Showing results 1 - 50 of 198
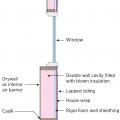
Example of the advanced framing technique, double-stud wall cavity, which will later be filled with blown insulation
A large bead of caulk is installed on the interior surface of the wall top and bottom plates to provide an air sealing gasket between the framing and the dry wall.
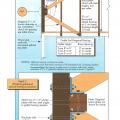
A raised wood pier foundation can raise the subfloor above the design flood elevation.
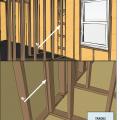
Add metal connectors to strengthen framing connections in an existing wall from inside the home by removing drywall.
Advanced framing details include corners that are constructed with fewer studs or studs aligned so that insulation can be installed in the corner.
Advanced framing details include framing aligned to allow for insulation at interior-exterior wall intersections.
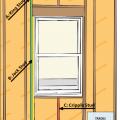
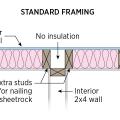
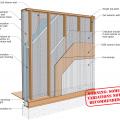
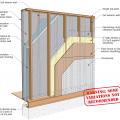
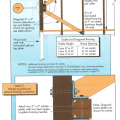
Advanced framing details include open headers and reduced framing around windows and two-stud corners to allow more room for insulation in the wall cavities while reducing lumber costs.
Advanced framing details include using the minimum amount of wall studs permitted by code.
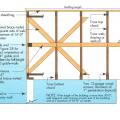
Advanced framing details throughout house limit use of lumber and makes space for bonus insulation.
Advanced framing techniques include constructing on a 2-foot grid where wall studs are placed 24 inches on center and aligned with roof and floor trusses for a continuous load path from roof to foundation.
Advanced framing techniques including 2x6 walls spaced at 24 inches on center and ladder blocking at wall intersections allow more space for insulation in the wall cavities while open-web floor joists provide space between floors for ducting.
After spraying the 2x6 wall cavities with 2 inches (R-13) of closed-cell spray foam, the walls are covered with netting and an additional 3.5 inches of fiberglass (R-13) is blown in.
Air seal and insulate double-walls that are half-height or full-height walls used as architectural features in homes.
Air seal the common wall between units in a multifamily structure to minimize air leakage.
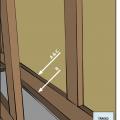
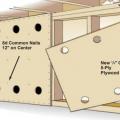
Angle support framing is added to brace a long gable overhang constructed using the ladder framing method.
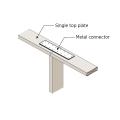
Attach the interior 2x4 wall to the exterior wall top plate with a flat metal connector plate
Baffles will keep insulation out of the soffit vents and wind out of the insulation in this vented attic.
Braced cripple wall construction in crawlspace anchored to framing and foundation
Brick veneer framed wall supported by a concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
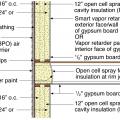
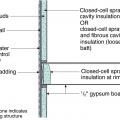
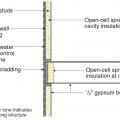
Closed-cell spray foam insulation is added to the wall cavities of an existing exterior wall
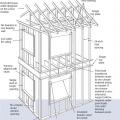
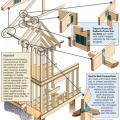
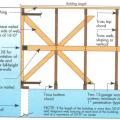
Connecting hardware helps tie the roof to the walls to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
Connecting hardware helps tie the walls to the top plates and rim joists to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
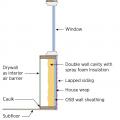
Construct a double wall consisting of two framed walls forming a wide wall cavity for more insulation in the home’s exterior walls.
Critical connections for providing a continuous load path in buildings and storm shelters
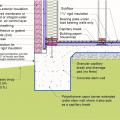
Drywall was removed and the existing 2x4 walls were filled with 3.5 inches of dense-packed cellulose. Outside, the ½-inch plywood was topped with house wrap, 1.5 inches closed-cell rigid foam, 1x3 furring strips, and fiber cement siding.
Each floor of this two-story modular home is constructed in a factory, including the 2x6, 24-inch on-center walls, R-21 fiberglass batt cavity insulation, and rigid exterior foam, housewrap, windows, and trim, then connected on site.
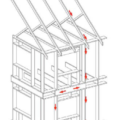
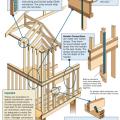
End wall failure under hurricane force winds due to inadequate bracing of the gable end wall.
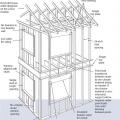
Example A of a gable truss and gable end wall bracing for a home in a hurricane region
Example B of a gable truss and gable end wall bracing for a home in a hurricane region