Showing results 1 - 50 of 133
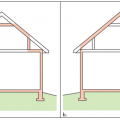
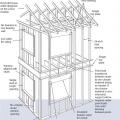
A 1- and ½-story home with a room located in the attic and the thermal boundary located at either a) the walls and ceiling of the attic room with small vented attic spaces or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
A low-sloped shed roof with the thermal boundary located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
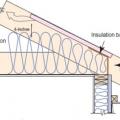
A site-built rafter roof with a raised top plate allows for more insulation underneath.
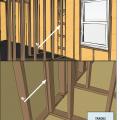
Advanced framing details include corners that are constructed with fewer studs or studs aligned so that insulation can be installed in the corner.
Advanced framing details include framing aligned to allow for insulation at interior-exterior wall intersections.
All ceiling, wall, floor, and slab insulation shall achieve RESNET-defined Grade I installation
Batt insulation should be cut to fit around wiring so that insulation can completely fill the wall cavity
Blown cellulose insulation completely fills the netted wall and ceiling cavities.
Ceiling, wall, floor, and slab insulation levels shall meet or exceed Builders Challenge levels
Closed-cell spray foam insulation is added to the wall cavities of an existing exterior wall
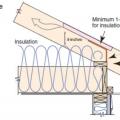
Design the roof with raised heel trusses to allow full insulation over the top plates of the exterior walls.
Expanded polystyrene insulation is installed with joints taped and lath attached in preparation for the application of stucco
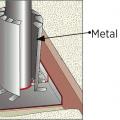
Exterior fiberglass insulation on this new home was (incorrectly) cut to terminate below-grade after backfill, which will expose the above-grade portions of the foundation wall to cold temperatures
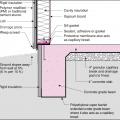
Exterior XPS basement insulation is correctly installed to completely cover the foundation wall
Faced fiberglass batt insulation can be stapled to the stud faces or slightly inset, but avoid compressing the batts
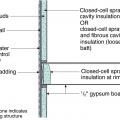
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.
Foil-faced rigid foam and spray foam can be used to insulate a basement on the interior; use good moisture management techniques to keep the basement dry
For slabs on grade in CZ 4 and higher, 100% of slab edge insulated to ≥ R-5 at the depth specified by the 2009 IECC and aligned with thermal boundary of the walls
In cathedral ceilings, parallel chord trusses allow thicker insulation levels over the exterior wall top plates.
Infrared thermography during depressurization testing reveals air leakage at corner of spray foam-insulated room where wood-to-wood seams in framing were not air sealed
Install continuous rigid foam insulation or insulated siding to help reduce thermal bridging through wood- or metal-framed exterior walls.
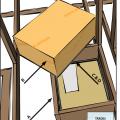
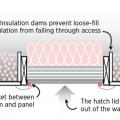
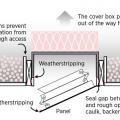
Install insulation under platforms constructed in the attic for storage or equipment.
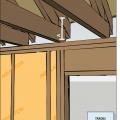
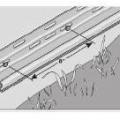
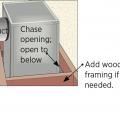
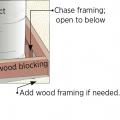
Install wood framing cross pieces in the attic rafter bays on each side of the duct chase
Install wood framing cross pieces in the attic rafter bays on each side of the duct chase
Lay out the rigid foam sheathing joints so they do not align with the window and door edges
Limited attic access can make inspections for missing air barriers and insulation challenging
Limited attic access may make it necessary to use a bore scope when inspecting for missing air barriers and insulation in existing buildings.
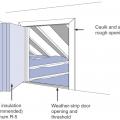
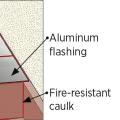
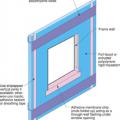
Proper flashing around windows is especially important when the rigid foam serves as the drainage plane in the wall
Raised heel energy trusses extend past the exterior wall and are deeper at the wall allowing room for full insulation coverage over the top plate of the exterior walls.