Showing results 2751 - 2800 of 4973
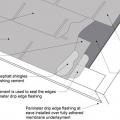
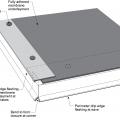
Right – If drip edge flashing is installed over fully adhered roof membrane at eaves, use flashing cement to seal the upper edge of the flashing
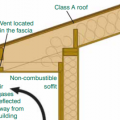
Right – In wildfire prone areas, using a flat soffit with venting on the fascia instead of an angled soffit with down-facing venting reduces the risk of catching rising embers.
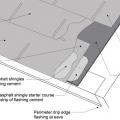
Right – Install asphalt shingles over a starter strip set in an 8-inch strip of flashing cement
Right – Insulated concrete form (ICF) blocks are stacked like bricks, then rebar is set horizontally and vertically in the plastic spacers, then concrete is poured; the rigid foam and spacers stay in place to add support and thermal resistance to the wall
Right – Insulated concrete forms (ICFs) provide the insulated stem wall for the slab-on-grade foundation for this SIP house.
Right – Insulation installed to correct depth and will be aligned with air barrier
Right – Interior grade is elevated and flood vents are located slightly above interior grade
Right – Interior wood-to-wood seams around a window are sealed with tape to prevent air leakage.
Right – Joists between floors are air sealed to the ceiling drywall with canned spray foam along each joist-to-drywall-seam.
Right – Ladder blocking allows the exterior wall to be insulated where intersected by an interior wall.
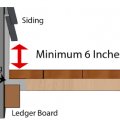
Right – Metal flashing is installed between the deck boards and house wall with the top of the flashing extending up behind the siding and the bottom of the flashing extending out and down over the ledger board
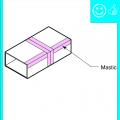
Right – Metal or fiberboard duct is mastic sealed at junction with duct register box
Right – Mineral wool batt insulation is cut to fit snuggly and to fully fill wall cavities with minimal voids and gaps.
Right – Moisture-resistant backing material has been used above and behind the tub enclosure.
Right – Mold- and termite-resistant borate-treated lumber are used to make the panels of this kit home which are connected with metal strapping for hurricane and wind resistance.
Right – Netted blown fiberglass insulation completely fills the wall cavities with no gaps or voids.
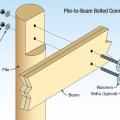
Right – Notch cut into pile takes less than 50% of cross section, cut is treated with wood preservative, and beam is installed with corrosion-resistant bolts.
Right – Open web floor joists can provide a space between floors for HVAC ducting.
Right – Open-cell spray foam is installed over closed-cell spray foam in this hybrid approach to achieve adequate attic ventilation while allowing some vapor permeability.
Right – Pavers provide a pervious ground surface allowing storm runoff to drain through to a gravel filtration and stormwater retention area below.
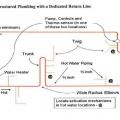
Right – PEX piping speeds hot water directly from the water heater to faucets through the attic in this slab-on-grade home.
Right – Photovoltaic solar panels are ready for installation on the roof of a DOE Zero Energy Ready certified home.
Right – Plastic tenting increases the height of the insulation above ducts that are located in the attic.
Right – Plumbing pipes have flanges that are sealed to the wall with caulk to prevent pest entry
Right – Polyethylene sheeting completely covers the aggregate and the footing with no tears or open seams
Right – Polyethylene sheeting is laid over aggregate and over footing to provide a capillary break between the ground and the slab and between the footing and the stem wall
Right – Polyethylene sheeting vapor barrier is installed and sealed to the crawlspace walls with mastic
Right – Possible Heat Pump Water Heater Locations on a Multifamily Floorplan including an interior corridor, eight apartments, and meeting rooms