Showing results 1 - 100 of 133
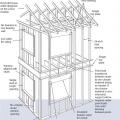
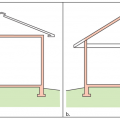
A 1- and ½-story home with a room located in the attic and the thermal boundary located at either a) the walls and ceiling of the attic room with small vented attic spaces or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
A low-sloped shed roof with the thermal boundary located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
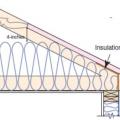
A site-built rafter roof with a raised top plate allows for more insulation underneath.
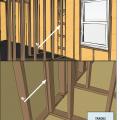
Advanced framing details include corners that are constructed with fewer studs or studs aligned so that insulation can be installed in the corner.
Advanced framing details include framing aligned to allow for insulation at interior-exterior wall intersections.
All ceiling, wall, floor, and slab insulation shall achieve RESNET-defined Grade I installation
Batt insulation should be cut to fit around wiring so that insulation can completely fill the wall cavity
Blown cellulose insulation completely fills the netted wall and ceiling cavities.
Ceiling, wall, floor, and slab insulation levels shall meet or exceed Builders Challenge levels
Closed-cell spray foam insulation is added to the wall cavities of an existing exterior wall
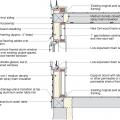
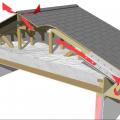
Design the roof with raised heel trusses to allow full insulation over the top plates of the exterior walls.
Expanded polystyrene insulation is installed with joints taped and lath attached in preparation for the application of stucco
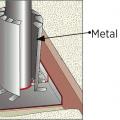
Exterior fiberglass insulation on this new home was (incorrectly) cut to terminate below-grade after backfill, which will expose the above-grade portions of the foundation wall to cold temperatures
Exterior XPS basement insulation is correctly installed to completely cover the foundation wall
Faced fiberglass batt insulation can be stapled to the stud faces or slightly inset, but avoid compressing the batts
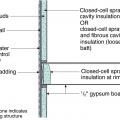
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.
Foil-faced rigid foam and spray foam can be used to insulate a basement on the interior; use good moisture management techniques to keep the basement dry
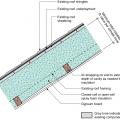
For slabs on grade in CZ 4 and higher, 100% of slab edge insulated to ≥ R-5 at the depth specified by the 2009 IECC and aligned with thermal boundary of the walls
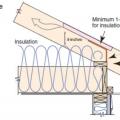
In cathedral ceilings, parallel chord trusses allow thicker insulation levels over the exterior wall top plates.
Infrared thermography during depressurization testing reveals air leakage at corner of spray foam-insulated room where wood-to-wood seams in framing were not air sealed
Install continuous rigid foam insulation or insulated siding to help reduce thermal bridging through wood- or metal-framed exterior walls.
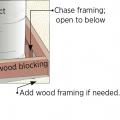
Install insulation under platforms constructed in the attic for storage or equipment.
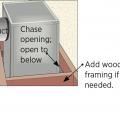
Install wood framing cross pieces in the attic rafter bays on each side of the duct chase
Install wood framing cross pieces in the attic rafter bays on each side of the duct chase
Lay out the rigid foam sheathing joints so they do not align with the window and door edges
Limited attic access can make inspections for missing air barriers and insulation challenging
Limited attic access may make it necessary to use a bore scope when inspecting for missing air barriers and insulation in existing buildings.
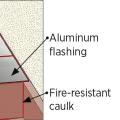
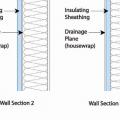
Proper flashing around windows is especially important when the rigid foam serves as the drainage plane in the wall
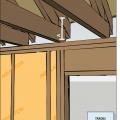
Raised heel energy trusses extend past the exterior wall and are deeper at the wall allowing room for full insulation coverage over the top plate of the exterior walls.
Right - Continuous wall sheathing and blocking has been installed to brace the raised heel trusses.
Right - New flashing has been installed to complete the air and water control layers at the window openings of this wall retrofit that includes insulating the wall cavities with spray foam
Right - Rigid foam slab edge insulation is installed along the exterior edge of a monolithic slab foundation.
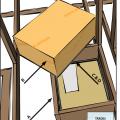
Right – Attic access hatch has been properly insulated by attaching a fiberglass batt, gasketed, and opening has blocking
Right – All insulated sheathing boards are installed according to the manufacturer’s recommended fastening schedule and taping specifications
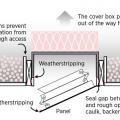
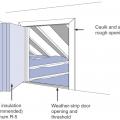
Right – Attic access door has foam and rubber weatherstripping installed that remains in contact when closed.
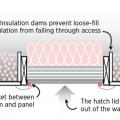
Right – Blocking has been installed around the perimeter of this attic access to prevent insulation falling into the house
Right – Full length 2x6 nailer has been installed to allow space for insulation at wall intersection
Right – Insulation installed to correct depth and will be aligned with air barrier
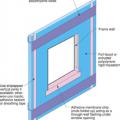
Right – Structural insulated sheathing can provide racking strength (lateral load resistance), and serve as an air barrier and thermal barrier if installed according to manufacturer’s specifications with taped, sealed seams
Right – This attic knee wall and the floor joist cavity openings beneath it are being sealed and insulated with spray foam.
Right-- IR photo shows how effectively spray foam insulated/air sealed attic kneewall and the floor cavities under kneewall
Right: All joints in the rigid foam are taped to keep stucco out of joints for even drying. Mesh tape (shown here) is used with expanded polystyrene (EPS); acrylic sheathing tape or self-adhered membrane is used with XPS
Rigid foam forms an insulating bond break between the foundation wall and the slab
Rigid foam insulated sheathing placed exterior to house wrap, interior to house wrap, or take the place of the house wrap
Siding has been removed so cellulose insulation can be dense-packed into the exterior walls of this home
Single framed wall converted to double wall and insulated with closed-cell spray foam
Single framed wall converted to double wall and insulated with open-cell spray foam
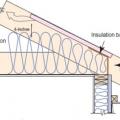
Sloped roof with cavity spray foam insulation, strapping, and gypsum board thermal barrier
Spray foam insulation is installed in open wall cavities to air seal and insulate
Standard roof trusses are narrow at the eaves, preventing full insulation coverage over the top plate of the exterior walls
Stucco is installed over rigid insulation, which is installed over a drainage plane consisting of a drainage gap and building wrap layer over the sheathing
The attic kneewall and the open floor cavities under kneewall are both sealed and insulated in one step with spray foam insulation
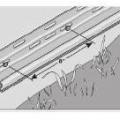
The soffit dam and baffle allow air to flow through the vents without disturbing the insulation covering the top plates
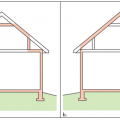
The thermal boundary for a gable roof can be located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
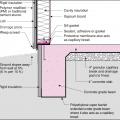
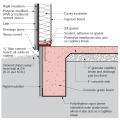
This basement is insulated on the exterior with rigid foam over dampproofing, with granular backfill and footing drains to facilitate drainage away from the foundation, a termite shield to protect from pests, and cellular PVC to protect the rigid foam.
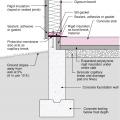
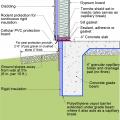
This exterior insulated slab-on-grade monolithic grade beam foundation is protected from pests by termite shield at the sill plate, borate-treated framing, flashing at end of wall insulation, brick veneer over slab-edge insulation, and rock ground cover.
This kneewall has no top plate and the resulting gap provides a wide-open pathway for air and vapor to travel between the living space and the attic