Showing results 1 - 50 of 75
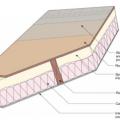
Example of the advanced framing technique, double-stud wall cavity, which will later be filled with blown insulation
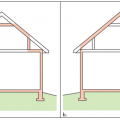
A 1- and ½-story home with a room located in the attic and the thermal boundary located at either a) the walls and ceiling of the attic room with small vented attic spaces or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
A low-sloped shed roof with the thermal boundary located at either a) the flat ceiling with a vented attic or b) the roof line for an unvented attic
A typical Las Vegas hot-dry climate home made of wood frame construction and insulated with R-25 expanded polystyrene externally over a drainage plane, with an unvented wood frame insulated attic and roof assembly.
Air-Impermeable Insulation for Condensation Control in Unvented Attics, per IRC Table 806.5.
Brick veneer framed wall supported by a concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
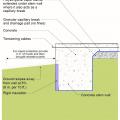
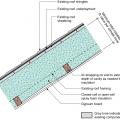
Concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing insulated on its top surface, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Detail of an unvented cathedralized attic showing air-impermeable spray foam insulation plus batt insulation installed on the underside of the roof deck.
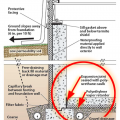
Externally insulated concrete slab-on-grade foundation with a turn-down footing, showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Externally insulated post-tensioned concrete slab-on-grade foundation wall with a turn-down footing showing anchorage of the wall to the foundation for seismic resistance
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.
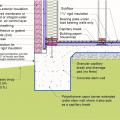
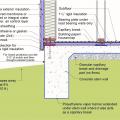
Good water management practices like sloping grade away from house, and installing gutters, perimeter drain pipe, a capillary break, and free-draining soils or drainage mat protect the foundation from water saturation.
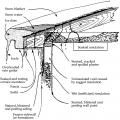
Ice dams formed by melting of snow on roofs can affect roofs, walls, ceilings, siding, and insulation.
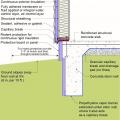
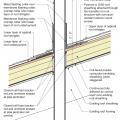
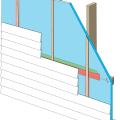
Insulating sheathing is installed on exterior of an existing framed wall with water control between existing sheathing and insulating sheathing
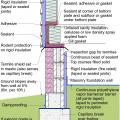
Pest proofing of this unvented crawlspace includes a metal termite shield that extends out from the sill plate, metal flashing wrapping the bottom of exterior rigid foam, and a termite inspection gap above interior rigid foam.
Pier foundations, hurricane strapping, borate- and pressure-treated lumber, and high-density spray foam insulation help protect this New Orleans home from costal flooding and storms (Source: Green Coast Enterprises).
Provide flashing and sealing integrated with the air and water control layers for vents and other roof penetrations
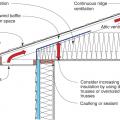
Right - Continuous wall sheathing and blocking has been installed to brace the raised heel trusses.
Right - Foil-faced polyisocyanurate insulating rigid foam sheathing is installed below the floor framing of this house built on piers; however, the seams should be sealed with metal taped and the plumbing elevated and protected.
Right - Foil-faced polyisocyanurate rigid foam is attached to the existing exterior wall with vertical wood furring strips
Right - Open-cell polyurethane spray foam to R-28 on underside of roof turns new attic into conditioned space for HVAC.
Right - Spray foam insulation has been sprayed onto the underside of the sloped roof and the gable end wall to provide a sealed, insulated attic for housing the HVAC ducts
Right - The basement foundation is insulated on the exterior and termite shield extends out past the top of the insulation.
Right - These raised heel roof trusses provide 16 inches of space over the outer walls for full insulation coverage at the attic perimeter.
Right - This foil-faced polyisocyanurate rigid foam is installed on an existing exterior wall and the seams are taped so the rigid foam can serve as a water control layer
Right - This new sealed attic has 5.5 inches (R-20) of spray foam insulation along the underside of the roof deck providing a conditioned attic space for the heating and cooling ducts.
Right - XPS foam insulation is attached to the existing exterior wall with wood furring strips that serve as a nail base for the siding and are installed vertically to allow for drainage and drying behind the siding
Right – Closed-cell polyurethane foam is sprayed on the underside of the roof deck to provide structural connections and seal seams in the sheathing to increase wind resistance
Right – Furring strips provide a drainage and ventilation gap between the siding and the cork insulation.
Right – Furring strips provide a drainage gap between the rigid foam and the siding.
Right – R-25 of open-cell spray foam lines this new home’s attic ceiling, to protect HVAC ducts from heat and cold.
Right – Ripped OSB provides furring strips for a ventilation gap behind the wood siding.
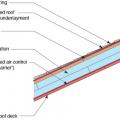
Right – Roof underlayment is fully adhered and roof deck seams are sealed so roof is resistant to high-wind events
Right – Roof underlayment is fully adhered and roof deck seams are sealed so roof is resistant to high-wind events
Right – The insulation has been located to the exterior of the thermal mass in this wall section
Right – This foil-faced foam sheathing has taped seams and proper flashing details so it can serve as a drainage plane.
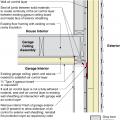
Rigid foam insulating sheathing installed over an existing garage ceiling with retrofits to air seal exterior wall before adding exterior wall insulating sheathing
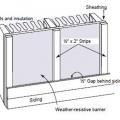
Rigid foam insulation can serve as the drainage plane when all seams are taped. Furring strips provide an air gap behind the cladding.
Sloped roof with cavity spray foam insulation sprayed on underside of roof deck and covered with sprayed-on thermal or ignition barrier coating.
Sloped roof with cavity spray foam insulation, strapping, and gypsum board thermal barrier
Spray foam insulation was installed on the underside of the roof deck and on gable end attic walls to create an unvented attic
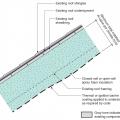
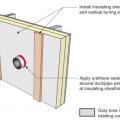
Step 4. Install insulating sheathing and vertical furring strips on the retrofitted exterior wall; seal around pipe or duct with urethane sealant.
Step 5. Install sheathing tape flashing over the duct or pipe and wood blocking on either side for later attachment of trim.