Showing results 1 - 32 of 32
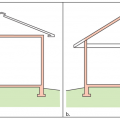
A 1- and ½-story home with a room located in the attic and the thermal boundary located at either a) the walls and ceiling of the attic room with small vented attic spaces or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
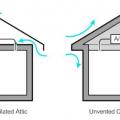
A low-sloped shed roof with the thermal boundary located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
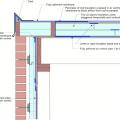
A piece of siding is used as sill extension and to provide slope in the opening for the window, which is deeper because exterior rigid foam has been added
Air seal door and window rough openings with backer rod, caulk, or nonexpanding foam
Correct air sealing methods for common attic bypass air leakage paths.
Install an ENERGY STAR labeled insulated door with an automatic closer. Weather strip the door frame
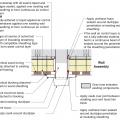
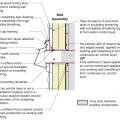
Insulating sheathing is installed on exterior of an existing framed wall with water control between existing sheathing and insulating sheathing
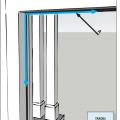
Plan view of duct or pipe penetration through exterior wall showing flashing and air sealing details
Plan view of electric box installation in exterior wall showing flashing and air sealing details
Right - Foil-faced polyisocyanurate insulating rigid foam sheathing is installed below the floor framing of this house built on piers; however, the seams should be sealed with metal taped and the plumbing elevated and protected.
Right - Spray foam insulation has been sprayed onto the underside of the sloped roof and the gable end wall to provide a sealed, insulated attic for housing the HVAC ducts
Right - The duct shows redundant sealing including the caulk, tape, and flashing
Right - The pipe penetration is properly flashed and furring strips are installed on each side in preparation for installing cladding
Right - The water and air control layers are properly integrated around the hose bib
Right - This duct penetration is properly flashed and integrated with the taped, foil-faced foam sheathing layer, which serves as the air and water barrier
Right – The seams are taped on the coated OSB sheathing of this home to provide a complete air barrier.
Right – This low-slope flat roof assembly has continuity of both the air and water barriers
Right – This low-slope roof and parapet assembly has continuity of both the air and water barriers
Right – Weatherstripping has been installed and remains in contact when the door is closed.
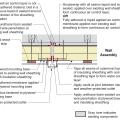
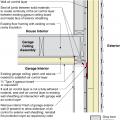
Rigid foam insulating sheathing installed over an existing garage ceiling with retrofits to air seal exterior wall before adding exterior wall insulating sheathing
Section view of duct or pipe penetration through exterior wall showing flashing and air sealing details
Section view of electric box installation in exterior wall showing flashing and air sealing details
The polyethylene ceiling vapor barrier is sealed to form an air barrier around the exhaust fan in this very cold climate location (≥ CZ 6).
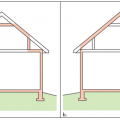
The thermal boundary for a gable roof can be located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
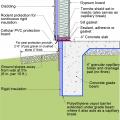
This basement is insulated on the exterior with rigid foam over dampproofing, with granular backfill and footing drains to facilitate drainage away from the foundation, a termite shield to protect from pests, and cellular PVC to protect the rigid foam.
This exterior insulated slab-on-grade monolithic grade beam foundation is protected from pests by termite shield at the sill plate, borate-treated framing, flashing at end of wall insulation, brick veneer over slab-edge insulation, and rock ground cover.
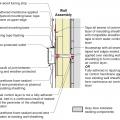
Unvented roof assembly at eave retrofitted with rigid foam, spray foam, and a fully adhered membrane seal at the top of wall-to-roof transition
Wire hardware mesh is fastened with a staple gun and screws to the wall to prevent pests from entering the building through small holes and cracks
Wrong – There is visible light around the door because no weather stripping has been installed.