Showing results 301 - 350 of 1165
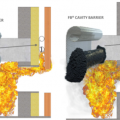
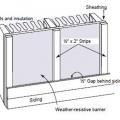
Fire barriers for ventilated wall cavities use thermally activated expansive materials to close off the ventilation space between the wall cladding and the sheathing during a fire while allowing air flow through the metal mesh during normal conditions
Fire barriers for ventilated walls use heat activated intumescent expansive materials to close off the ventilation space between the wall cladding and the sheathing during a fire while allowing air flow through the metal mesh during normal conditions
Fire resistance plans for a community include creating defensible space for each home and for the whole community, constructing with fire-resistant materials, and providing turn-around space for emergency response vehicles.
Fire suppression sprinklers can be set to activate only in the room where a fire is sensed.
Firewall separation. Results from building corners being discontinuous with tie-beams.
Flame Spread Classification and Ratings for Common Building Materials (adapted from Louisiana Office of State Fire Marshall 2021)
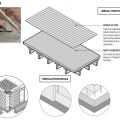
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.
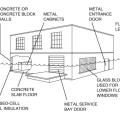
Flood damage-resistant materials include concrete and tile flooring, metal cabinets and doors, and glass-block windows.
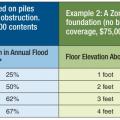
Flood Insurance Premiums Can be Reduced Significantly by Building above the BFE.
Flood vents allow floodwaters to enter and exit the crawlspace without causing hydrostatic pressure differences
Florida Wind-Borne Debris Region, Category II and III Buildings and Structures except health care facilities.
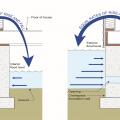
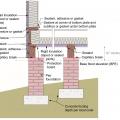
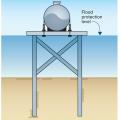
For homes built in high probability flood zones, move all possible plumbing equipment above the Base Flood Elevation (BFE), shown here as “Flood Protection Level;” equipment that cannot be moved should be watertight to resist floodwater
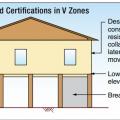
For homes built in V Zones a registered professional engineer or architect must certify that the lowest floor elevation is above the BFE and piles and structure are anchored to resist flotation, collapse, or lateral movement due to combined wind and water
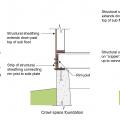
For homes built on an open foundation, provide a continuous air barrier by sealing all joints between the rigid insulation, floor support beams, rim joist, and bottom wall plate
For seismic resistance in basement, crawlspace, and crawlspace “cripple” wall foundations, connect the plywood or OSB sheathing to the wall framing, rim joist, and sill plate and anchor bolt the sill plate to the foundation
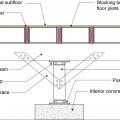
For seismic retrofit of crawlspace with posts and piers, add cross bracing to posts; add cross bracing and solid blocking between floor joists
Four types of residential fire sprinkler heads: pendent, concealed, sidewall, and concealed sidewall.
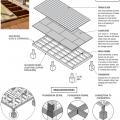
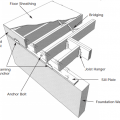
Framing anchors, anchor bolts, joist hangers, and bridging pieces all help to tie the components of the floor system together and to the foundation to increase resistance against seismic forces.
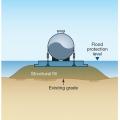
Fuel storage tanks are at risk of displacement during floods and should be securely anchored to the ground or base
Fuel tank anchored below ground in a flood-prone area anchored to a counterweight to counteract the buoyancy force.
Fuel tank is elevated above flood waters and anchored to supporting frame
Fuel tank is elevated above flood waters on a base of structural fill and anchored to the concrete pad
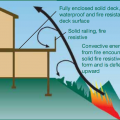
Fully enclosing the area under the deck increases its resistance to wildfire by minimizing the space where embers can lodge.
Furniture and heavy household items should be anchored to prevent tipping over during an earthquake and for everyday use if small children are in the home
Gable end vents allow in wind-driven rain because pressures that develop between the outside surface of the wall and the inside of the attic are sufficient to drive water uphill several inches.
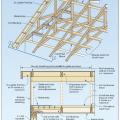
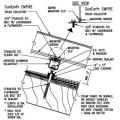
Gable-end bracing detail; nailing schedule, strap specification, brace spacing, and overhang limits should be adapted for the applicable basic wind speed.
Glass blocks allow in daylight while maintaining privacy and also provide protection against high winds and floods.
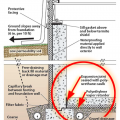
Good water management practices like sloping grade away from house, and installing gutters, perimeter drain pipe, a capillary break, and free-draining soils or drainage mat protect the foundation from water saturation.
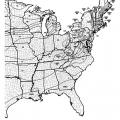
Ground Snow Loads for the United States (eastern), from 2021 IRC, Figure R301.2 (4)
Ground Snow Loads for the United States (western), from 2021 IRC, Figure R301.2 (3)
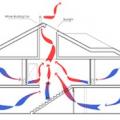
Having both low and high ventilation openings is necessary to promote airflow from the stack effect
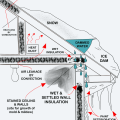
Heat loss through the roof of a home in a cold climate zone leads to snow melting to form ice dams.
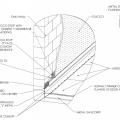
Heavy metal flashing protects the deck timbers and separates them from the wall at the wall-deck connection which is vulnerable to both ember entrapment and water damage.