Showing results 1 - 100 of 130
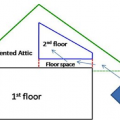
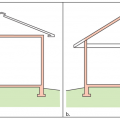
A 1- and ½-story home with a room located in the attic and the thermal boundary located at either a) the walls and ceiling of the attic room with small vented attic spaces or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
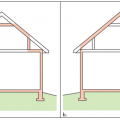
A low-sloped shed roof with the thermal boundary located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
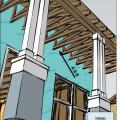
A site-built rafter roof with a raised top plate allows for more insulation underneath.
After all holes through the ceiling are air-sealed and the baffles have been installed, then the insulation can be installed.
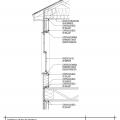
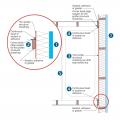
Air barrier is continuous across several components of the lower section of wall
Air seal and insulate double-walls that are half-height or full-height walls used as architectural features in homes.
Air seal the floor above an unconditioned basement or crawlspace and make sure floor insulation is in full contact with the underside of the subfloor.
Air seal the top, bottom, and sides of a cantilevered floor cavity and ensure that insulation is in full contact with all sides without voids.
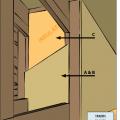
Air-seal and insulate the rim and band joists of walls separating an attached garage from the home’s conditioned space.
Air-seal the floor above a garage when there is living space above the garage and make sure floor insulation is in full contact with the underside of the subfloor.
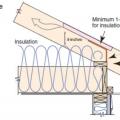
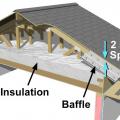
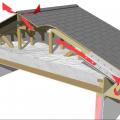
Baffles provide an air space over the insulation to guide ventilation air from the soffit vents up along the underside of the roof deck
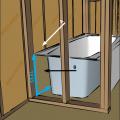
Draft stopping and air barrier at tub enclosure − plan view
Failure in attic insulation effectiveness caused by wind washing pushing insulation away from the edges of the attic space.
Floor cavity air pressure is measured by placing a tube into the floor cavity through a small drilled hole
Floor cavity pressure is measured by inserting a tube into the floor cavity using an extension pole
Identify what materials will constitute the continuous air barrier around the building envelope.
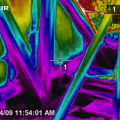
Infrared imaging shows cold conditioned air pouring out of the open floor cavities under this attic kneewall into the hot unconditioned attic
Install a continuous air barrier below or above ceiling insulation and install wind baffles.
Install a rigid air barrier to separate the porch attic from the conditioned space.
Limited attic access can make inspections for missing air barriers and insulation challenging
Limited attic access may make it necessary to use a bore scope when inspecting for missing air barriers and insulation in existing buildings.
Raised heel energy trusses extend past the exterior wall and are deeper at the wall allowing room for full insulation coverage over the top plate of the exterior walls.
Right - Air barrier is present and installed between the floor system and unconditioned space.
Right - Air barrier is present between the dropped ceiling/soffit and the attic.
Right - Air barrier is present between the dropped ceiling/soffit and the attic.
Right - Wind baffle installation will allow proper insulation depth over the top plate.
Right – Air barrier and penetrations sealed between porch attic and conditioned space
Right – Air barrier installed under staircase (picture taken from house looking into attached garage)
Right – Cantilever has been properly insulated, air sealed, and cavity has been blocked.
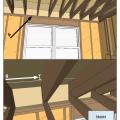
Right – This attic knee wall and the floor joist cavity openings beneath it are being sealed and insulated with spray foam.
Right – Wind baffle installation maintains necessary code clearance between baffle and roof deck
Right-- IR photo shows how effectively spray foam insulated/air sealed attic kneewall and the floor cavities under kneewall
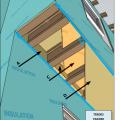
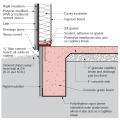
Stucco is installed over rigid insulation, which is installed over a drainage plane consisting of a drainage gap and building wrap layer over the sheathing
The air tightness of the garage-to-house air barrier can be tested with a blower door kit and two manometers
The attic kneewall and the open floor cavities under kneewall are both sealed and insulated in one step with spray foam insulation
The floor cavities under this attic kneewall are completely open to the unconditioned attic space and a prime target for wind washing
The soffit dam and baffle allow air to flow through the vents without disturbing the insulation covering the top plates
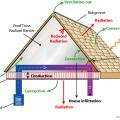
The thermal boundary for a gable roof can be located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
The wall behind the fireplace is an exterior wall and requires a thermal barrier that is continuous with the rest of the wall’s insulation
Wrong - No air barrier is present between the dropped ceiling/soffit and the attic.
Wrong - No air barrier is present between the dropped ceiling/soffit and the attic.
Wrong - No air barrier is present between the floor system and unconditioned space.
Wrong - No air barrier is present in the floor joists spanning over the garage and conditioned space of the home.
Wrong - The air barrier is not sealed (picture taken from garage looking into house).
Wrong - The band joist above this garage-house shared wall is not properly sealed.
Wrong - The rigid foam that was installed as an air barrier at the rim joist was not properly air-sealed.
Wrong - This IR image of a second-floor landing shows that attic air is flowing far into the interstitial floor cavity of the second-floor landing
Wrong - This IR image shows where hot attic air has penetrated into the floor cavity that lies behind the stairwell wall