Showing results 101 - 200 of 504
Failure of Roof Structure from Pressurization Due to Window Failure During a Hurricane.
Fill in the hole left by the missing top plate with a rigid air blocking material or rolled batt insulation that is spray foamed in place
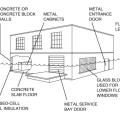
Flood damage-resistant materials include concrete and tile flooring, metal cabinets and doors, and glass-block windows.
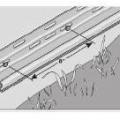
Floor cavity air pressure is measured by placing a tube into the floor cavity through a small drilled hole
Floor cavity pressure is measured by inserting a tube into the floor cavity using an extension pole
Foil-faced rigid foam and spray foam can be used to insulate a basement on the interior; use good moisture management techniques to keep the basement dry
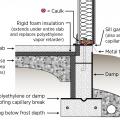
For slabs on grade in CZ 4 and higher, 100% of slab edge insulated to ≥ R-5 at the depth specified by the 2009 IECC and aligned with thermal boundary of the walls
Gaps at shared common walls can be a significant source of air leakage in multi-family buildings
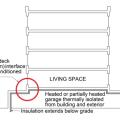
Heated or partially heated garages with podium decks should be thermally isolated from both ambient exterior space and interior conditioned space by insulating the interior of the garage walls and ceiling and extending the insulation below grade.
Heated recirculation plenum spaces can be installed in parking garages in cold climates to prevent pipes from freezing and warm the floor of occupied space directly above the garage.
ICFs provide continuous wall insulation from the roof to the footing with very little thermal bridging
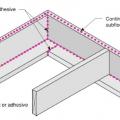
Identify what materials will constitute the continuous air barrier around the building envelope.
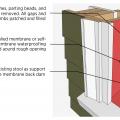
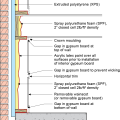
If water rises above the foundation and enters the wall cavity it will not damage the moisture-resistant closed-cell foam or exterior extruded polystyrene, while gaps in the paperless drywall allow airflow of easy removal of panels for drying and cleaning
In cathedral ceilings, parallel chord trusses allow thicker insulation levels over the exterior wall top plates.
Infrared imaging shows cold conditioned air pouring out of the open floor cavities under this attic kneewall into the hot unconditioned attic
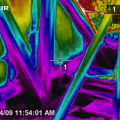
Infrared thermography during depressurization testing reveals air leakage at corner of spray foam-insulated room where wood-to-wood seams in framing were not air sealed
Install a continuous air barrier below or above ceiling insulation and install wind baffles.
Install a foam gasket along top plates before installing drywall
Install a housewrap drainage plane between the SIP panels and the exterior cladding
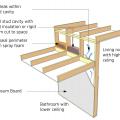
Install a rigid air barrier to separate the porch attic from the conditioned space.
Install an ENERGY STAR labeled insulated door with an automatic closer. Weather strip the door frame
Install continuous rigid foam insulation or insulated siding to help reduce thermal bridging through wood- or metal-framed exterior walls.
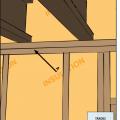
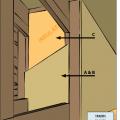
Install continuous top plates or blocking at the tops of walls adjacent to conditioned space to minimize air leakage.
Install insulation under platforms constructed in the attic for storage or equipment.
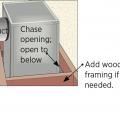
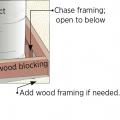
Install wood framing cross pieces in the attic rafter bays on each side of the duct chase
Install wood framing cross pieces in the attic rafter bays on each side of the duct chase
Insulating both exterior and garage-side faces of plaza deck can reduce thermal bridging. If garage is heated or partially heated, hybrid spray foam/batt insulation on garage side of plaza deck should extend to the perimeter of the garage.
Insulating the exterior and garage-side faces of the garage plaza deck can reduce thermal bridging. If the garage is heated or partially heated, the spray foam on the garage side of the plaza deck should extend to perimeter of garage.
Insulating the exterior and garage-side faces of the plaza deck can reduce thermal bridging. If the garage is heated or partially heated, the faced batt insulation on the garage side of the plaza deck should extend to perimeter of garage.
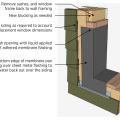
Lay out the rigid foam sheathing joints so they do not align with the window and door edges
Lifting plates attached to the wall provide good bracing to tighten up SIP panel seams
Light tubes adjacent to unconditioned space include lens separating unconditioned and conditioned space and are fully gasketed
Limited attic access can make inspections for missing air barriers and insulation challenging
Limited attic access may make it necessary to use a bore scope when inspecting for missing air barriers and insulation in existing buildings.
Make sure the beads of caulk are continuous the full length at each SIP panel seam, such as at the wall-roof seam, to maintain air barrier continuity
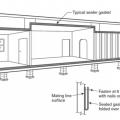
Marriage joints between modular home modules at all exterior boundary conditions fully sealed with gasket and foam
Peel-and-stick panel tape provides added assurance that SIP panel seams will remain airtight
Pressure manometers are used to determine the level of pressurization and rate of leakage when conducting blower door testing and building diagnostics
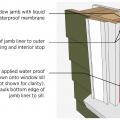
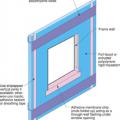
Proper flashing around windows is especially important when the rigid foam serves as the drainage plane in the wall
Raised heel energy trusses extend past the exterior wall and are deeper at the wall allowing room for full insulation coverage over the top plate of the exterior walls.
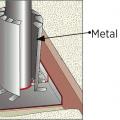
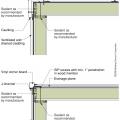
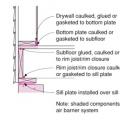
Right - A termite shield and a sill gasket are installed between the sill plate and the foundation on a raised slab foundation.
Right - Air barrier is present and installed between the floor system and unconditioned space.
Right - Air barrier is present between the dropped ceiling/soffit and the attic.
Right - Air barrier is present between the dropped ceiling/soffit and the attic.
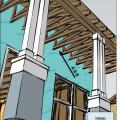
Right - Continuous wall sheathing and blocking has been installed to brace the raised heel trusses.
Right - Fiberglass/mineral wool insulation thermally isolates the garage from the interior occupied space above.
Right - Furring strips were installed with blocking to allow adequate room for 4 inches of mineral wool.
Right - Gasket installed at marriage wall connection prior to assembling modules
Right - Hole drilled to verify sealant is present - Hole will be sealed after verification
Right - Manometers are placed away from the indoor side of the fan during blower door testing
Right - Mineral Wool insulation is installed on the exterior of wall with furring strips.
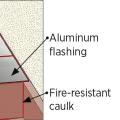
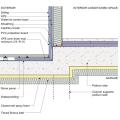
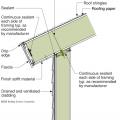
Right - New flashing has been installed to complete the air and water control layers at the window openings of this wall retrofit that includes insulating the wall cavities with spray foam
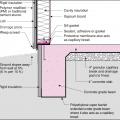
Right - Rigid foam slab edge insulation is installed along the exterior edge of a monolithic slab foundation.
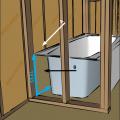
Right - The service penetrations through the structural slab in this garage plenum are air sealed.
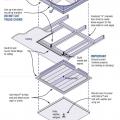
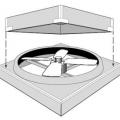
Right - This ceiling-mounted mini whole-house fan has built-in insulated covers to reduce heat loss when the fan is not in use
Right - This heated garage plenum is insulated along the bottom of the plenum space.
Right - This heated garage plenum is insulated and has an opening to access the interior, allowing for repairs and maintenance.