Showing results 1 - 50 of 73
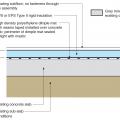
A continuous layer of polyethylene covers the crawlspace floor and is attached to the wall with wood nailing strips
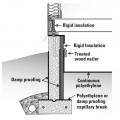
A paint-on waterproofing covers the exterior and tops of the concrete block foundation walls and piers to block moisture moving up through the concrete, while foil-faced R-13 insulation lines the inside surface of the exterior walls.
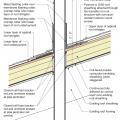
A roof drain is installed in an existing flat roof retrofitted with above-deck rigid foam insulation that is integrated with new air and water control layers
Because the above-grade potions of the wall lack exterior insulation, condensation and even ice form during cold winter conditions
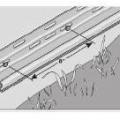
Capillary break at all crawlspace floors using ≥ 6 mil polyethylene sheeting, lapped 6-12 in., and lapped up each wall or pier and fastened with furring strips or equivalent
Closed-cell foam is sprayed into roof cavities along the masonry parapet wall to form a continuous air barrier between the wall and the sheathing of the flat roof
Closed-cell spray foam fills the roof joist cavities forming an air barrier between the masonry parapet wall and the roof sheathing
Concrete is poured into the rigid foam shell of the insulated concrete form (ICF) walls; a plastic water barrier has already been installed to protect the below-grade wall surfaces.
Existing low-slope (“flat”) roof and brick masonry walls with a new fully adhered air barrier membrane plus polyisocyanurate rigid foam insulation and a roofing membrane water control layer
Exterior fiberglass insulation on this new home was (incorrectly) cut to terminate below-grade after backfill, which will expose the above-grade portions of the foundation wall to cold temperatures
Exterior XPS basement insulation is correctly installed to completely cover the foundation wall
Extruded polystyrene (XPS) rigid foam is taped at the seams to provides a continuous air and weather-resistant barrier so no house wrap is needed; it also provides a continuous layer of insulation.
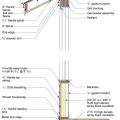
Foil-faced rigid foam and spray foam can be used to insulate a basement on the interior; use good moisture management techniques to keep the basement dry
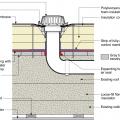
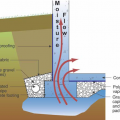
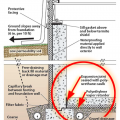
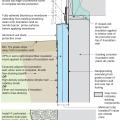
Good water management practices like sloping grade away from house, and installing gutters, perimeter drain pipe, a capillary break, and free-draining soils or drainage mat protect the foundation from water saturation.
ICF bricks are stacked to form hollow walls that are reinforced with steel rebar before the concrete is poured in
Over the taped rigid foam board, 2x4 furring strips provide a ventilating air gap and drainage plane under the engineered wood lap siding. The furring strips were attached with structural screws to provide an attachment surface for the siding.
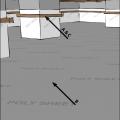
Polyethylene completely covers the floor of this crawlspace and is attached to the walls and piers as well
Polyethylene is being attached to the crawlspace floor and walls with plywood furring strips
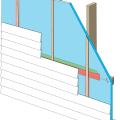
Polyisocyanurate rigid foam insulation is installed in multiple layers with staggered, taped seams over the flat roof
Proper flashing around windows is especially important when the rigid foam serves as the drainage plane in the wall
Provide flashing and sealing integrated with the air and water control layers for vents and other roof penetrations
Retrofit an existing roof by installing rigid foam, new moisture and air control layers, new sheathing, and new cladding plus cavity insulation in the roof rafters to create an unvented attic
Right - Basement slab with a capillary break of either gravel or a drainage mat.
Right - Retrofit of an existing basement slab by adding dimple plastic mat, rigid foam insulation, and a floating subfloor.
Right - The basement walls are wrapped with 3 inches of XPS rigid foam that will be taped at the seams then covered with a dimpled plastic water barrier.
Right - The existing basement slab is retrofitted by installing a dimple plastic drainage mat, rigid foam insulation, and a floating subfloor.
Right - These roof insulation panels are installed in multiple layers with joints offset both vertically and horizontally. The plywood nail base fastened to the roof framing holds the insulation layers together snuggly thus minimizing gaps
Right – A 1-inch layer of XPS rigid foam covers the 2x6 wall studs and is topped by ½-inch-thick plywood sheathing, which is covered with draining house wrap and serves as a nailing surface for siding and trim.
Right – Even house wrap is installed in the factory for these modular homes where each floor is factory assembled.
Right – Furring strips provide a drainage and ventilation gap between the siding and the cork insulation.
Right – Furring strips provide a drainage gap between the rigid foam and the siding.
Right – Furring strips were installed to provide a 3/8-inch drainage plane over the rigid foam and under the fiber cement lap siding.
Right – Polyethylene sheeting vapor barrier is installed and sealed to the crawlspace walls with mastic
Right – Ripped OSB provides furring strips for a ventilation gap behind the wood siding.
Right: All joints in the rigid foam are taped to keep stucco out of joints for even drying. Mesh tape (shown here) is used with expanded polystyrene (EPS); acrylic sheathing tape or self-adhered membrane is used with XPS
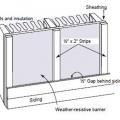
Rigid foam insulation can serve as the drainage plane when all seams are taped. Furring strips provide an air gap behind the cladding.
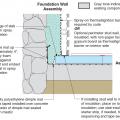
Rigid insulation and water control layers are installed on the exterior of a flat foundation wall; spray foam insulates the rim joist
Rigid mineral wool insulation is covered with ¼-inch wood battens which provides a air and drainage gap under the cedar and fiber cement siding.
Roofing membrane is installed over polyisocyanurate rigid foam insulation and insulation cover board that has been cut to fit around locations for blocking for the PV system rack
Roofing paper protects the top of the new plywood parapet while the base of the parapet is air sealed with spray foam and fibrous insulation is installed in the rafter cavities in this flat roof retrofit
Seams in the ICF block are sealed so the EPS foam surface can serve as the drainage plane; no house wrap is needed.
Spray foam extends down the foundation wall to the slab, which has been retrofitted by adding dimple plastic drainage mat and rigid foam insulation.
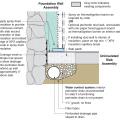
Spray foam extends down the inside of the foundation wall to the uninsulated slab; because the wall lacked exterior perimeter drainage, the slab was cut and an interior footing drain was installed.