Showing results 1 - 50 of 467
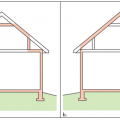
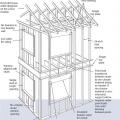
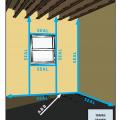
A 1- and ½-story home with a room located in the attic and the thermal boundary located at either a) the walls and ceiling of the attic room with small vented attic spaces or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
A blower door is installed in a doorway and is ready for testing
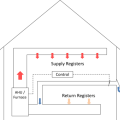
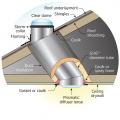
A central fan-integrated supply system uses a fresh air intake ducted to the home's central furnace or air handler unit to supply fresh air throughout the home
A home is tested at two points for enclosure air leakage
A low-sloped shed roof with the thermal boundary located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
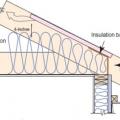
A site-built rafter roof with a raised top plate allows for more insulation underneath.
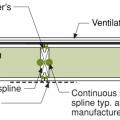
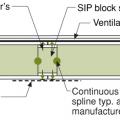
A structural spline made of a solid 2x is used where needed to meet structural load requirements at SIP panel seams
A surface spline reduces thermal bridging much more than a structural spline at SIP panel seams
Advanced framing details include corners that are constructed with fewer studs or studs aligned so that insulation can be installed in the corner.
Advanced framing details include framing aligned to allow for insulation at interior-exterior wall intersections.
Advanced framing details include using the minimum amount of wall studs permitted by code.
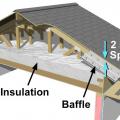
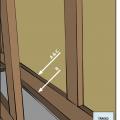
After all holes through the ceiling are air-sealed and the baffles have been installed, then the insulation can be installed.
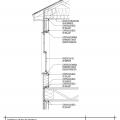
Air barrier is continuous across several components of the lower section of wall
Air seal and insulate double-walls that are half-height or full-height walls used as architectural features in homes.
Air seal around all duct shafts and flues installed through ceilings, walls, or flooring to keep conditioned air from leaking into unconditioned space.
Air seal around kitchen and bathroom exhaust fans to keep conditioned air from leaking into unconditioned space.
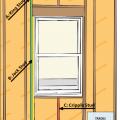
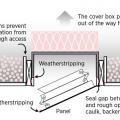
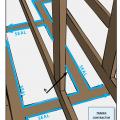
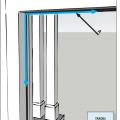
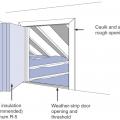
Air seal door and window rough openings with backer rod, caulk, or nonexpanding foam
Air seal the common wall between units in a multifamily structure to minimize air leakage.
Air seal the floor above an unconditioned basement or crawlspace and make sure floor insulation is in full contact with the underside of the subfloor.
Air seal the top, bottom, and sides of a cantilevered floor cavity and ensure that insulation is in full contact with all sides without voids.
Air-seal above-grade sill plates adjacent to conditioned space to minimize air leakage.
Air-seal and insulate the rim and band joists of walls separating an attached garage from the home’s conditioned space.
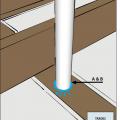
Air-seal around all plumbing and piping installed through walls, ceilings, and flooring adjacent to unconditioned space to prevent air leakage.
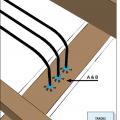
Air-seal around all wiring installed through walls, ceilings, and flooring to keep conditioned air from leaking into unconditioned space.
Air-seal around recessed can light fixtures that are installed through ceilings to keep conditioned air from leaking into unconditioned space.
Air-seal drywall to top plates at all attic/wall interfaces to minimize air leakage.
Air-seal the floor above a garage when there is living space above the garage and make sure floor insulation is in full contact with the underside of the subfloor.
All ceiling, wall, floor, and slab insulation shall achieve RESNET-defined Grade I installation
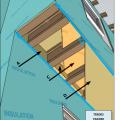
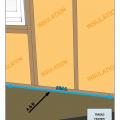
All seams between structural insulated panels (SIPs) foamed and/or taped per manufacturer's instructions
An all-terrain forklift is used to move and stage the panels
An insulated spline is another option for avoiding thermal bridging at SIP panel seams
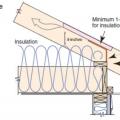
An unvented cathedralized attic has the air, thermal, and vapor control layers at the roof line