Showing results 151 - 200 of 489
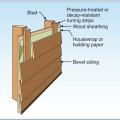
House wrap is sealed at all seams and overlaps flashing to serve as a continuous drainage plane over the exterior walls.
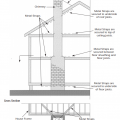
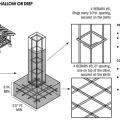
How to reinforce a chimney to resist earthquakes and high winds – side and top views.
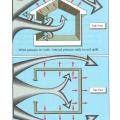
Hurricane force winds that breach external windows and doors can then cause failure of the entire building due to internal pressures on walls and roof.
Hurricane shutter styles include colonial, Bahama, roll-up, and accordion shutters.
Hurricane straps, hold-down connectors, and bolts help to transfer loads from the building’s walls to its foundation, increasing resistance to vertical and horizontal pressures acting on the building from wind, waves, or ground movement.
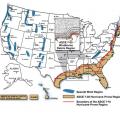
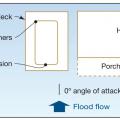
Hurricanes and resulting floods are among the most costly natural disasters impacting metropolitan areas (Source: U.S. Coast Guard)
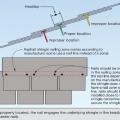
If both the shingles and the underlayment blow off the roof is more susceptible to water intrusion; sealed seams or a self-adhering underlayment provide greater protection.
Improper continuous load path design lacking bracing results in the failure of gable end walls under high wind conditions.
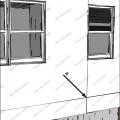
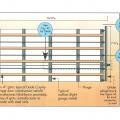
In areas prone to high winds and hurricanes, double vertical “jack trim” and horizontal “header” and “sill” studs are recommended on all sides of window and door openings.
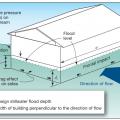
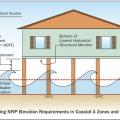
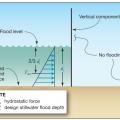
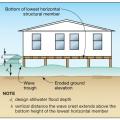
In Coastal A Zones and V Zones best practice is to construct the home so the bottom support of the lowest floor is above the 100-year wave crest elevation.
In coastal flood zones, in-ground pools should located as far landward on the lot as possible and be oriented perpendicular to the shoreline with rounded corners.
In high wind areas, provide lateral support to masonry end walls to resist high winds.
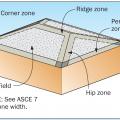
In high wind zones, if roof tiles are fastened with screws or nails, consider using clips on tiles at the corners, ridges, hips, and perimeters.
In high-wind regions, special hardware is used for most framing connections; toe-nailing is not acceptable.
In tropical climates such as Puerto Rico, some houses have metal jalousie louvers instead of glass windows; metal jalousies look like shutters, but typically offer little debris resistance.
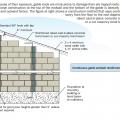
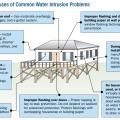
Inadequate connections between the foundation columns and footings or grade beams can lead to column connection failures during flooding.
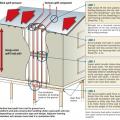
Install all layers of the drainage plane to overlap, not underlap, to direct bulk water down and out of the wall.
Install an ENERGY STAR labeled insulated door with an automatic closer. Weather strip the door frame
Install furring strips over house wrap to provide a rainscreen behind wood siding.
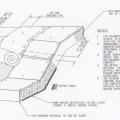
Installation of an erosion control blanket to minimize soil loss on sloped ground that has no established vegetation
Jalousie windows use shutters rather than glass over the window openings to allow for maximum ventilation. Screens may be installed to keep out insects.
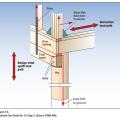
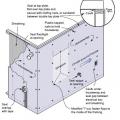
Key connection points for a continuous load path for earthquake and high wind disaster resistance
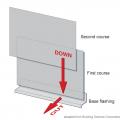
Kickout diverter flashing keeps bulk water from the roof from overflowing the gutter and continuously wetting the siding material.
Knee braces do not stiffen a pile foundation as much as diagonal bracing, but they present less obstruction to waves and debris, are less prone to compression buckling, and may be designed for both tension and compression loads.
Locating windows on adjacent and opposite sides of the house will allow cross ventilation regardless of wind direction
Loss of the fascia cover in high winds exposes the vinyl soffit to entry by wind-driven rain.
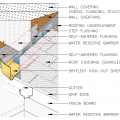
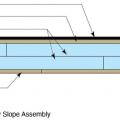
Low-slope roof assemblies constructed of two deck sheathing layers sandwiching rigid foam, and topped with mechanically fastened membrane
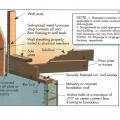
Lower-story wall anchorage to masonry (or concrete) base. Straps properly nailed at wall studs.