Showing results 251 - 300 of 1165
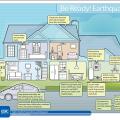
Earthquake-ready home actions include securing water heaters, shelves, and heavy furniture to walls and preparing utilities for emergency shut-off.
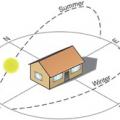
East- and west-facing walls receive significantly more sun than north- and south-facing walls in the summertime
Encourage dune formation by installing sand fences or pallets and planting dune grasses.
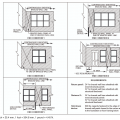
End conditions for braced wall lines with continuous sheathing, Figure R602.10.7 in the IRC
End wall failure under hurricane force winds due to inadequate bracing of the gable end wall.
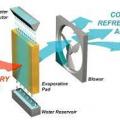
Evaporative coolers use a fan to draw outside air through a wetted pad which cools and humidifies it
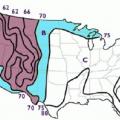
Evaporative cooling is most appropriate in areas where the summer design mean coincident wet bulb temperature is less than 70°F, shown in purple here and labeled as region “A”
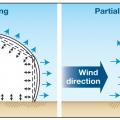
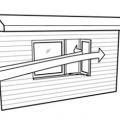
Even when wind is blowing parallel to a wall, an open casement window can create a zone of higher pressure near the window opening, driving airflow into the house
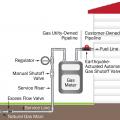
Every natural gas appliance has a shutoff valve in the gas line to the appliance that can be manually shut off if a leak happens at a specific appliance or in preparation for an impending natural disaster.
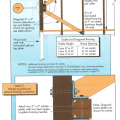
Example A of a gable truss and gable end wall bracing for a home in a hurricane region
Example B of a gable truss and gable end wall bracing for a home in a hurricane region
Example of a portable gasoline powered electric backup generator to be used during power outages.
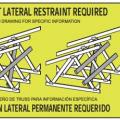
Example of a truss bracing requirement tag that some truss manufactures place strategically onto the truss to remind installers
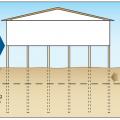
Example of an earth-sheltered home in hot climate Tempe, AZ uses the cooling properties of the ground to decrease cooling costs
Example of masonry construction. Wall separated from building envelope due to inadequate vertical wall reinforcing in connection to horizontal tie-beam.
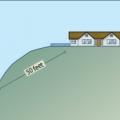
Example of setback from wildland vegetation Image title: Homes sited on hills in wildfire prone areas should be set back at least 50 feet from downslope wildland vegetation.
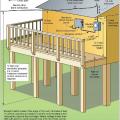
Example sketch of porch for calculations showing tributary areas for column uplift loads
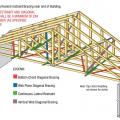
Example truss bracing for resisting wind loads as determined by design software used by truss manufactures
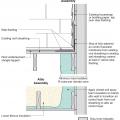
Examples of many common ceiling penetrations that will be difficult to insulate and air seal in this cathedral ceiling.
Excess Flow Valves and Earthquake-Actuated Gas Shutoff Valves are two different types of valves that automatically stop the flow of gas into the house: excess flow valves stop gas flow if there is a break in the line, earthquake valves stop gas flow if th
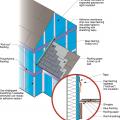
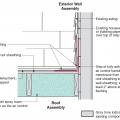
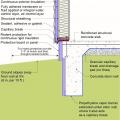
Existing wall-to-lower roof transition retrofitted with a new strip of fully adhered air control transition membrane, new step flashing, new roof underlayment, and new cladding
Existing wall-to-lower roof transition with a new strip of fully adhered air control transition membrane, new step flashing, new roof underlayment, and new cladding – view from eave
Existing wall-to-lower roof with attic transition with a new strip of fully adhered air control transition membrane, new step flashing, new roof underlayment, and new cladding – view from eave
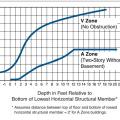
Expected flood damage (as a percent of building’s pre-damage market value) at flood depths above the bottom of the floor beam), for a building in the coastal V Zone and riverine A Zone.
Exterior electrical service components are raised and clearances are provided around components to minimize contact with flood waters and people
Exterior low-e storm windows were added to historic Halligan Hall on the U.S. Naval Academy campus in Annapolis, Maryland; frames were custom colored to match the existing seafoam green window trim
Exterior shading devices such as awnings or overhangs can significantly reduce cooling loads
External solar screens are an effective way to reduce solar heat gains through windows while maintaining view.
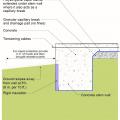
Externally insulated concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
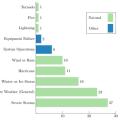
Extreme weather, such as wind, fire, flood, or extreme heat (included in the Severe Weather category above) causes most large electric disturbance events in the U.S (defined as affecting at least 50,000 customers) (data from 2000-2016)
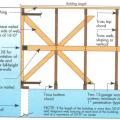
Failure at a gable end of a home under hurricane force wind conditions due to improper continuous load path design.
Failure in brick veneer connection under high wind conditions due to anchor corrosion, tie fastener pull-out, failure to embed ties into the mortar, poor bonding between ties and mortar, and poor-quality mortar; on left - five ties not embedded.
Failure of "S" tile roofing in high winds due to bond failure between mortar and tiles.
Failure of a freestanding concrete masonry end wall due to discontinuous tie-beam when exposed to hurricane force winds.
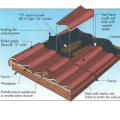
Failure of barrel tile roofing due to bond failure between underlayment, mortar, and tiles during a hurricane.
Failure of extruded concrete flat tile roofing due to bond failure between tile, mortar, and underlayment resulting from hurricane force winds.
Failure of Roof Structure from Pressurization Due to Window Failure During a Hurricane.
Failure of the wall to roof connection resulted in loss of roof under hurricane force winds.