Showing results 51 - 100 of 253
Failure of Roof Structure from Pressurization Due to Window Failure During a Hurricane.
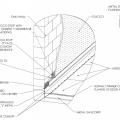
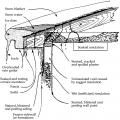
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.
Gable end vents allow in wind-driven rain because pressures that develop between the outside surface of the wall and the inside of the attic are sufficient to drive water uphill several inches.
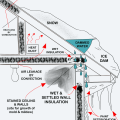
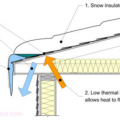
Heat loss through the roof of a home in a cold climate zone leads to snow melting to form ice dams.
High winds pulled the asphalt shingles and sheathing panels off this coastal home, although storm shutters protected the windows
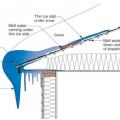
Ice dams form when warmth from the attic causes roof snow to melt and flow to roof eaves where it refreezes at the colder overhang and forms a buildup of ice causing more snowmelt to puddle where it can wick back through shingles and leak into the attic
Ice dams formed by melting of snow on roofs can affect roofs, walls, ceilings, siding, and insulation.
If a cool room is directly under an attic or roof, having lighter colored roofing (home on left) will reduce heat gain to the space as compared to darker roofing (home on right) because the temperature of the roof will be lower (see thermal image)
If snow level is estimated to exceed roof load limits, snow removal may be needed; hire professionals
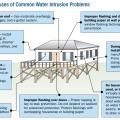
Improper flashing can allow rain water into walls, causing significant damage
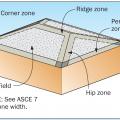
In high wind zones, if roof tiles are fastened with screws or nails, consider using clips on tiles at the corners, ridges, hips, and perimeters.
In high-flood-risk areas, install a roof hatch or openable skylight, min. 20x24 inches or 821 in.2 to serve as a means to access the roof for refuge
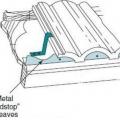
Install birdstop at the eave in tile roofs to minimize the accumulation of debris, a fire hazard, at the roof edge.
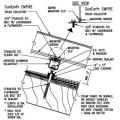
Install shingle starter strip then kick-out diverter; attach to roof deck but not sidewall
Install the house wrap. Cut house wrap to fit over diverter and tape top of cut wrap
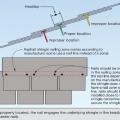
Integrate pre-formed vent pipe flashing, shingle-fashion, with roofing underlayment and shingles
Kickout diverter flashing keeps bulk water from the roof from overflowing the gutter and continuously wetting the siding material.
Lack of insulation over the top plate can lead to ice dam formation on a low sloped roof.
Loss of the fascia cover in high winds exposes the vinyl soffit to entry by wind-driven rain.
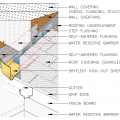
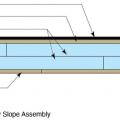
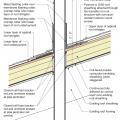
Low-slope roof assemblies constructed of two deck sheathing layers sandwiching rigid foam, and topped with mechanically fastened membrane
Metal birdstop is installed at the eaves of a tile roof to keep out birds, bats, rodents, and flying insects
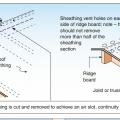
Nailing and ridge ventilation for roof sheathing used as a structural diaphragm in high-wind and seismic hazard areas.
Place first shingle and next section of sidewall flashing over upper edge of diverter
Poor installation can result in the loss of tile roofing in high wind regions, regardless of whether the tiles are attached with mortar, screws, nails, or foam adhesive.
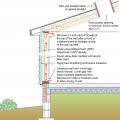
Provide flashing and sealing integrated with the air and water control layers for vents and other roof penetrations
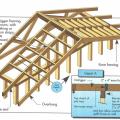
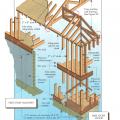
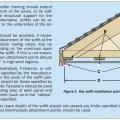
Provide structural supports that soffit panels can be nailed to at no less than 12 inches apart.