Showing results 1 - 53 of 53
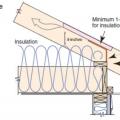
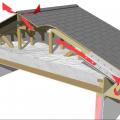
A site-built rafter roof with a raised top plate allows for more insulation underneath.
After all holes through the ceiling are air-sealed and the baffles have been installed, then the insulation can be installed.
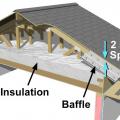
Baffles provide an air space over the insulation to guide ventilation air from the soffit vents up along the underside of the roof deck
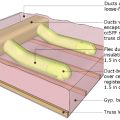
Buried ducts are laid on the floor of a vented attic then covered with spray foam and blown attic floor insulation
Closed-cell spray foam insulation covers the attic floor to provide a continuous air control layer.
Failure in attic insulation effectiveness caused by wind washing pushing insulation away from the edges of the attic space.
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.
Floor cavity air pressure is measured by placing a tube into the floor cavity through a small drilled hole
Floor cavity pressure is measured by inserting a tube into the floor cavity using an extension pole
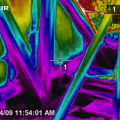
Infrared imaging shows cold conditioned air pouring out of the open floor cavities under this attic kneewall into the hot unconditioned attic
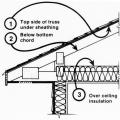
Install a continuous air barrier below or above ceiling insulation and install wind baffles.
Limited attic access may make it necessary to use a bore scope when inspecting for missing air barriers and insulation in existing buildings.
Radiant barrier sheeting can be stapled to the underside of the rafters or along the inside edge of the rafters
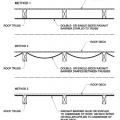
Raised ceiling duct chase installation technique
Raised heel energy trusses extend past the exterior wall and are deeper at the wall allowing room for full insulation coverage over the top plate of the exterior walls.
Right - Air barrier is present between the dropped ceiling/soffit and the attic.
Right - Air barrier is present between the dropped ceiling/soffit and the attic.
Right - Wind baffle installation will allow proper insulation depth over the top plate.
Right – Wind baffle installation maintains necessary code clearance between baffle and roof deck
Right-- IR photo shows how effectively spray foam insulated/air sealed attic kneewall and the floor cavities under kneewall
Roof decking has adhered radiant barrier that is perforated, in addition to the nail holes
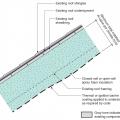
Sloped roof with cavity spray foam insulation sprayed on underside of roof deck and covered with sprayed-on thermal or ignition barrier coating.
Spray foam insulates and air-seals the ceiling deck and top plates of this vented attic.
Spray foam insulation used for raised ceiling duct chase
Spray foam insulation used for raised ceiling duct chase.
Standard 2 in. by 4 in. stud secures duct chase - made of rigid insulation in this example
The attic kneewall and the open floor cavities under kneewall are both sealed and insulated in one step with spray foam insulation
The builder installed this OSB under the roof rafters and air sealed the seams with tape then added a dropped drywall ceiling to provide a service cavity for ducts and wiring, while minimizing holes into the attic.
The drywall above the dropped ceiling duct chase extends beyond adjoining top plates for a continuous air barrier
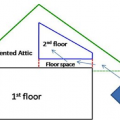
The floor cavities under this attic kneewall are completely open to the unconditioned attic space and a prime target for wind washing
The seams in the ceiling drywall are sealed from the attic side with spray foam.
The soffit dam and baffle allow air to flow through the vents without disturbing the insulation covering the top plates
The unvented attic is insulated along the underside of the roof deck with 7 inches (R-49) of closed-cell spray foam, providing vaulted ceilings and a conditioned knee wall space for ducting.
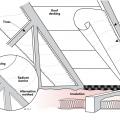
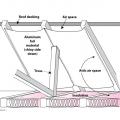
There are three potential locations for an attic radiant barrier – adhered to the underside of the roof decking, hanging from the rafters, or on the ceiling insulation
This finished retrofit installation of radiant barrier in attic shows the air spaces at the soffit and ridge to promote attic ventilation
This kneewall has no top plate and the resulting gap provides a wide-open pathway for air and vapor to travel between the living space and the attic
This vaulted ceiling has 7 inches of closed-cell spray foam plus an R-22 unfaced mineral wool batt for a total attic insulation value of R-68.
Three locations and methods for installing a roof deck radiant barrier in new construction
Wrong - Batt insulation does not provide complete coverage across the attic floor so ceiling joists are exposed resulting in thermal bridging.
Wrong - No air barrier is present between the dropped ceiling/soffit and the attic.
Wrong - No air barrier is present between the dropped ceiling/soffit and the attic.
Wrong - This IR image of a second-floor landing shows that attic air is flowing far into the interstitial floor cavity of the second-floor landing
Wrong: Closed-cell spray foam roof insulation was not thick enough to meet IRC levels so the foam surface is colder than the dew point of the interior air and condensation formed on surface of the foam
Wrong: Ducts are held above the ceiling plane with strapping to provide a good angle into top-entry boots. Once the ceiling insulation is added, this duct will protrude from the ceiling insulation and will not be buried