Showing results 1 - 50 of 214
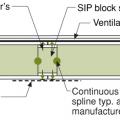
A structural spline made of a solid 2x is used where needed to meet structural load requirements at SIP panel seams
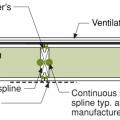
A surface spline reduces thermal bridging much more than a structural spline at SIP panel seams
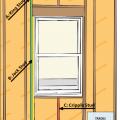
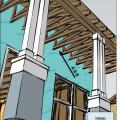
Advanced framing details include corners that are constructed with fewer studs or studs aligned so that insulation can be installed in the corner.
Advanced framing details include framing aligned to allow for insulation at interior-exterior wall intersections.
Advanced framing details include using the minimum amount of wall studs permitted by code.
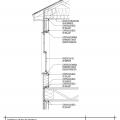
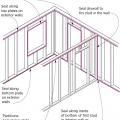
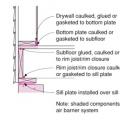
Air barrier is continuous across several components of the lower section of wall
Air seal and insulate double-walls that are half-height or full-height walls used as architectural features in homes.
Air seal the common wall between units in a multifamily structure to minimize air leakage.
Air-seal above-grade sill plates adjacent to conditioned space to minimize air leakage.
Air-seal drywall to top plates at all attic/wall interfaces to minimize air leakage.
An all-terrain forklift is used to move and stage the panels
An insulated spline is another option for avoiding thermal bridging at SIP panel seams
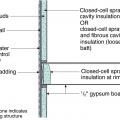
Closed-cell spray foam insulation is added to the wall cavities of an existing exterior wall
Construct exterior walls with insulated concrete forms (ICFs) that provide insulation without thermal bridging, as well as air sealing, a drainage plane, and high structural strength.
Construct exterior walls with structural insulated panels (SIPs) to provide an airtight wall with consistent insulation and very little thermal bridging.
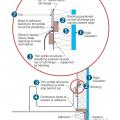
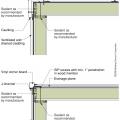
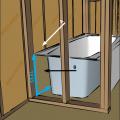
Draft stopping and air barrier at tub enclosure − plan view
Expanded polystyrene insulation is installed with joints taped and lath attached in preparation for the application of stucco
Exterior fiberglass insulation on this new home was (incorrectly) cut to terminate below-grade after backfill, which will expose the above-grade portions of the foundation wall to cold temperatures
Exterior XPS basement insulation is correctly installed to completely cover the foundation wall
Floor cavity air pressure is measured by placing a tube into the floor cavity through a small drilled hole
Floor cavity pressure is measured by inserting a tube into the floor cavity using an extension pole
Foil-faced rigid foam and spray foam can be used to insulate a basement on the interior; use good moisture management techniques to keep the basement dry
Gaps at shared common walls can be a significant source of air leakage in multi-family buildings
ICFs provide continuous wall insulation from the roof to the footing with very little thermal bridging
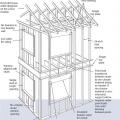
Identify what materials will constitute the continuous air barrier around the building envelope.
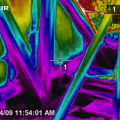
Infrared imaging shows cold conditioned air pouring out of the open floor cavities under this attic kneewall into the hot unconditioned attic
Infrared thermography during depressurization testing reveals air leakage at corner of spray foam-insulated room where wood-to-wood seams in framing were not air sealed
Install a foam gasket along top plates before installing drywall
Install a housewrap drainage plane between the SIP panels and the exterior cladding
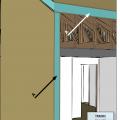
Install a rigid air barrier to separate the porch attic from the conditioned space.
Install continuous rigid foam insulation or insulated siding to help reduce thermal bridging through wood- or metal-framed exterior walls.