Showing results 1 - 23 of 23
Although crawlspaces are not recommended in flood-prone areas, they can be designed or retrofitted to greatly increase resistance to flood damage.
Closed-cell spray foam insulates the floor above a vented crawlspace; a protection board made of fiber cement is screwed in place under the floor joists to keep out pests
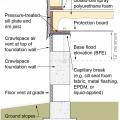
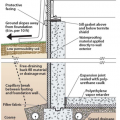
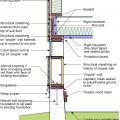
Comprehensive above-grade water management details for a crawlspace foundation include a capillary break over the crawlspace floor, slope the surface grade away, installing gutters that slope away, and capillary break under sill plate.
Comprehensive water management features include a capillary break (≥ 6-mil polyethylene sheeting) at all crawlspace floors
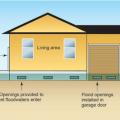
Flood vents allow floodwaters to enter and exit the crawlspace without causing hydrostatic pressure differences
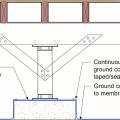
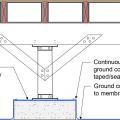
For seismic resistance in basement, crawlspace, and crawlspace “cripple” wall foundations, connect the plywood or OSB sheathing to the wall framing, rim joist, and sill plate and anchor bolt the sill plate to the foundation
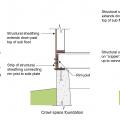
For seismic retrofit of crawlspace with posts and piers, add cross bracing to posts; add cross bracing and solid blocking between floor joists
Insulating a crawlspace foundation with “cripple wall” in warm climates; in Climate Zones 5+ replace the foil- or plastic-faced fiberglass batt/roll insulation with impermeable rigid insulation or closed-cell spray polyurethane foam
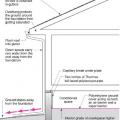
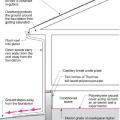
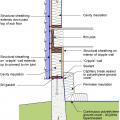
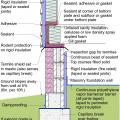
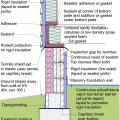
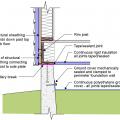
Pest proofing of this unvented crawlspace includes a metal termite shield that extends out from the sill plate, metal flashing wrapping the bottom of exterior rigid foam, and a termite inspection gap above interior rigid foam.
Provide a continuous air barrier from the rigid foam below the crawlspace floor joists to the rim joist to the exterior wall above
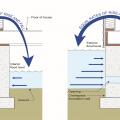
Right – Air vents near the top of the crawlspace wall are not used as flood vents, and flood vents are installed close to grade
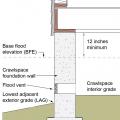
Right – Interior grade is elevated and flood vents are located slightly above interior grade
The goal of foundation moisture management is to construct the basement, crawlspace, or slab in a way that keeps moisture from getting in in the first place
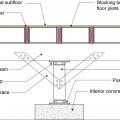
The polyethylene ground cover in the crawl space is lapped up sides of piers to posts to provide a continuous air and vapor barrier
The polyethylene ground cover in the crawlspace is continuous at interior posts and piers
The risk of hydrostatic pressure differences in a flood is reduced when the interior grade of the crawlspace is higher or equal to the exterior grade.
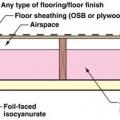
This floor assembly above a vented crawlspace controls vapor and heat transmission by using foil-faced isocyanurate rigid foam insulation installed underneath the floor joists and fiberglass insulation in the floor joist cavities
This house with interior insulated crawlspace is protected from pests with termite shield at sill plate, borate-treated framing, flashing at end of wall insulation, and a termite inspection gap at the top of the rigid foam
Vented crawlspace cripple wall has seismic retrofits – plywood is added on interior that fastens to extra blocking added at sill plate and connected to foundation with new anchor bolts
Wrong – This standard air vent has become blocked by flood debris and is located at the top of the foundation wall; it should not be used as a flood vent