Showing results 1 - 50 of 82
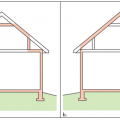
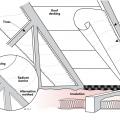
A 1- and ½-story home with a room located in the attic and the thermal boundary located at either a) the walls and ceiling of the attic room with small vented attic spaces or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
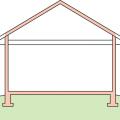
A low-sloped shed roof with the thermal boundary located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
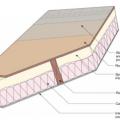
A typical Las Vegas hot-dry climate home made of wood frame construction and insulated with R-25 expanded polystyrene externally over a drainage plane, with an unvented wood frame insulated attic and roof assembly.
An unvented cathedralized attic has the air, thermal, and vapor control layers at the roof line
Detail of an unvented cathedralized attic showing air-impermeable spray foam insulation plus batt insulation installed on the underside of the roof deck.
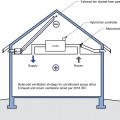
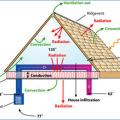
Ductwork located in a vented attic is subject to high attic temperatures and significant heat gain through the walls of the ducts
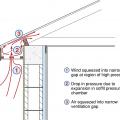
During high wind events, vortices form along the edges of the roof creating areas of localized negative pressure (“suction”) above the roof
Examples of many common ceiling penetrations that will be difficult to insulate and air seal in this cathedral ceiling.
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.
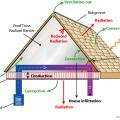
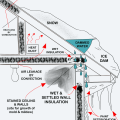
Heat loss through the roof of a home in a cold climate zone leads to snow melting to form ice dams.
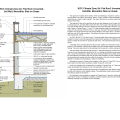
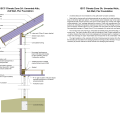
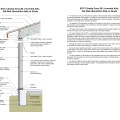
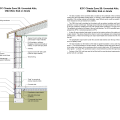
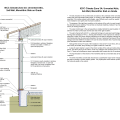
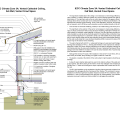
IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall/CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
IECC Climate Zone 2A: Unvented Attic with Spray Foam at Roof Deck, 2x6 Wall/CMU Wall, Elevated Slab
Limited attic access may make it necessary to use a bore scope when inspecting for missing air barriers and insulation in existing buildings.
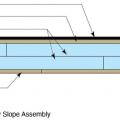
Low-slope roof assemblies constructed of two deck sheathing layers sandwiching rigid foam, and topped with mechanically fastened membrane
Radiant barrier sheeting can be stapled to the underside of the rafters or along the inside edge of the rafters
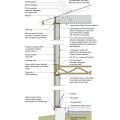
Retrofit an existing roof by installing rigid foam, new moisture and air control layers, new sheathing, and new cladding plus cavity insulation in the roof rafters to create an unvented attic
Right - An unvented attic with no soffit vents, borate-treated fascia board, metal drip edge, and concrete block construction on this south Florida home help make it resistant to hurricanes, pests, and wind-born wildfire embers.
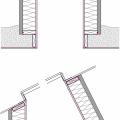
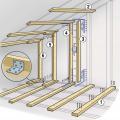
Right - Installation steps for the L-bent strap method of bracing a gable end wall
Right - Open-cell polyurethane spray foam to R-28 on underside of roof turns new attic into conditioned space for HVAC.
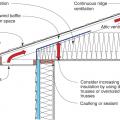
Right - Raised-heel roof trusses allow more room at the eaves for attic insulation.
Right - Spray foam insulation has been sprayed onto the underside of the sloped roof and the gable end wall to provide a sealed, insulated attic for housing the HVAC ducts
Right - These raised heel roof trusses provide 16 inches of space over the outer walls for full insulation coverage at the attic perimeter.
Right – An existing gable wall is reinforced with horizontal braces that butt up to the gable end wall and connect back to multiple trusses; retrofit studs make full contact with the wall and the compression blocks and are connected to the horizontal brac