Showing results 51 - 100 of 1165
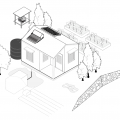
A resilient home with storm shutters, a sump pump that drains to a french drain, rainwater collection, solar thermal and PV, and raised garden beds.
A resilient multifamily building in Puerto Rico constructed of concrete on a raised slab foundation with a hip roof design for wind resistance and deep overhangs and permanent awnings to keep sun and rain off windows.
A reversible window fan can operate via thermostatic or remote control and can selectively exhaust air or bring in outdoor air
A roughed-in fire sprinkler head (left) and fire sprinkler riser (right), both using CPVC piping.
A screened-in porch will protect windows from rain, provide shade, and allow more airflow through windows than window screens would
A seismic shut off valve with a stopper to cease the flow of gas to a property during the event of an earthquake.
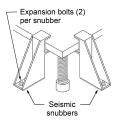
A seismic snubber is a type of bracket specifically designed to anchor heavy equipment to the floor to restrain it in the event of an earthquake.
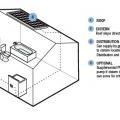
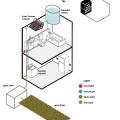
A self-sufficient water system for a home could include a rooftop cistern and solar thermal water heater.
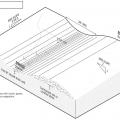
A shaded fuel break is created on forested lands when trees are thinned, tree canopies are raised by removing lower branches, and the understory vegetation is managed to reduce the fire threat.
A shallow, open floor plan allows free flow of cross ventilation through the house
A simple kit for anchoring a TV, appliance, or furniture to a wall may include straps, attachment hardware, and screws for attaching both to the appliance and to the wall
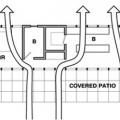
A single-story house floor plan showing braced wall line locations at A through E and 1 through 5
A swale and berm can be installed together across a slope to slow the downhill flow of water.
A thermosiphon solar hot water system heats a fluid in the solar collector; the heated fluid heats potable water in a roof top tank.
A typical Las Vegas hot-dry climate home made of wood frame construction and insulated with R-25 expanded polystyrene externally over a drainage plane, with an unvented wood frame insulated attic and roof assembly.
A variety of battery-powered fans can be used for a cool room without electric power; most charge off a USB charger so they can be solar charged
A wall assembly approved for use in the wildland-urban interface has 5/8-inch type X gypsum installed exterior of the wood sheathing and an exterior covering or siding that has a 1-hour fire-resistance rating
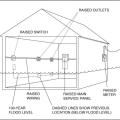
A water heater and furnace are protected from flood waters by a concrete floodwall, with a shielded, gasketed door.
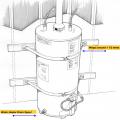
A water heater is anchored to 2 x 4 wood blocking that is attached to the wall studs.
Above-ground welded-steel cistern with hydrant for fire engine hose hookup installed on private land for residential fire suppression.
Accordion-type hurricane shutters protect sliding glass doors from high winds and wind-borne debris.
Add metal connectors to strengthen framing connections in an existing wall from inside the home by removing drywall.
Adding planted terraces to a sloped yard can slow down runoff and reduce erosion
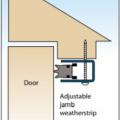
Adjustable weatherstripping can be installed around the interior side of the door frame to help keep out wind-blown rain and embers and hot gasses from wildfires (FEMA 577).
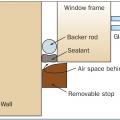
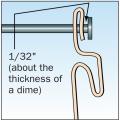
Air seal door and window rough openings with backer rod, caulk, or nonexpanding foam
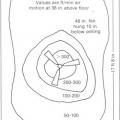
Air speeds generated by a typical ceiling fan are in the ideal range for providing occupant cooling without causing disruption
Air-Impermeable Insulation for Condensation Control in Unvented Attics, per IRC Table 806.5.
Airflow can be directed across thermal mass in the ceiling, floor, or elsewhere inside the home through various window and louver configurations
All electrical system components should be raised above the design flood elevation to protect against water and speed up recovery, unless properly designed to be water-tight per code requirements.
All holes through the top plates should be sealed with canned spray foam to prevent conditioned air from leaking into the attic.
All populated regions in the United States can experience an extreme heat event, whether northern or southern, humid or dry, or urban or rural
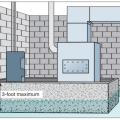
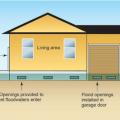
Although crawlspaces are not recommended in flood-prone areas, they can be designed or retrofitted to greatly increase resistance to flood damage.
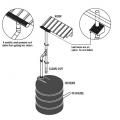
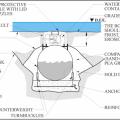
An alternative design includes strapping the tank to concrete counterweights on opposite sides of the tank.
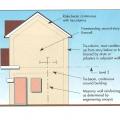
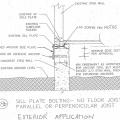
An anchor side plate is used to connect the concrete foundation to the sill plate from the exterior as part of a seismic retrofit when the sill plate is not accessible from the interior of the home
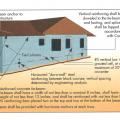
An earthquake-actuated automatic gas shutoff valve is attached to the natural gas pipeline between the meter and the house, downstream of the meter, to stop the flow of gas into the house if an earthquake occurs.
An engineered bioswale uses perforated pipe laid in rock and landscape fabric at the bottom of a vegetated trench to direct water away from a site.
An example of a vertical California Seismic Valve
An exterior metal staircase was added to this concrete building for roof access and refuge during tsunamis in Kesennuma, Japan
An exterior wall braced using the let-in-bracing (LIB) method with no exterior sheathing
An externally insulated slab-on-grade is pest-protected by a metal termite shield under sill plate, metal-flashing-wrapped foam under siding, a removable inspection strip of PVC-covered foam, and 2 feet of gravel next to the foundation.
An indoor water heater should be secured to the wall’s studs to prevent it from moving or tipping over in the event of an earthquake