Showing results 1 - 31 of 31
Because the above-grade potions of the wall lack exterior insulation, condensation and even ice form during cold winter conditions
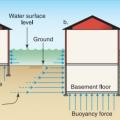
Buoyancy force on dry floodproofed homes with deep basements leads to possible foundation damage
Exterior fiberglass insulation on this new home was (incorrectly) cut to terminate below-grade after backfill, which will expose the above-grade portions of the foundation wall to cold temperatures
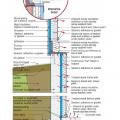
Exterior surface of below-grade walls finished as follows: For poured concrete, concrete masonry, and insulated concrete forms, finish with damp-proof coating
Exterior surface of below-grade walls finished as follows: For wood-framed walls, finish with polyethylene and adhesive or other equivalent waterproofing
Exterior XPS basement insulation is correctly installed to completely cover the foundation wall
Foil-faced rigid foam and spray foam can be used to insulate a basement on the interior; use good moisture management techniques to keep the basement dry
Right - Below-grade concrete has been properly sealed against moisture and is now having insulation installed.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam covers the interior of the foundation wall and wall framing is placed to the inside of the spray foam.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam is used to retrofit an existing rubble basement foundation wall.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam was applied to the interior of a foundation wall.
Right - Precast concrete basement walls come to the site with integrated rigid foam insulation and steel-faced concrete studs.
Right - The poured concrete basement walls are insulated along the inside with 2.5 inches of extruded polystyrene insulation.
Right - This concrete basement wall has exterior rigid insulation and comprehensive moisture management details.
Right – The insulated concrete forms that are below-grade have a damp-proof coating to prevent moisture seeping into the foundation
Right – The rim joists above the pre-insulated basement walls are sealed and insulated with spray foam to prevent air leakage at this juncture in the building envelope.
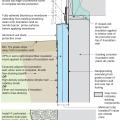
Rigid insulation and water control layers are installed on the exterior of a flat foundation wall; spray foam insulates the rim joist
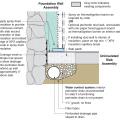
Spray foam extends down the inside of the foundation wall to the uninsulated slab; because the wall lacked exterior perimeter drainage, the slab was cut and an interior footing drain was installed.
The rim band connecting the insulated precast concrete basement walls to the floor joists above is spray foamed to provide air-sealing and insulation in this hard-to-seal juncture.
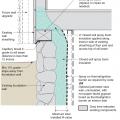
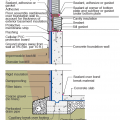
This basement is insulated on the exterior with rigid foam over dampproofing, with granular backfill and footing drains to facilitate drainage away from the foundation, a termite shield to protect from pests, and cellular PVC to protect the rigid foam.
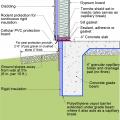
This exterior insulated slab-on-grade monolithic grade beam foundation is protected from pests by termite shield at the sill plate, borate-treated framing, flashing at end of wall insulation, brick veneer over slab-edge insulation, and rock ground cover.
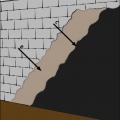
Wrong - The below-grade concrete does not have the correct construction to be impermeable to moisture because the lumber is untreated and against the concrete that lacks waterproofing.
Wrong – The insulated concrete forms at the foundation do not have a damp-proof coating