Showing results 1 - 50 of 265
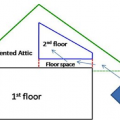
A 1- and ½-story home with a room located in the attic and the thermal boundary located at either a) the walls and ceiling of the attic room with small vented attic spaces or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
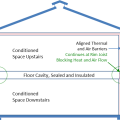
A floor cavity between the first and second floor can provide a conditioned space for HVAC ducts if the rim joists are insulated and air sealed, if sufficient space is available, and if open-web floor joists are used
A low-sloped shed roof with the thermal boundary located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
A simple vented attic with good air-sealing of the drywall ceiling air barrier, air flow from soffit vents to ridge vents protected by ventilation baffles, and lots of insulation covering the attic floor is unlikely to encourage ice dams.
A site-built rafter roof with a raised top plate allows for more insulation underneath.
A typical Las Vegas hot-dry climate home made of wood frame construction and insulated with R-25 expanded polystyrene externally over a drainage plane, with an unvented wood frame insulated attic and roof assembly.
Above the 20 inches of blown cellulose ultra-efficient attic insulation, Near Zero Maine installed a walkway in the attic to provide easy access to electric wiring.
Adhesive caulk is used to seal seams and attach the multiple layers of rigid insulation
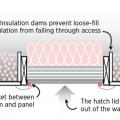
After all holes through the ceiling are air-sealed and the baffles have been installed, then the insulation can be installed.
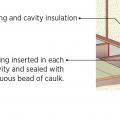
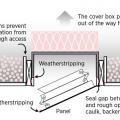
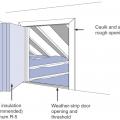
Air seal floor joist cavities under kneewall with rigid foam, plywood, or OSB caulked in place
Air-Impermeable Insulation for Condensation Control in Unvented Attics, per IRC Table 806.5.
An IR camera image shows gaps around HVAC flue pipes allow conditioned air to leak through blown fiberglass into the attic
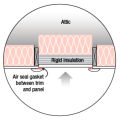
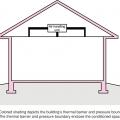
An unvented cathedralized attic has the air, thermal, and vapor control layers at the roof line
Attach a strong permanent cover to gable end vents before a severe storm strikes to prevent moisture intrusion.
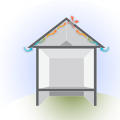
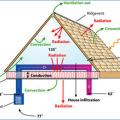
Attic ventilation fans exhaust hot air from the attic while replacing it with cooler air from the outside through intake vents
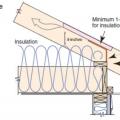
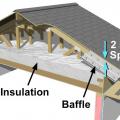
Baffles provide an air space over the insulation to guide ventilation air from the soffit vents up along the underside of the roof deck
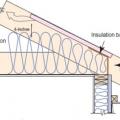
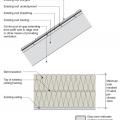
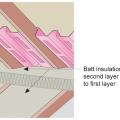
Batt insulation is installed in two layers in perpendicular directions against the baffle to full required insulation height
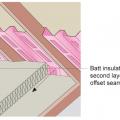
Batt insulation is installed in two layers with offset seams against the baffle to full code-required insulation height
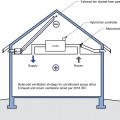
Buried ducts are laid on the floor of a vented attic then covered with spray foam and blown attic floor insulation
Clean the attic floor of debris prior to installing new attic insulation. Use baffles to provide a path for ventilation air entering the attic from the soffit vents
Closed-cell spray foam insulation covers the attic floor to provide a continuous air control layer.
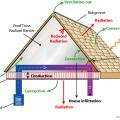
Correct air sealing methods for common attic bypass air leakage paths.
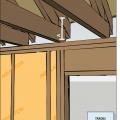
Design the roof with raised heel trusses to allow full insulation over the top plates of the exterior walls.
Detail of an unvented cathedralized attic showing air-impermeable spray foam insulation plus batt insulation installed on the underside of the roof deck.
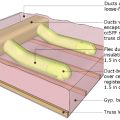
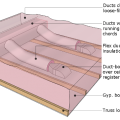
Ducts running parallel to trusses have limited width due to truss spacing
Ductwork located in a vented attic is subject to high attic temperatures and significant heat gain through the walls of the ducts
During high wind events, vortices form along the edges of the roof creating areas of localized negative pressure (“suction”) above the roof
Examples of many common ceiling penetrations that will be difficult to insulate and air seal in this cathedral ceiling.
Failure in attic insulation effectiveness caused by wind washing pushing insulation away from the edges of the attic space.
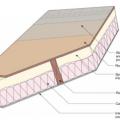
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.