Showing results 1 - 100 of 128
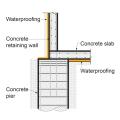
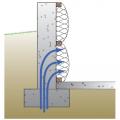
A method for preventing waterproofing issues at the intersection of a concrete pier, concrete retaining wall, and concrete slab.
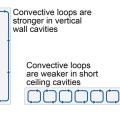
Airflow within drop-in ceiling assemblies is generally not a concern due to the limited vertical height. However, airflow within air gaps in walls is a concern due to the much larger vertical height.
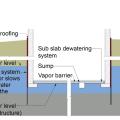
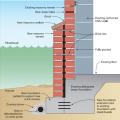
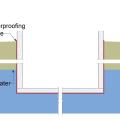
The “perimeter cutoff and dewatering” approach can be used to control groundwater in cases where the building foundation is below the groundwater table.
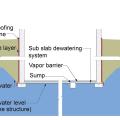
A common method of addressing significant groundwater leakage in the foundation is to line the entire foundation assembly, including the slab, with a drainage layer.
A common method of addressing significant groundwater leakage in the foundation is to line the interior perimeter of the foundation with a drainage layer.
A continuous drainage mat rainscreen made from vacuum-molded plastic provides uniform support for the siding and allows moisture to flow horizontally and diagonally in addition to vertically.
A liquid-applied water barrier covers the walls, serving as a drainage plane, air and vapor barrier, and secondary window flashing beneath the rigid foam that will be installed next.
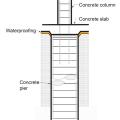
A method for preventing waterproofing issues at the intersection of a concrete column, concrete slab, and concrete pier.
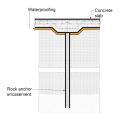
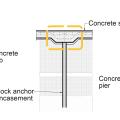
A method for preventing waterproofing issues at the intersection of a concrete slab and a rock anchor.
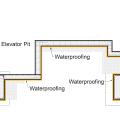
A method to ensure waterproofing continuity across the elevator pit of a multistory multifamily building.
A molded plastic drainage board rainscreen allows vertical drainage while providing uniform support for the siding and resisting compression from screws and nails.
A paint-on waterproofing covers the exterior and tops of the concrete block foundation walls and piers to block moisture moving up through the concrete, while foil-faced R-13 insulation lines the inside surface of the exterior walls.
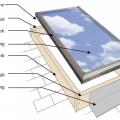
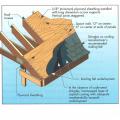
A piece of siding is used as sill extension and to provide slope in the opening for the window, which is deeper because exterior rigid foam has been added
A plastic fiber drainage mat rainscreen provides uniform support for the siding and allows moisture to flow horizontally and diagonally in addition to vertically.
A vapor barrier was installed on the floor of this crawlspace and extended up the walls then the foundation walls were covered with rigid foam.
Attach a strong permanent cover to gable end vents before a severe storm strikes to prevent moisture intrusion.
Bathroom exhaust fans are timer-operated to encourage removal of moisture from the home.
Because the above-grade potions of the wall lack exterior insulation, condensation and even ice form during cold winter conditions
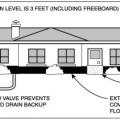
Building perimeter detail view of the recommended approach for groundwater management in cases where the foundation is entirely above the groundwater table.
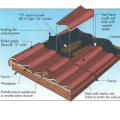
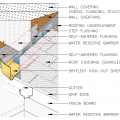
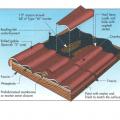
Composition shingle roofing system showing sheathing and hot-mopped underlayment
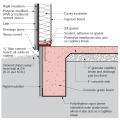
Effectively manage below-grade water in urban sites to prevent moisture issues in new and existing buildings. This foundation wall has been waterproofed to prevent water infiltration.
Exterior fiberglass insulation on this new home was (incorrectly) cut to terminate below-grade after backfill, which will expose the above-grade portions of the foundation wall to cold temperatures
Exterior XPS basement insulation is correctly installed to completely cover the foundation wall
Failure of "S" tile roofing in high winds due to bond failure between mortar and tiles.
Failure of barrel tile roofing due to bond failure between underlayment, mortar, and tiles during a hurricane.
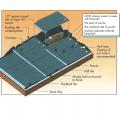
Failure of extruded concrete flat tile roofing due to bond failure between tile, mortar, and underlayment resulting from hurricane force winds.
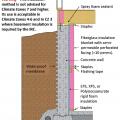
Foil-faced rigid foam and spray foam can be used to insulate a basement on the interior; use good moisture management techniques to keep the basement dry
In warm-humid climates, do not install Class 1 vapor retarders on the interior side of air-permeable insulation in above-grade walls, except at shower and tub walls.
Insulating a crawlspace foundation with “cripple wall” in warm climates; in Climate Zones 5+ replace the foil- or plastic-faced fiberglass batt/roll insulation with impermeable rigid insulation or closed-cell spray polyurethane foam
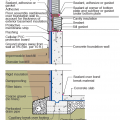
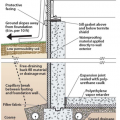
Interior and exterior footing drains keep moisture away from the foundation. Spray-on water proofing helps the concrete foundation walls resist moisture.
Intermittent water leaks have been injection sealed to prevent water infiltration into the foundation.
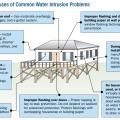
Kickout diverter flashing keeps bulk water from the roof from overflowing the gutter and continuously wetting the siding material.
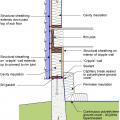
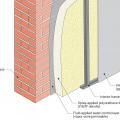
Masonry wall interior retrofit with fluid-applied water control layer and wood-framed wall with cavity insulation (climate zones 1-4 only)
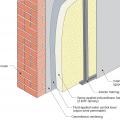
Masonry wall interior retrofit with fluid-applied water control layer, mineral wool rigid foam, and wood or metal stud service cavity (climate zones 1-4 only)
Masonry wall interior retrofit with fluid-applied water control layer, spray foam, and wood or metal stud service cavity
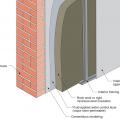
Masonry wall interior retrofit with parge coat, fluid-applied water control layer, mineral wool rigid foam, and wood or metal stud service cavity (climate zones 1-4 only)
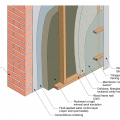
Masonry wall interior retrofit with parge coat, fluid-applied water control layer, rigid mineral wool, wood-framed wall with cavity insulation, smart vapor barrier, and wood or metal service cavity
Masonry wall interior retrofit with parge coat, fluid-applied water control layer, spray foam, and wood or metal stud service cavity
Masonry wall interior retrofit with parge coat, fluid-applied water control layer, wood-framed wall with cavity insulation, smart vapor barrier, and wood or metal service cavity
Moisture can migrate from below the foundation to the basement wall and insulation cavity in a conventional blanket insulation installation
Moisture from sprinkler seeped through the concrete block causing water stains and mold inside.
Moisture-resistant rigid foam insulation was installed to provide a continuous air and thermal barrier behind the tub-shower insert.
Mold on the sheathing in this attic occurred after attic ventilation was increased
On top of the ice-and-water shield, the builder installed horizontal beams that were raised 6 inches off the deck to allow room for spray foam insulation.
Proper gutter and downspout system terminates with final grade sloping away from the home
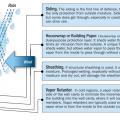
R-5 XPS rigid foam exterior sheathing provides an air seal, moisture barrier, and additional insulation value.
Recommended tile and mortar placement for extruded concrete flat tile roofing system
Redundant moisture barriers including siding, house wrap, and coated sheathing can help protect walls from excess moisture, while vapor retarders prevent vapor from entering the wall from the house, for example from a bathroom or kitchen.
Retrofit an existing roof by installing rigid foam above the roof deck with a ventilation space between the rigid foam and the new roof sheathing plus new moisture and air control layers and cavity insulation in the roof rafters.
Right - A continuous layer of rigid foam insulation is installed against the foundation, and the perforated fiberglass insulation blanket is installed over that and covered with a semipermeable facing.
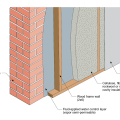
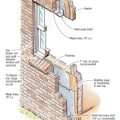
Right - Brick veneer is installed with a 1-inch air space behind the brick, metal flashing and weep holes above and below the windows and at the base of the wall to direct out water that gets behind the brick.
Right - Furring strips create an air gap to allow penetrating moisture to drain instead of wicking into walls; they also provide a nailing surface for siding.
Right - Metal drip edge on this south Florida CMU home protects the top of the fascia and edge of the roof deck from water, wind-blown rain and embers, and insects.
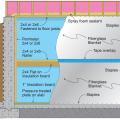
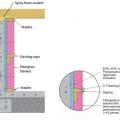
Right - Reduce condensation risks to blanket insulation by installing perforated vapor retarder covered fiberglass blankets over rigid foam that is air-sealed at all edges; staple the blanket to nailers and top/bottom plates and tape over the seams.
Right - Section view showing how to air-seal and insulate a basement wall with perforated blanket insulation by installing it over air-sealed rigid insulation board to reduce condensation risk in the fiberglass blanket.
Right - Tape flashing keeps moisture out around and below the window; extra tape reinforces the corners to prevent tearing of the house wrap and to keep water out of this critical juncture.
Right - The service penetration in the waterproofing membrane is well-sealed, and there is a drainage mat acting as a protective layer on the interior of the soldier piles and wood lagging.
Right - the vapor barrier is extended up the sides of the piers in this crawlspace, which is sealed and insulated to house the HVAC ducts.
Right - This cedar siding is installed over furring strips which allow an air and drainage gap behind the siding.
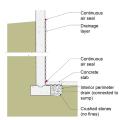
Right - This concrete basement wall has exterior rigid insulation and comprehensive moisture management details.
Right - This waterproofing membrane on the interior of a deep soldier pile foundation with wood lagging is continuous, and penetrations through the membrane have been sealed.
Right – A dehumidifier is installed next to the central heat pump’s air handler to pull air from the supply plenum, remove moisture, and re-introduce the air downstream in the supply plenum; this setup removes moisture efficiently.
Right – Because this home is in a coastal location that may flood the crawlspace is vented and the home is constructed on metal piers.
Right – Coated OSB sheathing provides a continuous air and moisture barrier around the home.
Right – Half-inch furring strips provide a rain screen and air gap between the weather-resistant membrane and the fiber cement siding on the exterior walls of this marine-climate home.
Right – The air- and water-barrier material lining the shower stall is mastic sealed to prevent leakage and rigid foam insulation is installed on the floor of the shower.
Right: All joints in the rigid foam are taped to keep stucco out of joints for even drying. Mesh tape (shown here) is used with expanded polystyrene (EPS); acrylic sheathing tape or self-adhered membrane is used with XPS
Right: This vent was correctly flashed providing proper waterproofing detailing for this siding penetration.
Spray foam adhesive provides an extra water resistant layer to the joints and seams on the inside of attics.
Staggering sheathing seams makes it harder for moisture to infiltrate the wall to the air gap, where furring strips will allow permeating moisture to drain if needed.
Stucco is installed over rigid insulation, which is installed over a drainage plane consisting of a drainage gap and building wrap layer over the sheathing
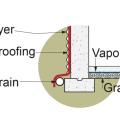
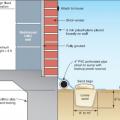
Tape seals gaps between the vapor barrier and pipes that penetrate through the subslab vapor barrier.
The “continuous waterproofing” approach can be used to control groundwater in cases where the building foundation is below the groundwater table.
The “draw down” approach can be used to control groundwater in cases where the building foundation is below the groundwater table.
The black coating on these walls is a liquid-applied asphalt-based air and moisture barrier.
The builder in this very cold climate installed three layers of unfaced mineral wool batt in the double wall with a code-required vapor barrier between the middle and inner layers of wall insulation that is taped to barriers in the ceiling and floor.
The builder installed 1.5 inches of soy-based spray foam on the outside of the walls over the OSB sheathing, then kept a ¾ inch gap between the foam and the brick veneer siding to allow moisture vapor from the bricks to dissipate.
The builder installed a rain screen product that provides an air gap and drainage plane between the coated OSB sheathing and the cladding; the fabric layer folded over the bottom edge forms an insect screen.
The builder laid down a 4-inch base of aggregate rock, then covered that with a plastic vapor barrier that is taped at all seams and around all penetrations before installing the rigid foam under-slab insulation.
The condensate line (amber-colored plastic tube) from the high-efficiency furnace drains into the sewer via the same drain pipe as the clothes washer
The entire roof of the home is covered with an ice-and-water shield to help protect against moisture damage.
The goal of foundation moisture management is to construct the basement, crawlspace, or slab in a way that keeps moisture from getting in in the first place
The HVAC equipment's condensate drain pan is equipped with a water-level detection device that will shut off the equipment if the water level pan in the pan gets too high
The leaks in this foundation wall have been injection sealed to prevent water infiltration into the foundation.
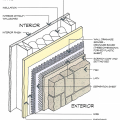
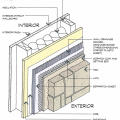
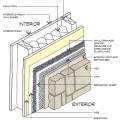
The Perfect Wall includes water, air, thermal, and vapor layers with continuous insulation exterior of the sheathing to reduce the condensation potential in the wall.