Showing results 301 - 400 of 898
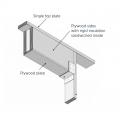
Insulated header made of two pieces of plywood that sandwich a layer of rigid foam insulation
Insulated headers can be hung with metal hangers instead of jack studs to reduce lumber usage
Insulated splines consisting of boards layered with rigid foam minimize energy loss at joints between the SIP wall panels.
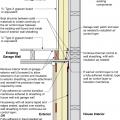
Insulating both exterior and garage-side faces of plaza deck can reduce thermal bridging. If garage is heated or partially heated, hybrid spray foam/batt insulation on garage side of plaza deck should extend to the perimeter of the garage.
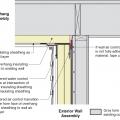
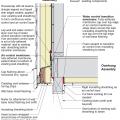
Insulating sheathing is extended up to the roof rafters and sealed around the framing with spray foam as part of this exterior wall retrofit
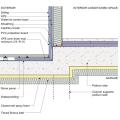
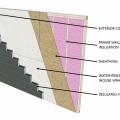
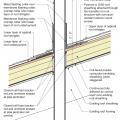
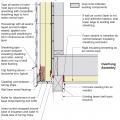
Insulating sheathing is installed on exterior of an existing framed wall with water control between existing sheathing and insulating sheathing
Insulating the exterior and garage-side faces of the garage plaza deck can reduce thermal bridging. If the garage is heated or partially heated, the spray foam on the garage side of the plaza deck should extend to perimeter of garage.
Insulating the exterior and garage-side faces of the plaza deck can reduce thermal bridging. If the garage is heated or partially heated, the faced batt insulation on the garage side of the plaza deck should extend to perimeter of garage.
Insulation was added to the walls and ceiling of this existing home from the inside as part of an extensive retrofit to avoid replacing original 1-inch shiplapped sheathing.
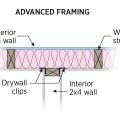
Interior wall attached with top plate metal connector, drywall clips support drywall, plan view
Interior wall attached with top plate metal connector, drywall clips support drywall, side view
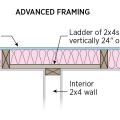
Ladder blocking where exterior walls intersect interior walls provides more space for insulation and reduces thermal bridging.
Ladder blocking where interior and exterior walls intersect uses less wood and provides more room for insulation than stacking studs in the exterior wall to nail the interior wall to.
Larsen trusses made of 9-inch I joists, set perpendicular to the exterior wall at 16 inches on center, provide a second wall cavity that can be filled with blown insulation, greatly increasing the insulation value in the walls.
Lay out the rigid foam sheathing joints so they do not align with the window and door edges
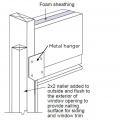
Ledger board, metal brackets, and vertical 2x4s have been installed in preparation for exterior spray foam in this retrofit exterior wall insulation technique
Limited attic access can make inspections for missing air barriers and insulation challenging
Limited attic access may make it necessary to use a bore scope when inspecting for missing air barriers and insulation in existing buildings.
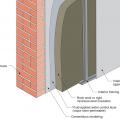
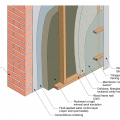
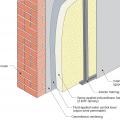
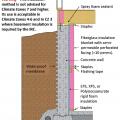
Masonry wall interior retrofit with fluid-applied water control layer and wood-framed wall with cavity insulation (climate zones 1-4 only)
Masonry wall interior retrofit with fluid-applied water control layer, mineral wool rigid foam, and wood or metal stud service cavity (climate zones 1-4 only)
Masonry wall interior retrofit with fluid-applied water control layer, spray foam, and wood or metal stud service cavity
Masonry wall interior retrofit with parge coat, fluid-applied water control layer, mineral wool rigid foam, and wood or metal stud service cavity (climate zones 1-4 only)
Masonry wall interior retrofit with parge coat, fluid-applied water control layer, rigid mineral wool, wood-framed wall with cavity insulation, smart vapor barrier, and wood or metal service cavity
Masonry wall interior retrofit with parge coat, fluid-applied water control layer, spray foam, and wood or metal stud service cavity
Masonry wall interior retrofit with parge coat, fluid-applied water control layer, wood-framed wall with cavity insulation, smart vapor barrier, and wood or metal service cavity
Masonry walls can be insulated with rigid foam insulation attached to the interior face of the concrete block as shown here.
Mineral wool batts are precisely cut to fit around electrical boxes in the wall cavities, preventing cold spots in walls.
Moisture can migrate from below the foundation to the basement wall and insulation cavity in a conventional blanket insulation installation
Moisture levels are checked in the blown cellulose insulation before enclosing the walls.
Moisture-resistant rigid foam insulation was installed to provide a continuous air and thermal barrier behind the tub-shower insert.
On top of the ice-and-water shield, the builder installed horizontal beams that were raised 6 inches off the deck to allow room for spray foam insulation.
One way to air seal and insulate kneewalls – add insulation and a rigid air barrier along roof line of unconditioned attic space outside kneewall
Over the taped rigid foam board, 2x4 furring strips provide a ventilating air gap and drainage plane under the engineered wood lap siding. The furring strips were attached with structural screws to provide an attachment surface for the siding.
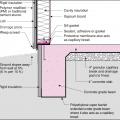
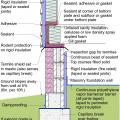
Pest proofing of this unvented crawlspace includes a metal termite shield that extends out from the sill plate, metal flashing wrapping the bottom of exterior rigid foam, and a termite inspection gap above interior rigid foam.
Pier foundations, hurricane strapping, borate- and pressure-treated lumber, and high-density spray foam insulation help protect this New Orleans home from costal flooding and storms (Source: Green Coast Enterprises).
Plan view (from above) showing how the existing garage wall gypsum board is cut away to air-seal the shared wall before adding rigid foam insulation on the garage and exterior walls of the home.
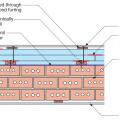
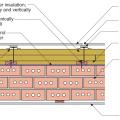
Plan view of exterior masonry brick wall retrofitted with furring strips, three layers of rigid foam insulation staggered and taped at the seams, and 1x4 furring strips to provide a nailing surface and ventilation gap under lap siding
Plan view of exterior masonry brick wall retrofitted with furring strips, three layers of rigid mineral wool insulation staggered and taped at the seams, and topped with metal hat channel providing a ventilation gap surface to nail under the lap siding
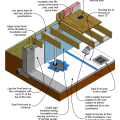
Polyethylene completely covers the floor of this crawlspace and is attached to the walls and piers as well
Polyethylene is being attached to the crawlspace floor and walls with plywood furring strips
Polyisocyanurate rigid foam insulation is installed in multiple layers with staggered, taped seams over the flat roof
Prescriptive Path: Supply ducts in unconditioned attic have insulation ≥ R-8. Performance Path: Supply ducts in unconditioned attic have insulation ≥ R-6
Proper flashing around windows is especially important when the rigid foam serves as the drainage plane in the wall
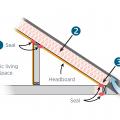
Provide flashing and sealing integrated with the air and water control layers for vents and other roof penetrations
Pull the insulation and outer liner of the flex duct over the collar to come in full contact with the liner and insulation of the trunk line or fitting and tape in place
R-5 XPS rigid foam exterior sheathing provides an air seal, moisture barrier, and additional insulation value.
Raised ceiling duct chase installation technique
Raised heel energy trusses extend past the exterior wall and are deeper at the wall allowing room for full insulation coverage over the top plate of the exterior walls.
Raised heel or energy trusses allow even the corners of the attic to be well insulated; this helps to prevent ice dams in winter and keeps rooms cooler in summer.
Retrofit an existing roof by installing rigid foam above the roof deck with a ventilation space between the rigid foam and the new roof sheathing plus new moisture and air control layers and cavity insulation in the roof rafters.
Retrofit an existing roof by installing rigid foam, new moisture and air control layers, new sheathing, and new cladding plus cavity insulation in the roof rafters to create an unvented attic
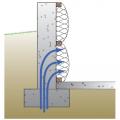
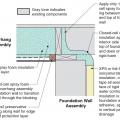
Retrofit of cantilevered foundation wall showing details at the inside corner for installing closed-cell spray foam in the wall and overhanging floor
Retrofit of cantilevered wall showing details at the inside corner for installing air sealing and rigid foam insulation in the wall and overhanging floor
Retrofit of cantilevered wall showing details at the outside corner for installing air sealing and rigid foam insulation in the wall and closed-cell spray foam in the overhanging floor
Retrofit of cantilevered wall with beam showing details at the outside corner for installing air sealing and rigid foam insulation in the wall and overhanging floor
Retrofit of cantilevered wall with beam showing details at the outside corner for installing air sealing and rigid foam insulation plus water control membrane in the wall and overhanging floor
Right - A continuous layer of rigid foam insulation is installed against the foundation, and the perforated fiberglass insulation blanket is installed over that and covered with a semipermeable facing.
Right - A corrugated metal closure conceals the exterior rigid insulation at the slab edge
Right - A technician applies a thin layer of closed-cell foam to air-seal an unvented attic assembly before filling the ceiling joists with batt or blown insulation.
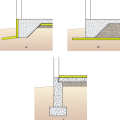
Right - Additional potential locations for slab-on-grade insulation include (a) under the slab and outside the perimeter with optional underground moisture block, (b) under the whole foundation, or (c) on top of the slab.
Right - Attach exterior insulation with insulation washers and tape the seams of the insulation is used as an air barrier.
Right - Baffles above the raised heel trusses and wind dams behind the trusses will keep wind from blowing the cellulose insulation away from the eaves.
Right - Baffles are installed in attic to keep blown insulation from blocking soffit vents and ventilation path
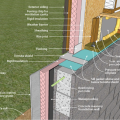
Right - Basement slab with a capillary break of either gravel or a drainage mat.
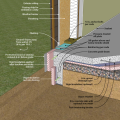
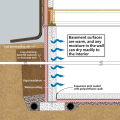
Right - Basement with exterior XPS or EPS insulation and insulation under the basement slab.
Right - Blown insulation in existing attic provides even coverage completely filling the attic space to a depth that covers the ceiling joists.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam covers the ceiling and joists to insulate and air-seal the ceiling deck.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam covers the interior of the foundation wall and wall framing is placed to the inside of the spray foam.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam insulation fills the wall cavities of the exterior walls in this home retrofit
Right - Closed-cell spray foam is installed as a skim coat to provide air tightness to an exterior wall cavity before installing batt or blown cavity insulation.
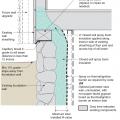
Right - Closed-cell spray foam is used to retrofit an existing rubble basement foundation wall.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam was applied to the interior of a foundation wall.
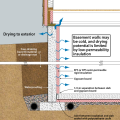
Right - Concrete masonry unit (CMU) basement wall showing exterior insulation and sill detail; above-grade wall has sheathing to the inside of the rigid foam.
Right - Continuous wall sheathing and blocking has been installed to brace the raised heel trusses.
Right - Fiberglass/mineral wool insulation thermally isolates the garage from the interior occupied space above.
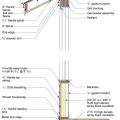
Right - Foil-faced polyisocyanurate insulating rigid foam sheathing is installed below the floor framing of this house built on piers; however, the seams should be sealed with metal taped and the plumbing elevated and protected.
Right - Foil-faced polyisocyanurate insulating rigid foam sheathing is installed rather than fibrous insulation below the floor framing of this house built on piers