Showing results 4301 - 4350 of 4973
When adding an addition to an existing home, the new construction must meet current code.
When architects and builders think of the house as a systems, all of the parts are designed to work together for a healthy, durable home that minimizes builder callbacks while cutting energy, maintenance, and repair costs down the road.
When averaged over several years, more fatalities are caused by extreme heat than by any other weather-related hazard
When condensation forms on the interior side of wall sheathing and is not able to dry out, it can lead to mold growth and rotting of wall sheathing and framing
When flood waters reach living areas, the resulting mold and contamination can greatly increase clean up time and costs.
When HVAC systems are installed in enclosed garages, it is preferable that the equipment is located within an air-sealed room that is connected to the conditioned space.
When installing fasteners in roof sheathing, common mistakes include using the wrong size fasteners, missing the framing members, overdriving nails, and using too many or too few fasteners.
When moisture is trapped inside walls, mold can grow unchecked, causing damage to the walls and health impacts for the occupants.
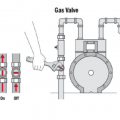
When no automatic gas shutoff valve is installed at the meter, the gas valve can be shut off using a wrench
When preserving a tree, construct a temporary fence around the tree canopy and post signs to keep out vehicles that might compact soil and construction waste that could contaminate the soil.
When rigid foam insulation is applied to the exterior side of the wall cavity under the cladding, with seams taped and an air gap provided, it acts as a vapor barrier, air barrier, and rain screen.
When the EIFS siding on this house gave way in high winds, it revealed severe rotting of the sheathing beneath the windows due to long-term water leakage.
When the lower break-away wall gave way in coastal flooding it peeled some of the EIFS siding off with it because there was no suitable break in the siding to allow it to detach cleanly.
When the soffits blew away in 140 to 160 mph hurricane winds, wind-driven rain was allowed to enter the attic.
When using I-joists, make sure to fill in the gaps on each side of the blocking material to air-seal the joist bay where a wall separates conditioned and unconditioned spaces.
When wiring is installed in ICF walls, openings made for wire runs should be air-sealed with caulk.
When wrapping metal ducts with insulation allow two inches of overlap and staple along the seam with outward clinching staples
Where the interior wall intersects the corridor wall in this multifamily building, the first intersecting wall stud is sealed to the corridor wall along both sides; other seams and penetrations in the exterior wall are also sealed
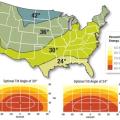
Where the optimal tilt angle for PV panels is 30°, if the roof is facing due south, the tilt angle (roof pitch) can vary 0° to 60° or roof direction can vary up to 65° to east or west and the roof can still collect 90% to 100% of available solar energy.
While windows typically make up only 7% of the total envelope area of a home, they are responsible for 48% of its heat loss
White walls and roofs; overhangs and awnings; and operable shutters and garden walls all help to keep out unwanted solar heat gain providing cool interiors for this Florida home.
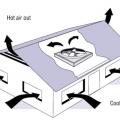
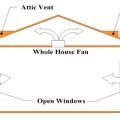
Whole house fans draw cool night-time air in through open windows and expel hot house air into the vented attic
Whole-house fans draw outside air through windows into the home and exhaust it into a vented attic
Whole-house fans operate when it is cooler outside than inside to exhaust hot air from the house and replace it with cooler outside air.
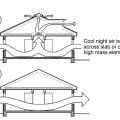
Whole-house fans or wind-driven cross ventilation can be used to draw air across thermal mass for a night flush strategy
Wide saddle support provides sturdy support for the turn without pinching the flex duct
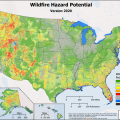
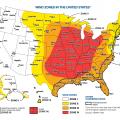
Wildfires across the United States claimed 10.12 million acres and 17,904 structures, including 9,700 homes in 2020
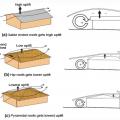
Wind path and uplift force for a gabled roof, a hip roof, and a pyramidal (another variant of a hip) roof design
Wind path and uplift force for gable ended roof, hip roof, and pyramidal (another variant of a hip) roofs
Windblown embers and firebrands are the most common cause of structural fires in wildfires, followed by fires started by radiant heat igniting surfaces or breaking windows and allowing embers in, followed by direct flame contact
Window and door rough openings in the ICF wall are surrounded with pressure-treated wood
Window attachments like insulated blinds, solar screens, and low-e storm windows provide many benefits including heating and cooling savings at a low first cost
Window coverings like insulated blinds, cellular shades, sun-blocking roller shades, and low-e storm windows can provide heating and cooling energy savings
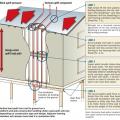
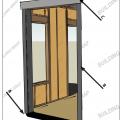
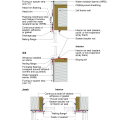
Window Detail: Framed Wall with Plywood or OSB Sheathing, a WRB, and Siding (Wood, Fiber Cement, Aluminum, or Vinyl)