Showing results 1 - 50 of 263
A dormer with an openable window (not shown) can provide access to the roof if flood waters rise too high and too quickly; the dormer should be properly insulated, flashed, and air sealed
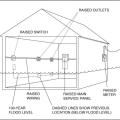
A FIRM will identify specific SFHAs (colored and hatched areas) and localized BFEs (wavy black lines)
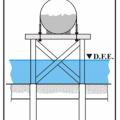
A fuel tank elevated above the design flood elevation on a platform in a high velocity flow area.
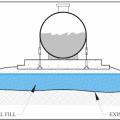
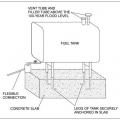
A fuel tank is strapped onto a concrete slab at the top of compacted fill above the DFE.
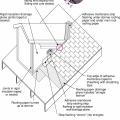
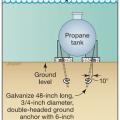
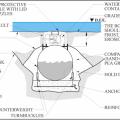
A fuel tank should be anchored with ground anchors designed for site conditions to maintain secure connection to its base in a flood or earthquake
A gable end failure due to improper bracing caused collapse of most of the trusses on this roof under hurricane force wind conditions.
A raised wood pier foundation can raise the subfloor above the design flood elevation.
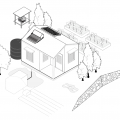
A resilient home with storm shutters, a sump pump that drains to a french drain, rainwater collection, solar thermal and PV, and raised garden beds.
A resilient multifamily building in Puerto Rico constructed of concrete on a raised slab foundation with a hip roof design for wind resistance and deep overhangs and permanent awnings to keep sun and rain off windows.
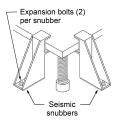
A seismic snubber is a type of bracket specifically designed to anchor heavy equipment to the floor to restrain it in the event of an earthquake.
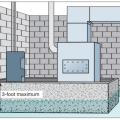
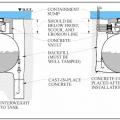
A water heater and furnace are protected from flood waters by a concrete floodwall, with a shielded, gasketed door.
All electrical system components should be raised above the design flood elevation to protect against water and speed up recovery, unless properly designed to be water-tight per code requirements.
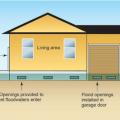
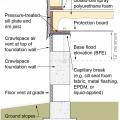
Although crawlspaces are not recommended in flood-prone areas, they can be designed or retrofitted to greatly increase resistance to flood damage.
An alternative design includes strapping the tank to concrete counterweights on opposite sides of the tank.
An engineered bioswale uses perforated pipe laid in rock and landscape fabric at the bottom of a vegetated trench to direct water away from a site.
An exterior metal staircase was added to this concrete building for roof access and refuge during tsunamis in Kesennuma, Japan
An underground fuel tank is anchored onto poured-in-place concrete counterweights.
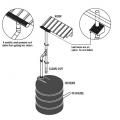
Anchoring a fuel tank to a concrete slab is recommended to avoid displacement if flooding occurs.
Backflow prevention devices keep water and sewage from entering the home during a flood preventing damage and health and safety issues.
Berms are compacted earth or gravel ridges that slow the flow of water from rain, riverine flooding, or storm surges in coastal areas.
Berms, swales, bioswales, ridges, and vegetation all help to control rainwater runoff on residential sites.
Bioswales or rain gardens filter storm water through vegetation and rock and sand substrate layers.
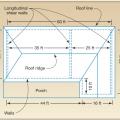
Building elevation and plan view of roof showing longitudinal shear walls; dimensions are wall-to-wall and do not include the 2-ft roof overhang.
Building siding extended down and over the breakaway wall so the upper wall was damaged when the lower wall broke away.
Buildings damaged by a hurricane storm surge: upper homes on gulf shoreline were hit by large waves above the lowest floor, lower left home on bay and right school 1.3 miles from gulf shoreline were hit by surge and small waves.
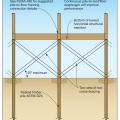
Built-up beam connections, knee brace connections, and diagonal brace connections for wood piles.
Closed-cell spray foam insulates the floor above a vented crawlspace; a protection board made of fiber cement is screwed in place under the floor joists to keep out pests
Closed-cell spray foam insulates the floor above an open foundation; a protection board made of fiber cement is screwed in place under the floor joists to keep out pests
Coastal flooding washed away most of the first floor of this home; however, the piers and roof are still standing.
Coastal flooding washed away this home but left the masonry piers, which are set in concrete bases.
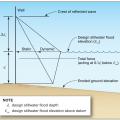
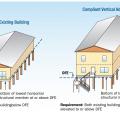
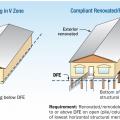
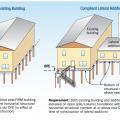
Comparison of a building that sits below the Design Flood Elevation and renovated to be above the DFE and to add a second story.
Comparison of a building that sits below the Design Flood Elevation and renovated to be above the DFE.
Comparison of a building that sits below the Design Flood Elevation and renovated to be above the DFE.
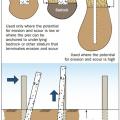
Concrete pier foundations can be used in place of wood piles in coastal areas where risk of erosion and scour is low.
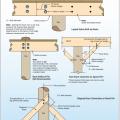
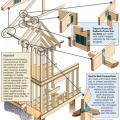
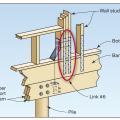
Connecting hardware helps tie the roof to the walls to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
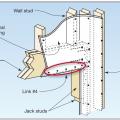
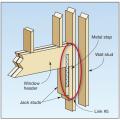
Connecting hardware helps tie the walls to the top plates and rim joists to ensure a continuous load path to improve a building’s resistance to high winds, floods, and earthquakes.
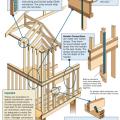
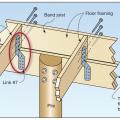
Connection of floor framing to support beam for a coastal home built on piles (band joist nailing to the floor joist is adequate to resist uplift forces).