Showing results 51 - 100 of 688
An engineered bioswale uses perforated pipe laid in rock and landscape fabric at the bottom of a vegetated trench to direct water away from a site.
An erosion control blanket protects the slope from erosion and provides favorable conditions for bank revegetation
An exhaust fan pulls damp air out of a retrofitted sealed crawlspace while drawing in dry air from the living space
An on-demand hot water pump speeds water delivery to the low-flow plumbing fixtures for significant water and energy savings.
An uninsulated (or existing insulated) basement slab is retrofitted to reduce moisture transmission by sealing with epoxy paint.
Any holes through the vapor barrier installed over the basement floor slab are thoroughly sealed as part of the foundation water barrier system.
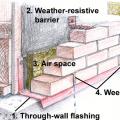
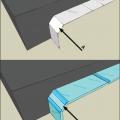
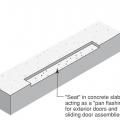
Apply self-adhesive flashing over top edge of the wall flashing, diverter, and housewrap
Backflow prevention devices keep water and sewage from entering the home during a flood preventing damage and health and safety issues.
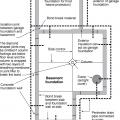
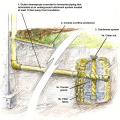
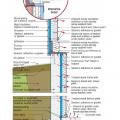
Basement plan showing sump pump location and perimeter drain that empties to the sump pit
Because the above-grade potions of the wall lack exterior insulation, condensation and even ice form during cold winter conditions
Before installing the windows, the window rough openings are sealed with a liquid-applied flashing that provides a seamless moisture and air barrier to protect the wall from water intrusion.
Before sealing and insulating the crawlspace, the windows were sealed, the window wells backfilled, and sumps pumps were installed that discharged to the gutter downspouts
Berms are compacted earth or gravel ridges that slow the flow of water from rain, riverine flooding, or storm surges in coastal areas.
Berms, swales, bioswales, ridges, and vegetation all help to control rainwater runoff on residential sites.
Bioswales or rain gardens filter storm water through vegetation and rock and sand substrate layers.
Bioswales receive rainfall and filter it through different substrate layers, preventing flooding and storm surges from occurring
Blocking installed on a flat roof for a PV system rack is sealed around the edges with sealant then will be covered with self-adhering roof membrane to prevent water leakage
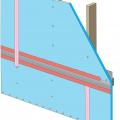
Brick wall assembly for a hot-humid climate with no Class I vapor retarder and with an air gap (drained cavity) to dissipate vapor driven into the wall by the sun.
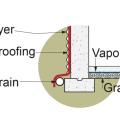
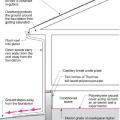
Building perimeter detail view of the recommended approach for groundwater management in cases where the foundation is entirely above the groundwater table.
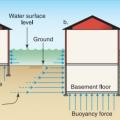
Buoyancy force on dry floodproofed homes with deep basements leads to possible foundation damage
Capillary break at all crawlspace floors using > 6 mil polyethylene sheeting, lapped 6-12 in., and secured in the ground at the perimeter using stakes
Capillary break at all crawlspace floors using ≥ 6 mil polyethylene sheeting, lapped 6-12 in., and lapped up each wall or pier and fastened with furring strips or equivalent
Capillary break at all crawlspace floors using ≥ 6 mil polyethylene sheeting, lapped 6-12 in., and placed beneath a concrete slab
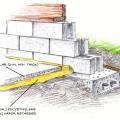
Capillary break beneath all slabs (e.g., slab on grade, basement slab) except crawlspace slabs using either: ≥ 6 mil polyethylene sheeting lapped 6-12 in., or ≥ 1 in. extruded polystyrene insulation with taped joints
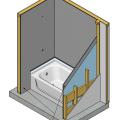
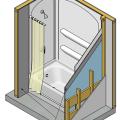
Cement board (shown in dark grey) is installed behind an installed tub and shower surround.
Check the moisture content of wall materials to ensure materials are dry before enclosing walls with drywall and siding.
Clean taping areas and install 3" tape on vertical joint of upper insulation overlapping the horizontal joint
Closed-cell foam is sprayed into roof cavities along the masonry parapet wall to form a continuous air barrier between the wall and the sheathing of the flat roof
Closed-cell spray foam fills the roof joist cavities forming an air barrier between the masonry parapet wall and the roof sheathing
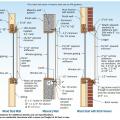
Comprehensive above-grade water management details for a crawlspace foundation include a capillary break over the crawlspace floor, slope the surface grade away, installing gutters that slope away, and capillary break under sill plate.
Comprehensive water management features include a capillary break (≥ 6-mil polyethylene sheeting) at all crawlspace floors
Concrete (4 inches thick at 5% slope) provides a pest-resistant perimeter around the foundation
Concrete is poured into the rigid foam shell of the insulated concrete form (ICF) walls; a plastic water barrier has already been installed to protect the below-grade wall surfaces.
Concrete pavers set in 4 inches of sand provide a pest-resistant ground break at the building perimeter.
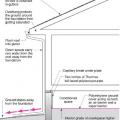
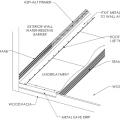
Continuous L-metal flashing integrated with underlayment at roof-wall intersections