Showing results 1 - 14 of 14
A single-story house floor plan showing braced wall line locations at A through E and 1 through 5
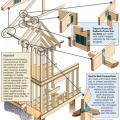
Connecting hardware helps tie the roof to the walls to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
Connecting hardware helps tie the walls to the top plates and rim joists to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
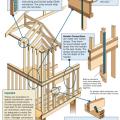
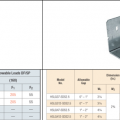
Correct seismic retrofit hardware for securing the sill plate to foundation wall
Durability concerns on a house continuously sheathed with a proprietary fiber structural panel used as bracing. Photo 1 of 2.
Durability concerns on a house continuously sheathed with a proprietary fiber structural panel used as bracing. Photo 2 of 2.
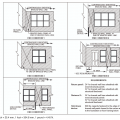
End conditions for braced wall lines with continuous sheathing, Figure R602.10.7 in the IRC
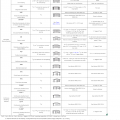
Right - Braced wall line spacing is correctly calculated for determining wall bracing in accordance with the IRC.
Right - Engineered portal frames are used for wall bracing to resist wind and earthquake loads.
Shear Strength Comparison Between a Foundation Stud Anchor (on left) and a Shear Transfer Angle (on right)
Wrong - Framing a dormer using only toe nailing and end nailing is not acceptable in areas subjected to high winds, hurricanes, or earthquakes.