Showing results 951 - 1000 of 1165
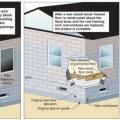
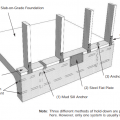
This left-to-right sequence shows the method of wall extension to flood-proof a masonry house on a slab foundation. Here the new, raised floor is wood-framed over a wet-floodproofed crawlspace, but using fill to create a new raised slab is also an option.
This metal shutter has top and bottom tracks that are permanently anchored to the wall (FEMA 577).
This MSHP operates with 120 volts power, has an EER of 18 Btu/Wh, uses about 800 W at full output, and operates remotely with a smart home control system
This plumbing pipe is wrapped with a stainless steel mesh skirt that is clamped to the pipe before the concrete slab is poured to to keep out bugs and rodents
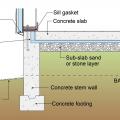
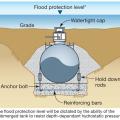
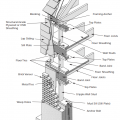
This raised-slab CMU and brick foundation includes flood-resistant features such as a sloped grade, capillary break under the slab (gravel or sand), vapor barrier under the slab (polyethylene sheet), and capillary break at the top of the foundation wall
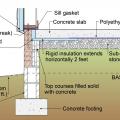
This raised-slab poured concrete foundation includes flood-resistant features such as a sloped grade, capillary break under the slab (gravel or sand), vapor retarder under the slab (rigid insulation), and capillary break at the top of the foundation wall
This reinforced concrete apartment building with exterior roof access in Minamisanriku, Japan, was designated as a vertical evacuation refuge during tsunamis; 44 people survived the 2011 Tohoku tsunami on the fenced roof
This roof was constructed to meet the IBHS Fortified Roof standard by sealing the decking seams with flashing tape, installing synthetic roof underlayment secured with metal drip edge and nailed every six inches, and using self-adhered starter shingles.
This room has several passive and low-energy cooling features including a ceiling fan, fully operable French doors, window shading, an outdoor water feature, and light-colored hard-scaping.
This search for metal roofing products on the CRRC Rated Roof Products Directory highlights the initial and 3-year aged SRI values for each product
This State of California-approved seismic gas shutoff valve will stop the flow of natural gas from the meter into the home if significant seismic activity is detected.
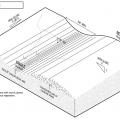
This swale and berm slow the flow of stormwater across a site to minimize erosion.
This synthetic stucco (EIFS) siding which was installed over EPS that was adhered to gypsum board failed in high winds when the gypsum board pulled over the fasteners that mechanically attached it to the studs.
This thermal image of an interior storm window shows how much temperature change occurs between the interior storm window panel on the right, at 50F and the existing glass on left at approximately 0F
This underground fuel tank is anchored to a concrete base to resist buoyancy forces
This underground storage tank in Rockaway River, NJ was lifted out of the ground by the buoyant force of flood waters
This underground storage tank was lifted out of the ground by the buoyant force of flood waters
This wall and window assembly has excessive framing around the windows, which can lead to heat gain in how climate zones.
This whole house fan is suspended from rafters and connected to the intake grille by a curved insulated duct, greatly reducing vibration and noise in the occupied space
This whole-house fan is suspended from rafters and connected to the intake grille by a curved acoustic duct, greatly reducing vibration and noise in the occupied space
This windows in this very old building in the Virgin Islands are protected from hurricanes with robust shutters constructed of 2x4 lumber, bolted connections, and heavy metal hinges.
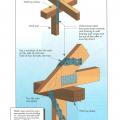
This wood-framed wall is connected with framing anchors, metal strapping and ties, and anchor bolts to secure the roof to the walls and walls to the foundation
Three different anchoring methods are shown for making the home more resistant to getting moved off its foundation in an earthquake.
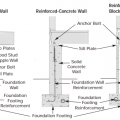
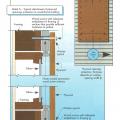
Three types of foundation walls: Stem-plus-wood stud cripple wall, reinforced concrete wall, and reinforced concrete block/masonry wall
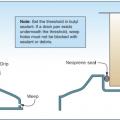
Threshold Sweep Flashing protects the door and helps to keep out wind-driven rain.
To avoid leakage if the hip or ridge shingles blow off, the underlayment should be lapped over the hip and ridge, unless there is a ridge vent.
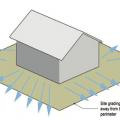
To control surface water, the land should slope away from the building on all sides
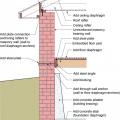
To increase a masonry-walled home’s resistance to seismic forces, solid wood blocking is added between the roof rafters, anchors are added to connect the brick wall to the rafters and floor joists, building diaphragms are added, foundation braced
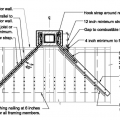
Top view showing how the chimney is attached to at least four ceiling joists running parallel to the exterior wall.
Top view showing how the chimney is attached to ceiling joists that run perpendicular to the exterior wall.
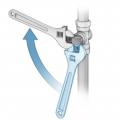
Turn valve clockwise from vertical (aligned with piping) to horizontal (perpendicular to piping) to shut off gas
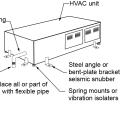
Two L-brackets or seismic snubbers are installed at each corner of the HVAC unit and a vibration isolator or spring mount is installed in each corner to anchor the unit while allowing for slight movement in an earthquake
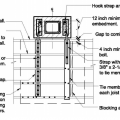
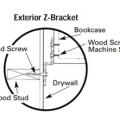
Types of brackets recommended for use in securing cabinets and drawers to the wall of the home.
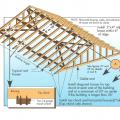
Typical hurricane strap to roof framing detail. Rafter or prefabricated roof truss.
Typical installation of plywood openings protection for masonry (including CBS) building.
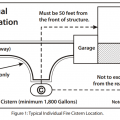
Typical siting and emergency vehicle turnaround requirements for a private residential cistern for fire protection.