2021 IECC Climate Zone 2A Building Assembly: Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Pier Foundation
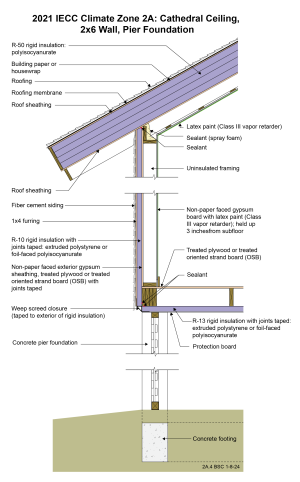
2021 IECC Climate Zone 2A: Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Pier Foundation
Notes
Drawing 2A.4: IECC CZ 2A: Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Pier Foundation
- Unvented attics and cathedral ceiling assemblies are more resistant to wind uplift under hurricane conditions.
- Note that the drawing calls out polyisocyanurate as an option for the rigid insulation on the roof but does not list other rigid foam options. This is because some materials may not be rated to withstand the temperatures that could be common if the roof is a dark shingle roof. Cooler roofs (lighter colors, different roofing materials, "cool" coatings) alleviate this concern. Check with manufacturers of specific insulation products to understand temperature tolerances and see the Cool Roof Rating Council for information on cool roof options. Another option is to use a vented over-roof system to keep the insulation layers cooler. See assembly drawings in Climate Zone 4C for an example of a vented over-roof assembly.
- Note that this assembly does not have an attic (vented or unvented). If the assembly did have an attic space, Section R402.2.1 of the 2021 IECC may apply, depending on the interpretation of the local code official. If so, R-38 could be used over the attic rather than R-49 as long as the R-38 insulation extended over the full width of the exterior wall top plate.
- The wall and roof cavity framing is uninsulated to facilitate drying should flooding or hurricane rainwater events occur. The interior surface of the wall and ceiling are Class III vapor retarders for the same reason – to allow drying to the interior. Avoid vinyl wallpaper and oil-based paint or coatings in Climate Zone 2A. These wall coverings are vapor impermeable and increase the risk of condensation within the wall.
- The rigid insulation on the underside of the floor framing prevents moisture from the underside of the elevated pier foundation from damaging the floor framing and floor finishes. The protection board is necessary to prevent rodents and other animals from damaging the assembly.
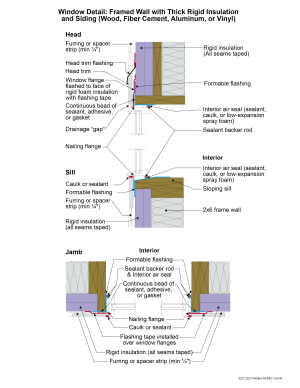
2021 IECC Window Detail: Framed Wall with Thick Rigid Insulation and Siding (Wood, Fiber Cement, Aluminum or Vinyl)
Notes
Window Detail 5A - Framed Wall with Thick Rigid Insulation and Siding (Wood, Fiber Cement, Aluminum or Vinyl)
- Note: Always follow the window manufacturer’s installation guidance. Not following manufacturer guidance may void the warranty.
- This is a “drained wall”. The exterior face of the rigid insulation is carefully taped at all seams, allowing it to act as the water control layer. Drainage occurs between the siding and the exterior face of the rigid insulation. A drainage gap is provided by furring installed vertically over the exterior face of the rigid insulation at stud locations.
- The window openings are drained to the exterior face of the rigid foam since it is acting as the water control layer.
- The rough opening at the windowsill is sloped and flashed to the rigid foam with a formable flashing.
- The upper portion of the head trim flashing goes under the furring and is taped directly to the rigid foam with flashing tape. The furring is “cut through” by the head trim flashing, so that the furring below the flashing (behind the head trim) is separate from the furring above the flashing (behind the siding). During construction the head trim is installed first on short pieces of furring. It is flashed directly to the rigid foam as described above. The rest of the furring is installed with the siding.
- With thick rigid foam installed on the exterior, providing nailing surfaces for trim and siding can be a challenge. Furring strips are one approach to accomplish this. Some form of structural wood may be needed around the windows to accommodate trim. There are many ways to accomplish this. In the assembly shown, wide lumber is used to create the rough opening, allowing nail-able wood to extend to the exterior surface of the rigid foam but also creating a thermal bridge.
- A formable membrane connects the rigid foam to the wood frame. It should extend inwards at least past the point where the interior air seal is located around all sides of the window frame. This creates water-resistant surfaces inside the cavity between the window flanges and the interior air seal, in case any water gets behind the flanges. The head and jamb window flanges are flashed to the rigid foam using a self-adhered flashing membrane or flashing tape. The sill window flange is not flashed, to allow any water that may get behind the flanges to escape.
- This assembly relies heavily on the use of proper tapes, flashings, and membranes that will adhere securely and durably to the rigid foam. Products should only be used if they have been well-established to be appropriate for this application.
- Note the gap between the head trim and the top of the window assembly frame. This gap allows water to drain and allows the bottom of the trim to dry out more easily. If installed without this gap, capillary action can draw water into the tight space between the head trim and the window assembly frame. Note also the gap between the siding and the head trim flashing, which serves the same purposes.
- Consider installing rigid head flashing (rigid head flashing is not shown in the schematic). Rigid head flashing is similar to the head trim flashing shown in the schematic, but it goes over the top of the window frame instead of over the head trim. This is required by some manufacturers. It should be installed against the head nailing flange and over the top of the window frame. The vertical and horizontal portion of the flashing should be sealed directly to the window frame and flange with sealant. The red flashing membrane strip shown overlapping the head nailing flange in the schematic would now overlap the rigid head flashing. Use rigid head flashing with a drip edge to guide water away from the window assembly.
- Backer rod for the interior air sealant should be installed after the window is installed, leveled, and shimmed. Use the correct size backer rod.
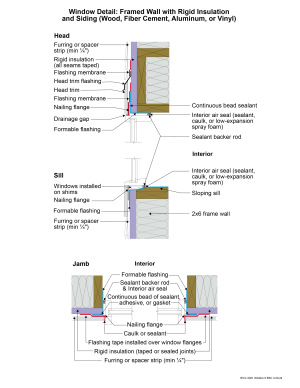
2021 IECC Window Detail: Framed Wall with Rigid Insulation and Siding (Wood, Fiber Cement, Aluminum or Vinyl)
Notes
Window Detail 6 - Framed Wall with Rigid Insulation and Siding (Wood, Fiber Cement, Aluminum or Vinyl)
- Note: Always follow the window manufacturer’s installation guidance. Not following manufacturer guidance may void the warranty.
- This is a “drained wall”. The exterior face of the rigid insulation is carefully taped at all seams, allowing it to act as the water control layer. Drainage occurs between the siding and the exterior face of the rigid insulation. A drainage gap is provided by furring installed vertically over the exterior face of the rigid insulation at stud locations.
- The window openings are drained to the exterior face of the rigid foam since it is acting as the water control layer.
- The rough opening at the windowsill is sloped and flashed to the rigid foam with a formable flashing.
- The upper portion of the head trim flashing goes under the furring and is taped directly to the rigid foam with flashing tape. The furring is “cut through” by the head trim flashing, so that the furring below the flashing (behind the head trim) is separate from the furring above the flashing (behind the siding). During construction, the head trim is installed first on short pieces of furring. It is flashed directly to the rigid foam as described above. The rest of the furring is installed with the siding.
- A formable flashing membrane connects the rigid foam to the wood frame. It should extend inwards at least past the point where the interior air seal is located around all sides of the window frame. This creates water-resistant surfaces inside the cavity between the window flanges and the interior air seal, in case any water gets behind the flanges. The head and jamb window flanges are flashed to the rigid foam using a self-adhered flashing membrane. The sill window flange is not flashed, to allow any water that may get behind the flanges to escape.
- This assembly relies heavily on the use of proper tapes, flashings, and membranes that will adhere securely and durably to the rigid foam. Products should only be used if they have been well-established to be appropriate for this application.
- Note the gap between the head trim and the top of the window assembly frame. This gap allows water to drain and allows the bottom of the trim to dry out more easily. If installed without this gap, capillary action can draw water into the tight space between the head trim and the window assembly frame. Note also the gap between the siding and the head trim flashing, which serves the same purposes.
- Consider installing rigid head flashing (rigid head flashing is not shown in the schematic). Rigid head flashing is similar to the head trim flashing shown in the schematic, but it goes over the top of the window frame instead of over the head trim. This is required by some manufacturers. It should be installed against the head nailing flange and over the top of the window frame. The vertical and horizontal portion of the flashing should be sealed directly to the window frame and flange with sealant. The red flashing membrane strip shown overlapping the head nailing flange in the schematic would now overlap the rigid head flashing. Use rigid head flashing with a drip edge to guide water away from the window assembly.
- Backer rod for the interior air sealant should be installed after the window is installed, leveled, and shimmed. Use the correct size backer rod.