Scope
Air-seal the common wall between units in a multifamily structure to minimize air leakage and provide a control layer for sound, smoke, fire, and air quality.
- In multifamily buildings, air-seal the gap between the drywall shaft wall (i.e., common wall) and the structural framing between units at all exterior boundaries.
- Confirm with local code officials which air-sealing materials are preferred for fire safety reasons.
- Possible air-sealing materials include fireproof spray foam for sealing the bottom plate to subfloor and bottom and top plates to sheathing in wood-framed walls, fire-rated caulk around plumbing and wiring, and two-part urethane foam for masonry block walls.
See the Compliance Tab for links to related codes and standards and voluntary federal energy-efficiency program requirements.
Description
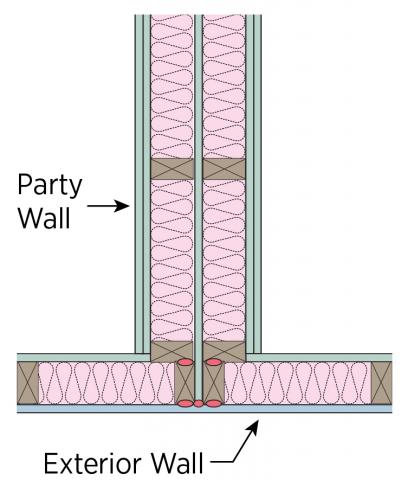
Common walls (also called party walls, adiabatic walls, or shared partition walls) between units in multifamily housing (e.g., townhouses, duplexes, and apartments) should be constructed as airtight assemblies for sound, smoke, fire, and air quality control. However, experience has shown that these common walls can often be significant sources of air and heat loss if gaps or cracks exist in the connections between each unit’s walls (Figure 1). For more information, see the guide on Air Sealing and Compartmentalization in Multifamily Buildings.
To reduce air leakage, common wall assemblies should be air-sealed at all boundaries. Wood-framed walls are sealed with fireproof spray foam (Figure 2). Masonry block party walls, which form “chimneys” because of their open cores, can be air sealed with two-component urethane foam, which also reduces sound and odor transfer, as well as dust, insect, and moisture entry. These walls are fire-rated assemblies for each unit. Acceptable materials for air sealing common walls can vary significantly around the country. Confirm with local code officials which material is preferred for fire safety reasons. Any plumbing and wiring penetrations through the drywall surfaces of the common walls should be sealed with fire-rated sealant materials (BSC 2009). The 2009 IECC requires that air barriers be installed in common walls; for more information, see the Compliance tab in this resource guide (Otis and Maxwell 2012).
Air-sealing of common walls might be done by the framer. This task should be included in the contract for the appropriate trade depending on the workflow at the specific job site.
How to Air-Seal a Common Wall
- Check local code requirements to determine appropriate fire-rated materials for air-sealing common walls between dwelling units. Such materials include intumescent caulks, fire-rated (high-temperature) caulks, and fire-rated one-component foam (Otis and Maxwell 2012).
- Use caulk, foam or equivalent material to seal the drywall to the top plates and bottom plates of the common walls. Also seal at the seam between the top and bottom plates and the exterior sheathing.
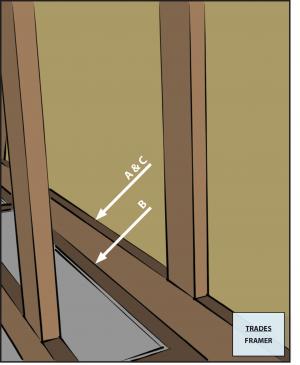
- Caulk the first stud of each partition wall to the exterior wall studs (Figure 3).
Success
Common walls (also called party walls, adiabatic walls, or shared partition walls) between units in multifamily buildings should be visually checked to ensure that the gap between the drywall and the structural framing is sealed with caulk, foam or other sealing material. Air barrier effectiveness is measured at the whole-house level for single-family homes, and at the dwelling unit level for multifamily buildings. Blower door testing, which is conducted as part of the building energy performance test, may help indicate whether common walls have been successfully sealed.
Climate
No climate specific information applies.
Training
CAD
Compliance
More
More Info.
Access to some references may require purchase from the publisher. While we continually update our database, links may have changed since posting. Please contact our webmaster if you find broken links.
The following authors and organizations contributed to the content in this Guide.
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Steven Winter Associates, lead for the Consortium for Advanced Residential Buildings (CARB), a DOE Building America Research Team
Sales
Tight Air Sealed Home = Comprehensive Draft Protection

Poorly air-sealed homes are less comfortable and cost more to maintain because they provide a pathway for drafts, cold spots, moisture, and insects into the home. Comprehensive draft protection includes a continuous air barrier around the whole house along with caulking and sealing in all holes and cracks. This includes around wiring, plumbing, ducts, and flues; where wall framing meets flooring; around windows; where drywall meets top plates and sill plates; where rim joists meet foundation walls and subfloors; etc. Spray foam insulation can be used at rim joists, floors above unconditioned space, and in attics to insulate and air seal at the same time.