Showing results 101 - 150 of 733
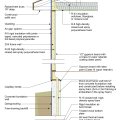
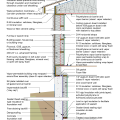
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, 2x4 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
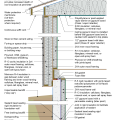
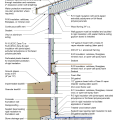
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Exterior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
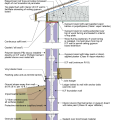
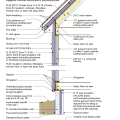
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, ICF Wall, ICF Basement Foundation
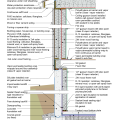
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Interior Double Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Attic, Strapped 2x6, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Slab on Grade
2021 IECC Climate Zones 7 and 8: Vented Over-Roof, Unvented Cathedral Ceiling, 2x6 Wall, Interior Insulated Basement
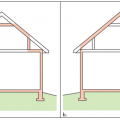
A 1- and ½-story home with a room located in the attic and the thermal boundary located at either a) the walls and ceiling of the attic room with small vented attic spaces or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
A blower door is used to test air leakage in this multifamily building during construction
A builder, energy efficiency consultant, and crew supervisor inspect a spray foam installation.
A caulk gun is a simple but power tool for sealing narrow cracks between framing and around penetrations.
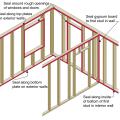
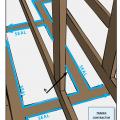
A continuous bead of sealant is installed to air seal along the top and bottom plates at all exterior walls and intersecting interior walls as well as around windows in exterior walls
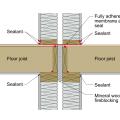
A flexible membrane was installed across the floor joists to prevent air movement between the floor joists in this multifamily 1-hr partition wall assembly
A large bead of caulk is installed on the interior surface of the wall top and bottom plates to provide an air sealing gasket between the framing and the dry wall.
A low-sloped shed roof with the thermal boundary located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
A manometer is used to measure pressure differentials between indoors and outdoors when testing whole-house air leakage.
A piece of siding is used as sill extension and to provide slope in the opening for the window, which is deeper because exterior rigid foam has been added
A rigid air barrier of non-paper-faced gypsum board is installed before the bathtub is installed and all seams are caulked
A second layer of rigid insulation is installed over the 2 in. by 4 in. retaining strip
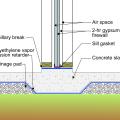
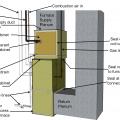
A sill gasket is installed under the two layers of fire-rated gypsum providing air sealing at the foundation slab in this 2-hour fire wall separating two units in a multifamily row house building
A sill-sealing foam gasket is placed under 8-inch plywood base and two beads of caulk air seal the 2x6 sill plate to it; two more beads of caulk will top the 2x6 which will serve as a spline for the SIP wall panel.
A technician assembles the spray sealant injection system to seal HVAC ducts from the inside
Adding air-sealing and rigid foam insulation at the wall-to-overhanging floor juncture at the outside corner of an existing home
Adhesive caulk is used to seal seams and attach the multiple layers of rigid insulation
Air leaking through the home's envelope wastes a lot of energy and increases energy costs.
Air seal a heat pump or air conditioner air handler cabinet at all seams, holes, and junctions
Air seal all holes and seams in the furnace cabinet with mastic, foil tape, or putty
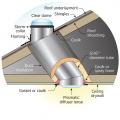
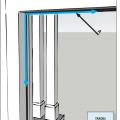
Air seal around all duct shafts and flues installed through ceilings, walls, or flooring to keep conditioned air from leaking into unconditioned space.
Air seal around kitchen and bathroom exhaust fans to keep conditioned air from leaking into unconditioned space.
Air seal connection of the ceiling sheathing to the exterior wall of a 1-hr fire-rated partition wall of a multifamily building
Air seal door and window rough openings with backer rod, caulk, or nonexpanding foam
Air seal duct boot to ceiling by installing fiberglass mesh tape and mastic over seam
Air seal the common wall between units in a multifamily structure to minimize air leakage.
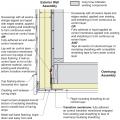
Air-seal above-grade sill plates adjacent to conditioned space to minimize air leakage.
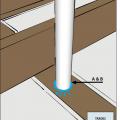
Air-seal around all plumbing and piping installed through walls, ceilings, and flooring adjacent to unconditioned space to prevent air leakage.
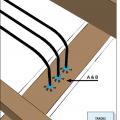
Air-seal around all wiring installed through walls, ceilings, and flooring to keep conditioned air from leaking into unconditioned space.
Air-seal around recessed can light fixtures that are installed through ceilings to keep conditioned air from leaking into unconditioned space.
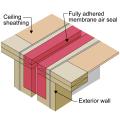
Air-seal drywall to top plates at all attic/wall interfaces to minimize air leakage.