Showing results 51 - 100 of 192
Over the coated sheathing air barrier, the builder installed a continuous layer of 2-inch rigid foam and then covered this with a yellow mesh rain screen layer.
Over the taped rigid foam board, 2x4 furring strips provide a ventilating air gap and drainage plane under the engineered wood lap siding. The furring strips were attached with structural screws to provide an attachment surface for the siding.
Polyisocyanurate rigid foam insulation is installed in multiple layers with staggered, taped seams over the flat roof
Proper flashing around windows is especially important when the rigid foam serves as the drainage plane in the wall
R-5 XPS rigid foam exterior sheathing provides an air seal, moisture barrier, and additional insulation value.
Retrofit an existing roof by installing rigid foam, new moisture and air control layers, new sheathing, and new cladding plus cavity insulation in the roof rafters to create an unvented attic
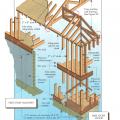
Right - A continuous load path connects the roof and wall framing to the foundation.
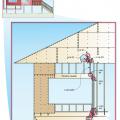
Right - Braced wall line spacing is correctly calculated for determining wall bracing in accordance with the IRC.
Right - Foil-faced polyisocyanurate insulating rigid foam sheathing is installed below the floor framing of this house built on piers; however, the seams should be sealed with metal taped and the plumbing elevated and protected.
Right - Foil-faced polyisocyanurate rigid foam is attached to the existing exterior wall with vertical wood furring strips
Right - Here, air control is established by taping the seams of the plywood panel sheathing. The roof sheathing is also trimmed flush with the wall sheathing to allow a simple and airtight connection between the roof and wall assemblies
Right - Mastic is being installed to air seal the wood-to-wood joints in this wall.
Right - Mold- and water-resistant fiber glass insulating sheathing is installed after panelized walls are assembled on site.
Right - Open-web floor and ceiling trusses provide space for ducts in conditioned space.
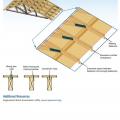
Right - Raised-heel trusses increase the roof height above the eaves allowing more space for insulation above exterior wall top plates; exterior wall sheathing extends up to keep wind from soffit vents from disrupting insulation.
Right - Seam-sealing flashing tape is installed with roller to fully adhere to the OSB.
Right - Seams in coated sheathing and joints around window are properly sealed and flashed with tape and all nail holes are covered with paint-on sealant.
Right - The air control membrane installed over the roof sheathing is continuous. It connects to the air control of the wall around the entire perimeter without interruption. The roof overhangs have been cut off to make this connection continuous
Right - The seams in the OSB sheathing are sealed with a sprayer-applied sealant.
Right - These roof insulation panels are installed in multiple layers with joints offset both vertically and horizontally. The plywood nail base fastened to the roof framing holds the insulation layers together snuggly thus minimizing gaps
Right - This foil-faced polyisocyanurate rigid foam is installed on an existing exterior wall and the seams are taped so the rigid foam can serve as a water control layer
Right - Wood board sheathing seams are being sealed with low-expanding spray foam.
Right – A flexible tape is used to air-seal around wiring holes in the coated sheathing.
Right – A rigid corrugated rain screen product is installed shingle-fashion with overlapping edges behind rock veneer.
Right – A rigid rain screen product completely covers the wall behind the cladding and window framing.
Right – All insulated sheathing boards are installed according to the manufacturer’s recommended fastening schedule and taping specifications
Right – Battens are installed above the cork insulation to provide a ventilating layer between the insulation and the roof sheathing and cladding.
Right – Battens were installed above the cork insulation to provide a ventilating layer between the insulation and the roof sheathing on this “hot roof” design.
Right – Coated OSB provides a weather-resistant air barrier for this envelope of this home.
Right – Coated OSB sheathing provides a continuous air and moisture barrier around the home.
Right – Coated sheathing is taped at all seams to serve as an exterior air barrier on the walls.
Right – Foam gasket is installed on the surface of the framing before plywood sheathing is installed on these factory-constructed wall panels.
Right – Furring strips provide a drainage and ventilation gap between the siding and the cork insulation.
Right – Furring strips were installed to provide a 3/8-inch drainage plane over the rigid foam and under the fiber cement lap siding.
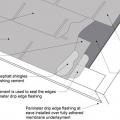
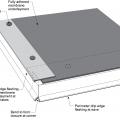
Right – If drip edge flashing is installed over fully adhered roof membrane at eaves, use flashing cement to seal the upper edge of the flashing
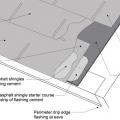
Right – Install asphalt shingles over a starter strip set in an 8-inch strip of flashing cement