Showing results 1 - 50 of 139
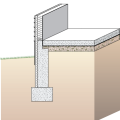
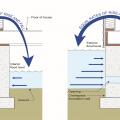
A concrete slab floor can be elevated above local grade as a strategy to prevent flood damage.
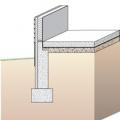
A concrete slab-on-grade foundation with exterior insulation, which can be elevated above the local grade as a flood-prevention strategy.
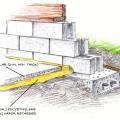
A vapor barrier was installed on the floor of this crawlspace and extended up the walls then the foundation walls were covered with rigid foam.
Air seal the floor above an unconditioned basement or crawlspace and make sure floor insulation is in full contact with the underside of the subfloor.
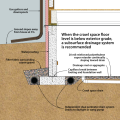
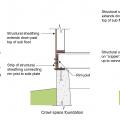
Although crawlspaces are not recommended in flood-prone areas, they can be designed or retrofitted to greatly increase resistance to flood damage.
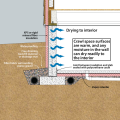
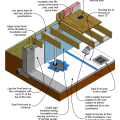
An exhaust fan pulls damp air out of a retrofitted sealed crawlspace while drawing in dry air from the living space
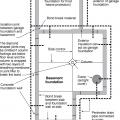
Basement plan showing sump pump location and perimeter drain that empties to the sump pit
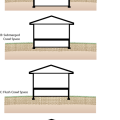
Basic foundation types: deep basement, submerged crawl space, flush crawl space, and slab-on-grade
Because the above-grade potions of the wall lack exterior insulation, condensation and even ice form during cold winter conditions
Before sealing and insulating the crawlspace, the windows were sealed, the window wells backfilled, and sumps pumps were installed that discharged to the gutter downspouts
Braced cripple wall construction in crawlspace anchored to framing and foundation
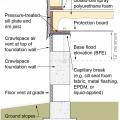
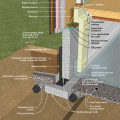
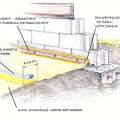
Capillary break at all crawlspace floors using > 6 mil polyethylene sheeting, lapped 6-12 in., and secured in the ground at the perimeter using stakes
Capillary break at all crawlspace floors using ≥ 6 mil polyethylene sheeting, lapped 6-12 in., and lapped up each wall or pier and fastened with furring strips or equivalent
Capillary break at all crawlspace floors using ≥ 6 mil polyethylene sheeting, lapped 6-12 in., and placed beneath a concrete slab
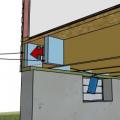
Caulk may be used to seal the cracks in the band joist area
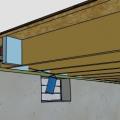
Closed-cell spray foam insulates the floor above a vented crawlspace; a protection board made of fiber cement is screwed in place under the floor joists to keep out pests
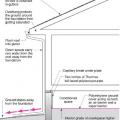
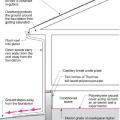
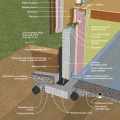
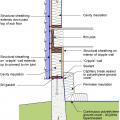
Comprehensive above-grade water management details for a crawlspace foundation include a capillary break over the crawlspace floor, slope the surface grade away, installing gutters that slope away, and capillary break under sill plate.
Comprehensive water management features include a capillary break (≥ 6-mil polyethylene sheeting) at all crawlspace floors
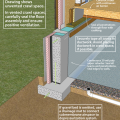
Crawl space interior insulation with EPS or XPS semi-permeable insulation on inside wall
Exterior XPS basement insulation is correctly installed to completely cover the foundation wall
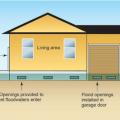
Flood vents allow floodwaters to enter and exit the crawlspace without causing hydrostatic pressure differences
Foil-faced rigid foam and spray foam can be used to insulate a basement on the interior; use good moisture management techniques to keep the basement dry
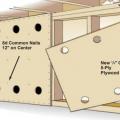
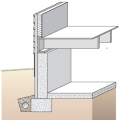
For seismic resistance in basement, crawlspace, and crawlspace “cripple” wall foundations, connect the plywood or OSB sheathing to the wall framing, rim joist, and sill plate and anchor bolt the sill plate to the foundation
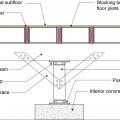
For seismic retrofit of crawlspace with posts and piers, add cross bracing to posts; add cross bracing and solid blocking between floor joists
ICF bricks are stacked to form hollow walls that are reinforced with steel rebar before the concrete is poured in
Insulating a crawlspace foundation with “cripple wall” in warm climates; in Climate Zones 5+ replace the foil- or plastic-faced fiberglass batt/roll insulation with impermeable rigid insulation or closed-cell spray polyurethane foam
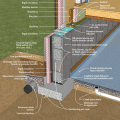
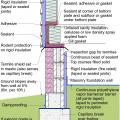
Pest proofing of this unvented crawlspace includes a metal termite shield that extends out from the sill plate, metal flashing wrapping the bottom of exterior rigid foam, and a termite inspection gap above interior rigid foam.