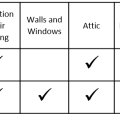
Showing results 101 - 200 of 578
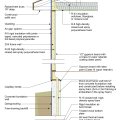
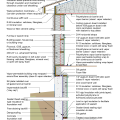
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, 2x4 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
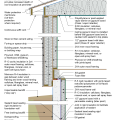
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
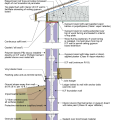
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, ICF Wall, ICF Basement Foundation
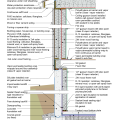
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
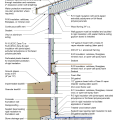
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Slab on Grade
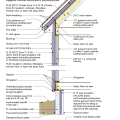
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Over-Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
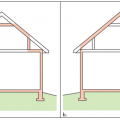
A 1- and ½-story home with a room located in the attic and the thermal boundary located at either a) the walls and ceiling of the attic room with small vented attic spaces or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
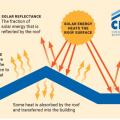
A cool roof utilizes materials with high solar reflectance and thermal emittance to reflect solar energy and reduce heat gain to the home
A detached garage offers more space to place solar panels with likely fewer roof penetrations and more options for roof pitch and orientation.
A dormer with an openable window (not shown) can provide access to the roof if flood waters rise too high and too quickly; the dormer should be properly insulated, flashed, and air sealed
A low-sloped shed roof with the thermal boundary located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
A masonry chimney is reconstructed to withstand seismic forces by adding an insert to the existing firebox
A masonry chimney is reconstructed to withstand seismic forces by completely retrofitting the firebox and chimney using light-frame construction on the top of the foundation
A masonry chimney is reconstructed to withstand seismic forces by maintaining the current firebox but replacing the chimney section with a metal flue and light-weight chimney enclosure.
A masonry chimney is shortened and capped at roof level to reduce its chances of detaching in high winds or earthquakes; the fireplace can no longer be used.
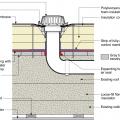
A roof drain is installed in an existing flat roof retrofitted with above-deck rigid foam insulation that is integrated with new air and water control layers
A strip of OSB sheathing is installed along the perimeter when retrofitting a flat roof with a parapet
A thermosiphon solar hot water system heats a fluid in the solar collector; the heated fluid heats potable water in a roof top tank.
A typical Las Vegas hot-dry climate home made of wood frame construction and insulated with R-25 expanded polystyrene externally over a drainage plane, with an unvented wood frame insulated attic and roof assembly.
A typical older masonry home with unreinforced brick walls, wood floors, and a wood roof
A waterproof layer of thermoplastic olefin is laid down before installing the solar panels.
Add metal connectors to strengthen framing connections in an existing wall from inside the home by removing drywall.
All holes through the top plates should be sealed with canned spray foam to prevent conditioned air from leaking into the attic.
All vents are routed to gable walls and eaves rather than through the roof to minimize the risk of leaks and provide an uninterrupted plane for PV panels.
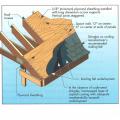
Along with continuous ridge vents, the builder installed permanent roof anchors on all the roof sections, providing a simple, low-cost and permanent safe structural tie-off points for workers conducting any future roof work.
An unvented cathedralized attic has the air, thermal, and vapor control layers at the roof line
Angle support framing is added to brace a long gable overhang constructed using the ladder framing method.
Apply self-adhesive flashing over top edge of the wall flashing, diverter, and housewrap
Architectural awnings offer year-round weather protection and keep overhead summer sun off windows while allowing lower winter sun to provide beneficial warmth.
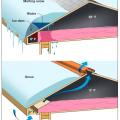
Attic ventilation can reduce the likelihood of ice dam formation by cooling the roof deck.
Because all of the structural load is carried by the SIP roof and wall panels, no trusses are needed, allowing the home to have vaulted ceilings and open interiors throughout.
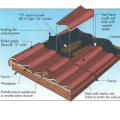
Blocking installed on a flat roof for a PV system rack is sealed around the edges with sealant then will be covered with self-adhering roof membrane to prevent water leakage
Bolted metal hurricane strapping ties the roofing to the framing and the framing to the foundation walls for resistance to high winds.
Builders in hot climates may uses a radiant barrier product that comes adhered to the underside of the roof sheathing to reduce solar heat gain into the home.
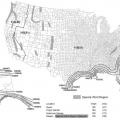
Buildings damaged by a hurricane storm surge: upper homes on gulf shoreline were hit by large waves above the lowest floor, lower left home on bay and right school 1.3 miles from gulf shoreline were hit by surge and small waves.
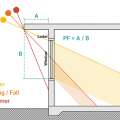
Calculate projection factor (PF) by dividing overhang (A) by length of window (B).
Ceiling joists extend out to provide very strong roof overhangs that will resist uplift pressures in high winds.
Chimneys and roof valleys are flashed with metal flashing that is integrated with roof shingles.
Clifton View Homes employs a SIP precision construction system consisting of structural insulated panels that come to the site precut for quick assembly, providing a continuous thermal blanket around the home.
Climate-specific features include bug- and moisture-resistant concrete block construction and borate-treated interior framing; a hurricane-resistant spray-foamed hip roof; and ventless roof soffits to keep out wind-driven rain.
Closed-cell foam is sprayed into roof cavities along the masonry parapet wall to form a continuous air barrier between the wall and the sheathing of the flat roof
Closed-cell spray foam fills the roof joist cavities forming an air barrier between the masonry parapet wall and the roof sheathing
Commercially available “roof hatch” products provide an openable access to the roof for maintenance and emergency egress that meets code dimensional requirements
Composition shingle roofing system showing sheathing and hot-mopped underlayment
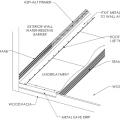
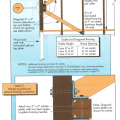
Continuous L-metal flashing integrated with underlayment at roof-wall intersections
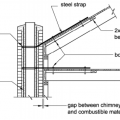
Cross section showing points of reinforcement and attachment to secure the chimney to the roof and ceiling joists.
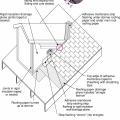
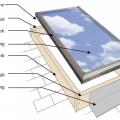
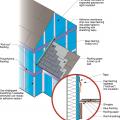
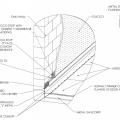
Detail of an unvented cathedralized attic showing air-impermeable spray foam insulation plus batt insulation installed on the underside of the roof deck.
Drifting of snow led to heavy accumulation between the gables which required snow removal to reduce risk of roof collapse
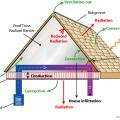
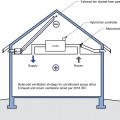
Ductwork located in a vented attic is subject to high attic temperatures and significant heat gain through the walls of the ducts
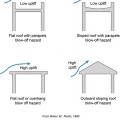
During high wind events, high localized areas of negative pressure (“suction”) occur above roof membranes
During high wind events, sloped roofs and flat roofs experience higher uplift forces than flat roofs with parapets
During high wind events, vortices form along the edges of the roof creating areas of localized negative pressure (“suction”) above the roof
End wall failure under hurricane force winds due to inadequate bracing of the gable end wall.
ENERGY STAR reflective shingles cover the roof, which is ideally angled for solar panels.
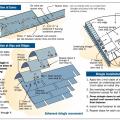
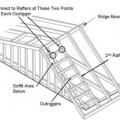
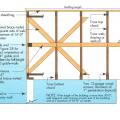
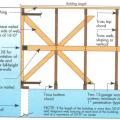
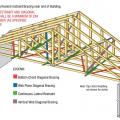
Example A of a gable truss and gable end wall bracing for a home in a hurricane region
Example B of a gable truss and gable end wall bracing for a home in a hurricane region
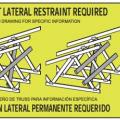
Example of a truss bracing requirement tag that some truss manufactures place strategically onto the truss to remind installers
Example truss bracing for resisting wind loads as determined by design software used by truss manufactures
Examples of many common ceiling penetrations that will be difficult to insulate and air seal in this cathedral ceiling.
Examples of Related Projects that Can be Done while Conducting a Roof Replacement or Bathroom Remodel
Existing flat roof and wood-framed walls are retrofitted with a new fully adhered air barrier membrane plus polyisocyanurate rigid foam insulation and a roofing membrane water control layer
Existing low-slope (“flat”) roof and brick masonry walls with a new fully adhered air barrier membrane plus polyisocyanurate rigid foam insulation and a roofing membrane water control layer
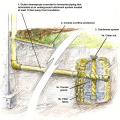
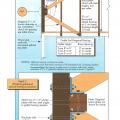
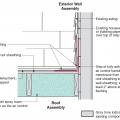
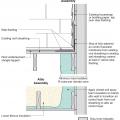
Existing wall-to-lower roof transition retrofitted with a new strip of fully adhered air control transition membrane, new step flashing, new roof underlayment, and new cladding
Existing wall-to-lower roof transition with a new strip of fully adhered air control transition membrane, new step flashing, new roof underlayment, and new cladding – view from eave
Existing wall-to-lower roof with attic transition with a new strip of fully adhered air control transition membrane, new step flashing, new roof underlayment, and new cladding – view from eave
Failure of "S" tile roofing in high winds due to bond failure between mortar and tiles.
Failure of barrel tile roofing due to bond failure between underlayment, mortar, and tiles during a hurricane.
Failure of extruded concrete flat tile roofing due to bond failure between tile, mortar, and underlayment resulting from hurricane force winds.
Failure of Roof Structure from Pressurization Due to Window Failure During a Hurricane.
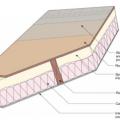
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.
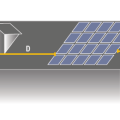
For houses with solar photovoltaic roof panels, any potential shading structure should be twice as far away from the photovoltaic array as it is tall.