Showing results 1 - 50 of 128
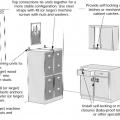
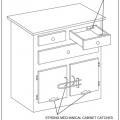
A combination of brackets and self-locking drawers. Drawer closures should be used to protect the home during seismic events.
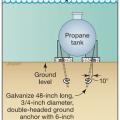
A fuel tank should be anchored with ground anchors designed for site conditions to maintain secure connection to its base in a flood or earthquake
A masonry chimney is reconstructed to withstand seismic forces by adding an insert to the existing firebox
A masonry chimney is reconstructed to withstand seismic forces by completely retrofitting the firebox and chimney using light-frame construction on the top of the foundation
A masonry chimney is reconstructed to withstand seismic forces by maintaining the current firebox but replacing the chimney section with a metal flue and light-weight chimney enclosure.
A masonry chimney is shortened and capped at roof level to reduce its chances of detaching in high winds or earthquakes; the fireplace can no longer be used.
A resilient multifamily building in Puerto Rico constructed of concrete on a raised slab foundation with a hip roof design for wind resistance and deep overhangs and permanent awnings to keep sun and rain off windows.
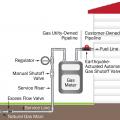
A seismic shut off valve with a stopper to cease the flow of gas to a property during the event of an earthquake.
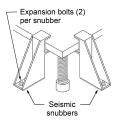
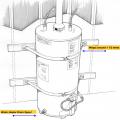
A seismic snubber is a type of bracket specifically designed to anchor heavy equipment to the floor to restrain it in the event of an earthquake.
A simple kit for anchoring a TV, appliance, or furniture to a wall may include straps, attachment hardware, and screws for attaching both to the appliance and to the wall
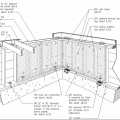
A single-story house floor plan showing braced wall line locations at A through E and 1 through 5
A water heater is anchored to 2 x 4 wood blocking that is attached to the wall studs.
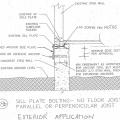
An anchor side plate is used to connect the concrete foundation to the sill plate from the exterior as part of a seismic retrofit when the sill plate is not accessible from the interior of the home
An earthquake-actuated automatic gas shutoff valve is attached to the natural gas pipeline between the meter and the house, downstream of the meter, to stop the flow of gas into the house if an earthquake occurs.
An example of a vertical California Seismic Valve
An indoor water heater should be secured to the wall’s studs to prevent it from moving or tipping over in the event of an earthquake
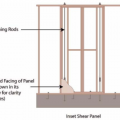
An Inset Shear Panel constructed with 2x4 dimensional lumber installed into a 2x6 stud bay
Anchor bolts should be at least 1/2-inch diameter and should be embedded at least 7 inches into the foundation, spaced not more than 6 feet apart, and between 3.5 and 12 inches from each end of the sill plates.
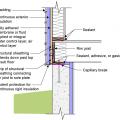
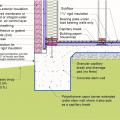
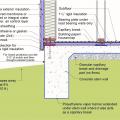
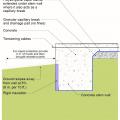
Brick veneer framed wall supported by a concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Brick veneer is supported by a concrete stem wall thermally separated from the slab-on-grade foundation with turn-down footing which is also insulated on top; anchorage for seismic resistance is also shown
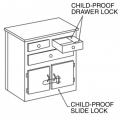
Child-proof slide locks can be used on drawers and cabinets to prevent their accidental, unintended use.
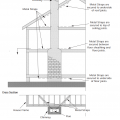
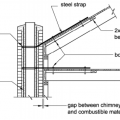
Chimney retrofit includes metal strap reinforcement at different levels of the home
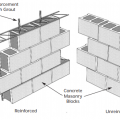
CMU construction can be reinforced with vertical rebar and horizontal steel reinforcement (left) or unreinforced (right), depending on structural requirements
Comparison of costs for preventing vs. repairing earthquake damage from unreinforced masonry chimney failure
Concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
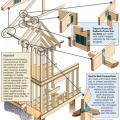
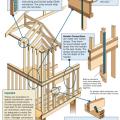
Connecting hardware helps tie the roof to the walls to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
Connecting hardware helps tie the walls to the top plates and rim joists to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
Correct seismic retrofit hardware for securing the sill plate to foundation wall
Critical connections for providing a continuous load path in buildings and storm shelters
Cross section showing points of reinforcement and attachment to secure the chimney to the roof and ceiling joists.
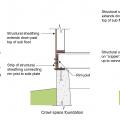
Detail for reinforcing a cripple wall to resist earthquake movement by installing anchor bolts and plywood reinforcement.
Durability concerns on a house continuously sheathed with a proprietary fiber structural panel used as bracing. Photo 1 of 2.
Durability concerns on a house continuously sheathed with a proprietary fiber structural panel used as bracing. Photo 2 of 2.
Earthquake-actuated automatic gas shutoff valves are installed on the downstream or homeowner’s side of the meter.
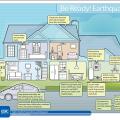
Earthquake-ready home actions include securing cabinets, shelves, and heavy furniture or electronics to walls and preparing utilities for disruptive movement.
Earthquake-ready home actions include securing water heaters, shelves, and heavy furniture to walls and preparing utilities for emergency shut-off.
End conditions for braced wall lines with continuous sheathing, Figure R602.10.7 in the IRC
Every natural gas appliance has a shutoff valve in the gas line to the appliance that can be manually shut off if a leak happens at a specific appliance or in preparation for an impending natural disaster.
Excess Flow Valves and Earthquake-Actuated Gas Shutoff Valves are two different types of valves that automatically stop the flow of gas into the house: excess flow valves stop gas flow if there is a break in the line, earthquake valves stop gas flow if th
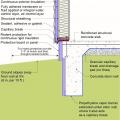
Externally insulated concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
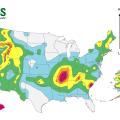
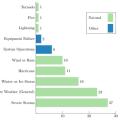
Extreme weather, such as wind, fire, flood, or extreme heat (included in the Severe Weather category above) causes most large electric disturbance events in the U.S (defined as affecting at least 50,000 customers) (data from 2000-2016)
For seismic resistance in basement, crawlspace, and crawlspace “cripple” wall foundations, connect the plywood or OSB sheathing to the wall framing, rim joist, and sill plate and anchor bolt the sill plate to the foundation