab-edge insulation, and rock ground cover.
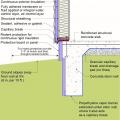
This exterior wall retrofit permits drying to the exterior of a sill plate installed on an untreated flat foundation wall
This exterior wall retrofit permits drying to the exterior of a sill plate installed on an untreated irregular foundation wall
This home has a cost-saving shallow frost-protected foundation that uses rigid foam laid vertically at the base of the 16-inch-deep footers to protect the foundation from frost damage.
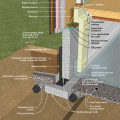
This house with an insulated slab is protected from pests with a termite shield at the sill plate, borate-treated framing, insect screen covering bottom of furring air gap, and brick veneer over slab-edge insulation
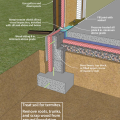
This house with interior insulated crawlspace is protected from pests with termite shield at sill plate, borate-treated framing, flashing at end of wall insulation, and a termite inspection gap at the top of the rigid foam
This Texas homes uses a slab foundation including a 4-in.-thick post-tensioned monolithic slab with turned-down edges poured over a 6-mil polyethylene vapor barrier and capillary break; slab edge insulation is not used due to termite risk.
Unvented crawl space with interior insulation - designed for termite resistance in heavily infested areas
Wrong - Moisture from within the basement foundation wall can migrate into the insulation cavity in a conventional blanket insulation installation.
Wrong - Polyethylene sheeting should be lapped up sides of walls and pillars and taped
Wrong - The basement blanket insulation is loosely attached to the interior of the basement wall, does not cover the entire wall, is not sealed at the edges, and is not installed over rigid foam that covers the entire surface of the foundation walls.
Wrong – The polyethylene sheeting vapor barrier is not attached to the piers with mechanical fasteners
Wrong – When more than one layer of insulation is installed, the seams should be staggered to discourage ground water from reaching the foundation wall.