Showing results 1 - 36 of 36
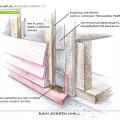
Install mesh insect barrier along the bottom of the rain screen behind the exterior cladding of above-grade walls
A cone or disc of plastic or sheet metal can be installed on pipes and downspouts to prevent rodents from climbing up the outside and gaining access to the roof
A layer of pea gravel or crushed stone, 4 inches thick and sloped 5%, provides a pest-resistant ground break around the perimeter of a slab foundation
A layer of pea gravel or crushed stone, 4 inches thick and sloped 5%, provides a pest-resistant ground break around the perimeter of a basement foundation
An externally insulated slab-on-grade is pest-protected by a metal termite shield under sill plate, metal-flashing-wrapped foam under siding, a removable inspection strip of PVC-covered foam, and 2 feet of gravel next to the foundation.
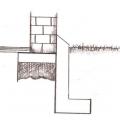
Bees made a nest in the drainage plane behind a brick veneer wall by entering via unscreened weep holes
Concrete (4 inches thick at 5% slope) provides a pest-resistant perimeter around the foundation
Concrete pavers set in 4 inches of sand provide a pest-resistant ground break at the building perimeter.
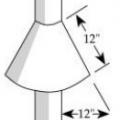
Construct a vertical curtain wall of 29-gauge corrugated iron, concrete, or bricks that extends down 2 feet and out 8 to 12 inches to prevent rats from burrowing under crawlspace foundations
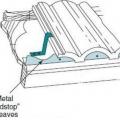
Metal birdstop is installed at the eaves of a tile roof to keep out birds, bats, rodents, and flying insects
Metal termite shields make it easier to see termite tunnels and may discourage termite access to wood framing
Pest proofing of this unvented crawlspace includes a metal termite shield that extends out from the sill plate, metal flashing wrapping the bottom of exterior rigid foam, and a termite inspection gap above interior rigid foam.
Pest protection measures include a termite shield under the rim joist and extending out on either side of the stem wall, insect screening under the furring air gap, and brick veneer to protect slab-edge insulation.
Right - An unvented attic with no soffit vents, borate-treated fascia board, metal drip edge, and concrete block construction on this south Florida home help make it resistant to hurricanes, pests, and wind-born wildfire embers.
Right - Metal drip edge on this south Florida CMU home protects the top of the fascia and edge of the roof deck from water, wind-blown rain and embers, and insects.
Right - The basement foundation is insulated on the exterior and termite shield extends out past the top of the insulation.
Right- This house uses CMU construction for flood and termite resistance as well as thermal mass
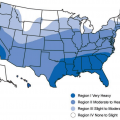
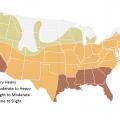
Termite Infestation Probability Map, Adapted from the 2021 International Residential Code (IRC), Figure R301.2(7)
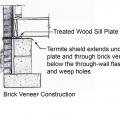
Termite shield extends under sill plate and through brick veneer below the through-wall flashing and weep holes.
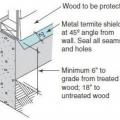
Termite shield is installed at the top of the foundation wall before installing sill plates; all seams and holes are sealed with epoxy
The green framing is lumber that was pressure treated with borate to increase its resistance to termites, mold, and moisture
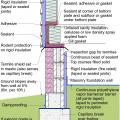
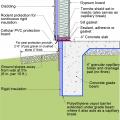
This basement is insulated on the exterior with rigid foam over dampproofing, with granular backfill and footing drains to facilitate drainage away from the foundation, a termite shield to protect from pests, and cellular PVC to protect the rigid foam.
This exterior insulated slab-on-grade monolithic grade beam foundation is protected from pests by termite shield at the sill plate, borate-treated framing, flashing at end of wall insulation, brick veneer over slab-edge insulation, and rock ground cover.
This house with an insulated slab is protected from pests with a termite shield at the sill plate, borate-treated framing, insect screen covering bottom of furring air gap, and brick veneer over slab-edge insulation
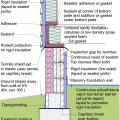
This house with interior insulated crawlspace is protected from pests with termite shield at sill plate, borate-treated framing, flashing at end of wall insulation, and a termite inspection gap at the top of the rigid foam
This plumbing pipe is wrapped with a stainless steel mesh skirt that is clamped to the pipe before the concrete slab is poured to to keep out bugs and rodents
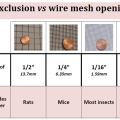
Use copper or stainless steel mesh plus caulk or foam around holes in exterior walls or epoxy in cracks in concrete to keep out rodents and termites.
Wire hardware mesh is fastened with a staple gun and screws to the wall to prevent pests from entering the building through small holes and cracks