Showing results 1 - 50 of 52
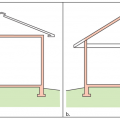
A 1- and ½-story home with a room located in the attic and the thermal boundary located at either a) the walls and ceiling of the attic room with small vented attic spaces or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
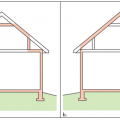
A low-sloped shed roof with the thermal boundary located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
A site-built rafter roof with a raised top plate allows for more insulation underneath.
Design the roof with raised heel trusses to allow full insulation over the top plates of the exterior walls.
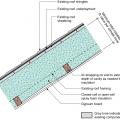
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.
In cathedral ceilings, parallel chord trusses allow thicker insulation levels over the exterior wall top plates.
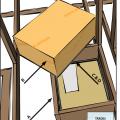
Install insulation under platforms constructed in the attic for storage or equipment.
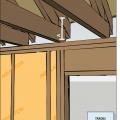
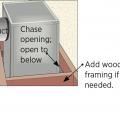
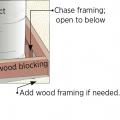
Install wood framing cross pieces in the attic rafter bays on each side of the duct chase
Install wood framing cross pieces in the attic rafter bays on each side of the duct chase
Limited attic access can make inspections for missing air barriers and insulation challenging
Limited attic access may make it necessary to use a bore scope when inspecting for missing air barriers and insulation in existing buildings.
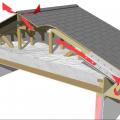
Raised heel energy trusses extend past the exterior wall and are deeper at the wall allowing room for full insulation coverage over the top plate of the exterior walls.
Right - Continuous wall sheathing and blocking has been installed to brace the raised heel trusses.
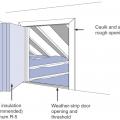
Right – Attic access hatch has been properly insulated by attaching a fiberglass batt, gasketed, and opening has blocking
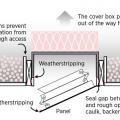
Right – Attic access door has foam and rubber weatherstripping installed that remains in contact when closed.
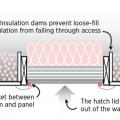
Right – Blocking has been installed around the perimeter of this attic access to prevent insulation falling into the house
Right – Insulation installed to correct depth and will be aligned with air barrier
Right – This attic knee wall and the floor joist cavity openings beneath it are being sealed and insulated with spray foam.
Right-- IR photo shows how effectively spray foam insulated/air sealed attic kneewall and the floor cavities under kneewall
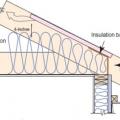
Sloped roof with cavity spray foam insulation, strapping, and gypsum board thermal barrier
Standard roof trusses are narrow at the eaves, preventing full insulation coverage over the top plate of the exterior walls
The attic kneewall and the open floor cavities under kneewall are both sealed and insulated in one step with spray foam insulation
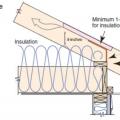
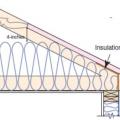
The soffit dam and baffle allow air to flow through the vents without disturbing the insulation covering the top plates
The thermal boundary for a gable roof can be located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
This kneewall has no top plate and the resulting gap provides a wide-open pathway for air and vapor to travel between the living space and the attic
Wrong – No blocking installed to prevent attic insulation from falling into stairs and opening
Wrong – The backing on this knee wall was not air sealed prior to adding insulation.
Wrong – The batt insulation on this knee wall is not properly supported and there is no air sealed rigid backing to provide a solid air barrier.
Wrong – The framing and wind baffle installation will not allow for required insulation depth.