Showing results 1 - 42 of 42
These folding louvered porch doors provide effective shade from low-angle east and west sunlight and can open for views; the photovoltaic panels overhead allow in filtered natural light
An NFRC glazing system energy performance label will report U-factor, solar heat gain coefficient, visible transmittance, and air leakage; if the window is ENERGY certified, the ENERGY STAR label will be located next to the NFRC label
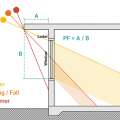
Calculate projection factor (PF) by dividing overhang (A) by length of window (B).
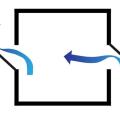
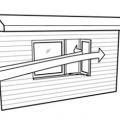
Casement windows or wing walls can create zones of higher pressure (right) and lower pressure (left) to encourage cross ventilation when wind is flowing parallel to window openings
Clerestory windows bring light in from above, reflecting it off of surfaces, making it more appealing than the direct light that comes from skylights
Even when wind is blowing parallel to a wall, an open casement window can create a zone of higher pressure near the window opening, driving airflow into the house
Exterior shading devices such as awnings or overhangs can significantly reduce cooling loads
External solar screens are an effective way to reduce solar heat gains through windows while maintaining view.
Infrared photometry shows the impact of a roof overhang on the south façade of a home, where the unshaded patio stonework is significantly hotter than the shaded portions of the patio and wall surfaces (temperature scale shown is in Celsius).
Landscaping and Bahama shutters can provide important shade for a designated cool room
Multi-layer honeycomb cellular shades such as these can provide summertime energy savings by blocking and reflecting solar heat, as well as wintertime energy savings by providing added insulation.
Pleated blinds provide cooling savings in summer by blocking and reflecting sunlight, while allowing some diffuse daylight to pass through.
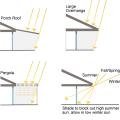
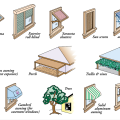
Porch roofs, pergolas, and large overhangs can effectively shade windows and doors facing south, southeast, southwest, or even due east or west for most of the day if the overhang is very deep and sufficiently wide.
Right - Covered porches protect the south-facing windows and doors of this building from solar heat gain.
Right - These interior solar screens help control glare and solar heat gain while maintaining view to the outside.
Right - These retractable awnings provide shade to this outdoor living space and reduce heat gain and glare within the home.
Right - This house has key features to block heat such as such as tree shading for the west wall and roof, minimized west-facing windows, and a porch roof, floor, and wing walls creating deep architectural overhangs and fins to shade south-facing windows
Right – Deep overhangs, pergolas, and covered entryways minimize heat gain in this commercial building in the hot-dry climate.
Right – deeply inset entryways and overhangs provide shade to reduce solar heat entry to this building.
Right – Horizontal overhangs on this house block sunlight in the summer while allowing it in during winter
Right – Strategically placed trees provide shade to the south-facing windows of this building.
Right – the building on the right employs light-colored walls, deep tinting, and deeply recessed windows to minimize solar heat gain
Right – thermal mass walls, small windows, and recessed porch and trees on the south side of this southwest home help to minimize solar heat gain.
Right – this commercial building employs good techniques to resist solar heat gain: awnings and pergolas over windows, recessed windows and entryways, deep tinting on glass, and shade plants.
Right – This model home for the Solar Decathlon competition incorporates vertical trellises and retractable exterior blinds to control solar heat gain.
Right- Landscaping shades the entry on the south west corner of this hot dry climate building.
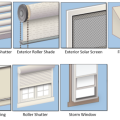
Seven categories of exterior window shading attachments, identified on the DOE Efficient Window Coverings website.
Sheer shades can provide very effective daylighting and glare control while maintaining a softened view to the outside
The design of this home incorporates multiple methods to reduce summertime solar gains including roll-down exterior blinds, wide exterior horizontal louvers, minimized east/west-facing windows, and vegetation.
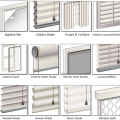
The DOE Efficient Window Coverings website identifies twelve categories of interior window shading attachments.
The Efficient Window Coverings website allows direct comparison of various window attachment types based on thermal, visual, functional, and installation and durability criteria.
The light-colored exterior roll-down shades on this building, and the shaded entryway provide very effective control of solar heat gain
The operable windows in this house are located at occupant level to provide comfort ventilation.
The patio roof on this home provides full shade to large glass doors and windows, reducing the home's heat gains.
The south face of this home has an overhanging second floor, a pergola, and a roof eave to provide effective window and door shading for both floors in the summer without blocking view, diffuse daylighting, breezes, or ingress/egress
The window awnings on this house provide a simple but very effective way to reduce solar gains while still allowing view, daylight, and ventilation through the windows
There are multiple options for exterior shading of east and west facing glazing systems to avoid direct beam radiation
These aluminum Bahama shutters shade west-facing windows from afternoon sun and are approved for hurricane protection
This hot climate zone home uses high quality batt insulation to insulate truss-joist headers.
Wrong - this building provides no overhangs, minimal window shading, and clear window glass resulting in high solar heat gain.
Wrong – The south side of this building in Arizona has very little architectural or landscape shading to block solar heat gain.
Wrong – This multi family building appears to be done in traditional southwest architecture but the lack of useful overhangs, dark colored walls, and lack of tinting on windows will result in significant solar heat gain.