Showing results 1 - 250 of 281
Right: dedicated tank connections for HPWH inlet and outlet provide hydraulic separation
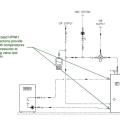
These schematics illustrate temporary deployment locations for probes during the commissioning process; these probes connect to smartphone commissioning applications.
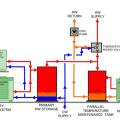
A central heat pump water heating system with a parallel loop tank temperature maintenance configuration uses a multi pass heat pump water heater to provide all the heat for hot water circulation temperature maintenance.
A central heat pump water heating system with a parallel loop tank temperature maintenance configuration uses a multi-pass heat pump water heater to provide all the heat for hot water circulation temperature maintenance
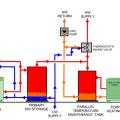
A central heat pump water heating system with a temperature maintenance swing tank configuration uses the water from the primary storage tank to provide most of the heat for hot water circulation temperature maintenance
A duct leakage test is performed on a ducted heat pump system using a duct tester (blower fan) and a digital manometer.
A flanged window unit is installed with straps that fasten to the interior surfaces of the plywood extension box; furring strips on each side of the window will be attached after the flanged window is installed and flashed
A flow grid is inserted into the filter grille/slot to directly measure airflow.
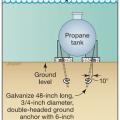
A fuel tank should be anchored with ground anchors designed for site conditions to maintain secure connection to its base in a flood or earthquake
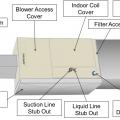
A nitrogen pressure test was completed on this ductless mini-split heat pump using a digital manifold gauge.
A simple vented attic with good air-sealing of the drywall ceiling air barrier, air flow from soffit vents to ridge vents protected by ventilation baffles, and lots of insulation covering the attic floor is unlikely to encourage ice dams.
A static pressure measurement is taken on this air handler using probes on the supply and return sides of the fan.
A vacuum decay test is performed on this ductless mini-split heat pump using a digital micron gauge for accurate measurement; a deep vacuum is achieved quickly by using large diameter, vacuum-rated hoses, and removing valve cores
After attaching netting to the 2x6 studs, workers fill the wall cavities with R-23 of blown fiberglass made from recycled bottles.
After inserting the new filter, replace the filter slot cover to minimize air leakage and heat loss.
Air handler platforms used as return air plenums can draw air from vented attics and crawlspaces through other connected framing cavities
All ceiling, wall, floor, and slab insulation shall achieve RESNET-defined Grade I installation
An IR camera image shows gaps around HVAC flue pipes allow conditioned air to leak through blown fiberglass into the attic
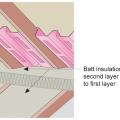
Batt insulation is installed in two layers in perpendicular directions against the baffle to full required insulation height
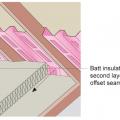
Batt insulation is installed in two layers with offset seams against the baffle to full code-required insulation height
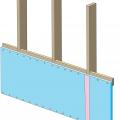
Batt insulation should be cut to fit around wiring so that insulation can completely fill the wall cavity
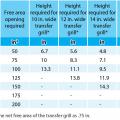
Bedrooms pressure-balanced and provide 1 sq. in. of free area opening per 1 CFM of supply air or achieve a Rater-measured pressure differential ≤ 3 Pa
Bedrooms pressure-balanced and provide 1 sq. in. of free area opening per 1 CFM of supply air or achieve a Rater-measured pressure differential ≤ 3 Pa
Blown cellulose insulation completely fills the netted wall and ceiling cavities.
Building cavities not used as supply or return ducts unless they meet Items 3.2, 3.3, 4.1, and 4.2 of this Checklist
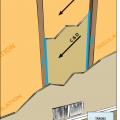
Cavity used for return is not insulated and is not air sealed, which will pull in air from outside
Ceiling, wall, floor, and slab insulation levels shall meet or exceed Builders Challenge levels
Central heat pump water heaters like this fully packaged system provide efficient, reliable domestic hot water for multifamily buildings; storage tanks are within the enclosure, and the heat pump is seen just outside.
Clean taping areas and install 3" tape on vertical joint of upper insulation overlapping the horizontal joint
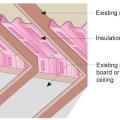
Clean the attic floor of debris prior to installing new attic insulation. Use baffles to provide a path for ventilation air entering the attic from the soffit vents
Closed-cell spray foam insulation covers the attic floor to provide a continuous air control layer.
Condensation can form between the interior removable storm window and the existing window if the storm window is not air tight
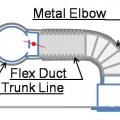
Consider using a metal duct elbow instead of flex duct at boot connections to prevent compressions
Contractors install gasket between the second-story top plate and the rim joist to air seal at this wall to attic transition (Source: S&A Homes).
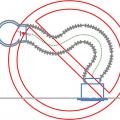
Coordinate with other trades including framers, plumbers, and electricians to prevent needless looping of flex duct
Deep energy retrofit showing insulation sprayed on exterior of walls over existing siding
Door has been undercut to allow for specified amount of air flow therefore contributing to pressure balancing
Duct to boot connection of jump duct not fastened and sealed
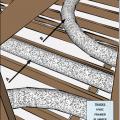
Ducts sagging because supports not installed at regular intervals
Example of an HVAC installer’s balancing report form
Expanded polystyrene insulation is installed with joints taped and lath attached in preparation for the application of stucco
Faced fiberglass batt insulation can be stapled to the stud faces or slightly inset, but avoid compressing the batts
Fan housing was oriented in the correct direction to allow proper exhaust duct installation
Flat roof with cavity spray foam plus loose-fill insulation and gypsum board thermal barrier.
Flexible ducts in unconditioned space not installed in cavities smaller than outer duct diameter; in conditioned space not installed in cavities smaller than inner duct diameter
Flexible ducts supported at intervals as recommended by mfr. but at a distance ≤ 5 ft
For factory-made interior removable storm windows, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for measuring the window frame
Furnace filters come in many sizes; verify the correct size when purchasing for proper fit in the filter slot.
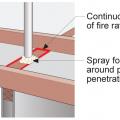
HVAC ducts, cavities used as ducts, and combustion inlets and outlets may pass perpendicularly through exterior walls but shall not be run within exterior walls unless at least R-6 continuous insulation is provided on exterior side of the cavity
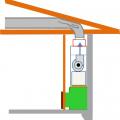
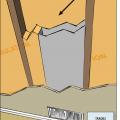
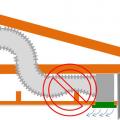
If a dropped soffit is used to house a duct, the soffit space must equal the duct diameter plus the insulation thickness
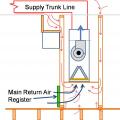
If airflow must be limited to a supply register, use balancing dampers at the trunk line rather than looping duct to control airflow
If filter is inaccessible, locate the air filter between the return air plenum and the air handler box
If furnace is accessible, locate the air filter between the return air plenum and the air handler box
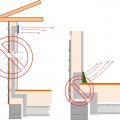
If HVAC duct must be installed in an exterior wall, separate it from the exterior with at least R-6 of continuous rigid insulation
If the furnace is hard to access, locate filters at return registers covered by hinged grilles that are easy to open from inside the home
Improperly installed fuel tanks can break free from attachments under the force of flood waters, risking broken fuel lines which could cause fire or explosion. Here, the tank is tethered only by the gas piping, which is not designed to perform this functi
Inadequate amount of insulation installed with compression, misalignment, and voids
Infrared thermography during depressurization testing reveals air leakage at corner of spray foam-insulated room where wood-to-wood seams in framing were not air sealed
Insert the new furnace/air handler filter in the filter slot of the furnace or air handler with the arrow pointed in the direction of air flow.
Install all layers of the drainage plane to overlap, not underlap, to direct bulk water down and out of the wall.
Install bottom layer of rigid insulation
Install supply registers in floors or ceilings to avoid routing ducts through exterior walls
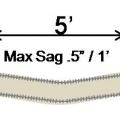
Install supports every 5 feet so that maximum allowable sag in flexible duct is no more than one-half inch per foot
Install supports every 5 feet so that maximum allowable sag in flexible duct is no more than one-half inch per foot
Install the filter media box between the return air plenum and the air handler box
Insulating a crawlspace foundation with “cripple wall” in warm climates; in Climate Zones 5+ replace the foil- or plastic-faced fiberglass batt/roll insulation with impermeable rigid insulation or closed-cell spray polyurethane foam
Insulating sheathing is extended up to the roof rafters and sealed around the framing with spray foam as part of this exterior wall retrofit
Insulation was added to the walls and ceiling of this existing home from the inside as part of an extensive retrofit to avoid replacing original 1-inch shiplapped sheathing.
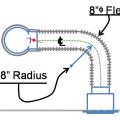
Lay out duct so that no radius of a bend or turn is less than the diameter of the airway
Leaks at the air filter cover panel can draw in unconditioned or undesirable air
Ledger board, metal brackets, and vertical 2x4s have been installed in preparation for exterior spray foam in this retrofit exterior wall insulation technique
Limited attic access can make inspections for missing air barriers and insulation challenging
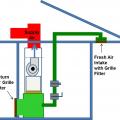
Locate the fresh air intake away from pollution sources and in an easily accessible location
Most residential heat pumps are installed incorrectly and with energy-wasting faults.
Open floor trusses used as return air plenums can draw air from any place connected to that floor
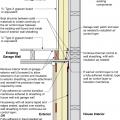
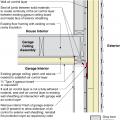
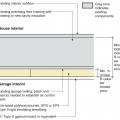
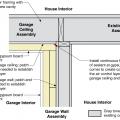
Plan view (from above) showing how the existing garage wall gypsum board is cut away to air-seal the shared wall before adding rigid foam insulation on the garage and exterior walls of the home.
Pulling flex duct taut when installing greatly reduces the amount of friction caused by the ducting
Quality installation and commissioning are critical to optimizing heat pump performance.
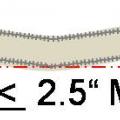
R-6 flexible duct has 2 inches of insulation around the inner liner so a 12-inch duct requires a 16x16-inch chase
Remove the plastic wrap, but not the cardboard frame, before installing the furnace/air handler filter in the filter slot or above the return grate; note, the metal wire over the filter fabric can be very sharp.
Right - Aluminum accordion coverings are permanently installed and can be deployed quickly but must be manually closed from the outside.
Right - Aluminum or polycarbonate panels attach to permanently mounted railings and require installation from the exterior.
Right - Baffles are installed in attic to keep blown insulation from blocking soffit vents and ventilation path
Right - Blown insulation in existing attic provides even coverage completely filling the attic space to a depth that covers the ceiling joists.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam covers the ceiling and joists to insulate and air-seal the ceiling deck.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam covers the interior of the foundation wall and wall framing is placed to the inside of the spray foam.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam is used to retrofit an existing rubble basement foundation wall.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam was applied to the interior of a foundation wall.
Right - Foil-faced polyisocyanurate rigid foam is attached to the existing exterior wall with vertical wood furring strips
Right - Install backflow prevention devices on plumbing pipes to prevent wastewater from entering the home's plumbing system.
Right - Panels of 7/16-inch treated plywood are inexpensive but take time to install and are difficult to install on higher windows.
Right - Retrofit of an existing basement slab by adding dimple plastic mat, rigid foam insulation, and a floating subfloor.
Right - Rigid foam slab edge insulation is installed along the exterior edge of a monolithic slab foundation.
Right - Spray foam insulation air-seals the ceiling-to-drywall seams at the wall top plate.
Right - Spray foam insulation has been sprayed onto the underside of the sloped roof and the gable end wall to provide a sealed, insulated attic for housing the HVAC ducts
Right - The wall top plates are sealed with foam before installing insulation on the ceiling deck.
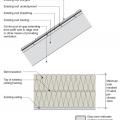
Right - These roof insulation panels are installed in multiple layers with joints offset both vertically and horizontally. The plywood nail base fastened to the roof framing holds the insulation layers together snuggly thus minimizing gaps
Right - This foil-faced polyisocyanurate rigid foam is installed on an existing exterior wall and the seams are taped so the rigid foam can serve as a water control layer
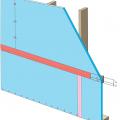
Right - XPS foam insulation is attached to the existing exterior wall with wood furring strips that serve as a nail base for the siding and are installed vertically to allow for drainage and drying behind the siding
Right – an instructor shows a student how to cut batt insulation around wiring rather than compressing the batt behind the wiring.
Right – Flex ducts are properly supported with straps that don’t pinch the insulation; closed-cell spray foam will be applied to the underside of the roof deck of this hot-humid climate home to provide an insulated attic space for the HVAC ducts.
Right – HVAC furnace filter is properly installed in cabinet with gasketed cover to prevent air leakage
Right – Photovoltaic solar panels are ready for installation on the roof of a DOE Zero Energy Ready certified home.
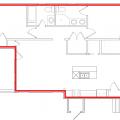
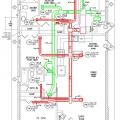
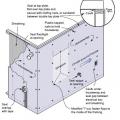
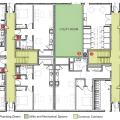
Right – Possible Heat Pump Water Heater Locations on a Multifamily Floorplan including an interior corridor, eight apartments, and meeting rooms
Right – Possible Heat Pump Water Heater Locations on a Multifamily Floorplan including interior corridor closets, under-stair closes, and utility rooms
Right – Possible Heat Pump Water Heater Locations on Full Plate Floorplan in a Multifamily Building
Right – Spray foam insulation is sprayed on the underside of the roof deck to provide a conditioned space in this low attic for the HVAC ducts.
Right – Subfloors are installed in a clean, dry, well-lit factory setting for these modular, factory-built homes.
Right – The walls of this home were constructed with “insulated studs” fashioned on site by adding 2-inch-thick strips of rigid foam to the inside face of 2x4 studs then topping that with a plywood nailing surface.
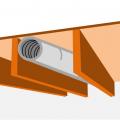
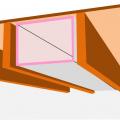
Right – This attic knee wall and the floor joist cavity openings beneath it are being sealed and insulated with spray foam.
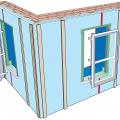
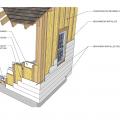
Right – This home’s above-grade walls are constructed in a factory where wall panels of 2x6 studs are assembled and sheathed with a coated OSB product, then windows are installed and flashed before shipping the panels to the site for assembly by crane.
Right – Walls, windows, and wiring are installed in the factory for these modular homes, which are installed at the site on basement foundations made of insulated concrete wall panels.
Right – Windows are installed and flashed in the factory for these modular homes.
Right-- IR photo shows how effectively spray foam insulated/air sealed attic kneewall and the floor cavities under kneewall
Right--The polyethylene ground cover for this insulated crawlspace is taped at seams and around posts before the insulation and slab are installed.
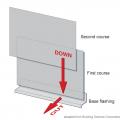
Right: Flashing the butt joints in lap siding installations is a better practice than relying on caulk to seal the joints.
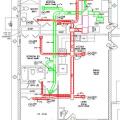
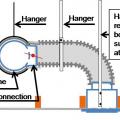
Right: Maintenance valves are installed at the inlet and outlet of this central heat pump water heater
Right: This heat pump water heater is in a basement within the thermal boundary but not actively conditioned. It has over 770 ft² of space with easy access to the control panel and clearance for airflow to the air intake (top) and exhaust (side)
Right: This heat pump water heater is installed in a small space so the, intake air is ducted from an adjacent room; the water heater since on a pad of foam insulation and has a good drain line configuration but the waterpipes lack insulation
Right: This heat pump water heater is installed in a utility closet where it can use heat from the clothes washer and heat pump clothes dryer and has access to a floor drain for condensate
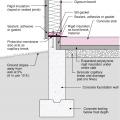
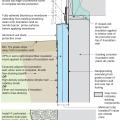
Rigid foam forms an insulating bond break between the foundation wall and the slab
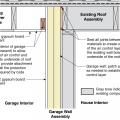
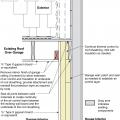
Rigid foam insulating sheathing installed over an existing garage ceiling with retrofits to air seal exterior wall before adding exterior wall insulating sheathing
Rigid foam insulating sheathing is installed on existing garage ceiling and covered with a new gypsum board fire protection layer installed over the foam.
Rigid foam insulation and a thin slab were installed over the dirt and gravel of this sealed crawlspace
Rigid foam insulation is installed on the garage side of the shared garage wall and roof of an existing home
Rigid insulation and water control layers are installed on the exterior of a flat foundation wall; spray foam insulates the rim joist
Run-out ducts are installed over partition walls
Seal the drywall to top-plate seams and the lower edge of baffles to the top plate to prevent the air coming from soffit vents from flowing under baffles into insulation.
Side view showing air-sealing and rigid foam insulation is installed over existing wall and ceiling under a room above, then covered with new gypsum board.
Side view showing how the existing garage wall and ceiling are air-sealed prior to installing rigid foam insulation on the garage side of the shared wall of an existing home.
Siding has been removed so cellulose insulation can be dense-packed into the exterior walls of this home
Single framed wall converted to double wall and insulated with closed-cell spray foam and loose-fill fibrous insulation
Sleepers (tapered wood furring strips) are installed over the existing board sheathing to slope the new sheathing toward the drain in this flat roof retrofit
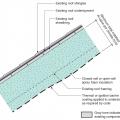
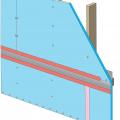
Sloped roof with cavity spray foam insulation sprayed on underside of roof deck and covered with sprayed-on thermal or ignition barrier coating.
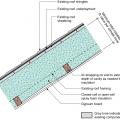
Sloped roof with cavity spray foam insulation, strapping, and gypsum board thermal barrier
Some builders create pan joists by attaching a solid sheet good to the bottom of a floor joist to create a return air pathway
Spray foam extends down the foundation wall to the slab, which has been retrofitted by adding dimple plastic drainage mat and rigid foam insulation.
Spray foam extends down the inside of the foundation wall to the uninsulated slab; because the wall lacked exterior perimeter drainage, the slab was cut and an interior footing drain was installed.
Spray foam insulation extends down the foundation wall to the slab, which has been retrofitted by cutting the slab to install drainage mat against the wall and a new perimeter footing drain, along with rigid foam plastic above the slab.
Spray foam insulation is installed in open wall cavities to air seal and insulate
Spray foam is installed between new studs over the existing siding in this deep energy retrofit
Straps are spaced too far apart causing the straps to compress the duct under its own weight
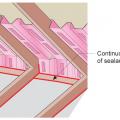
Tape horizontal joint with minimum 3" wide tape placing tape offset high on the joint, adhearing to the upper sheet without wrinkles
Tape the joint between the top insulation sheet and the Z-flashing with 2" wide tape to improve air tightness
Terminate 4" tape with 2" wide tape placing tape offset high on the joint, 2/3 of the tape should be adhered to the sheet of insulation
The attic kneewall and the open floor cavities under kneewall are both sealed and insulated in one step with spray foam insulation
The drywall above the dropped ceiling duct chase extends beyond adjoining top plates for a continuous air barrier
The furnace filter slot cover should fit tightly to minimize air leakage but it should not be taped or caulked to enable frequent filter replacements.
The original corner seam is air-sealed with caulk, then rigid foam is installed on the existing garage ceiling and walls, and finally covered with drywall.
The PNNL Quality Install Tool simplifies and standardizes the documentation of HVAC installations and efficiency upgrades through photo-based prompts
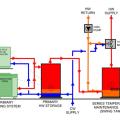
This central heat pump water heating system with a hot water circulation loop that returns to the primary storage tank relies on a single pass heat pump to provide both primary DHW heating and hot water circulation temperature maintenance
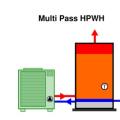
This central heat pump water heating system with a hot water circulation loop that returns to the primary storage tank relies on a multi pass heat pump to provide both primary DHW heating and hot water circulation temperature maintenance
This fully packaged/skid-mounted central heat pump water heating system was shipped to the building on a truck and craned into location
This fully specified central heat pump water heating system has four individual outdoor heat pump units plumbed in parallel to indoor storage tanks
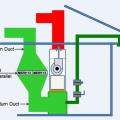
This mechanical room contains both the storage tanks (right) and heat pumps (left) of a central heat pump water heating system
This new filter is inserted into furnace filter slot on the return side of the furnace with the arrow on the side of the filter frame pointing in the direction of airflow, which is toward the furnace.
This packaged central heat pump water heating system has the heat pumps on the exterior of the blue enclosure, and the storage tanks, temperature maintenance equipment, mixing valve, and control modules on the inside
This retrofit central heat pump water heater system utilizes the existing water heater as a swing tank to provide temperature maintenance for the hot water circulation loop
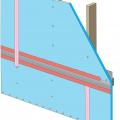
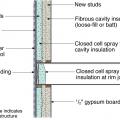
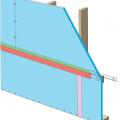
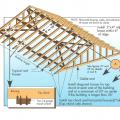
Three inches of closed-cell spray foam (R-19) and 7.5 inches (R-28) of open-cell spray foam was installed below the roof sheathing in this cathedral ceiling.
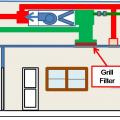
To increase surface area and reduce pressure drop for high MERV filters, the return duct can be constructed to permit the installation of two furnace filters side by side
Types of heat pump water heaters commonly used in central heat pump water heating systems include single pass units, multi pass units, and integrated units
Unfaced fiberglass batt insulation is installed to completely fill the wall cavities and is sliced to fit around wiring, piping, and other obstructions in the wall cavities
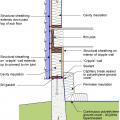
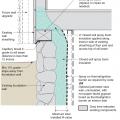
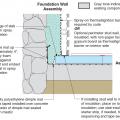
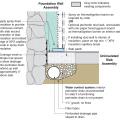
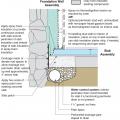
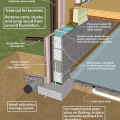
Unvented concrete masonry unit crawl space with exterior insulation - designed for termite resistance in moderately infested areas
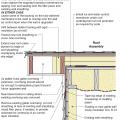
Unvented roof assembly at eave retrofitted with rigid foam, spray foam, and a fully adhered membrane seal at the top of wall-to-roof transition
Unvented roof assembly at eave retrofitted with rigid foam, spray foam, and taped top edge of existing house wrap or building paper
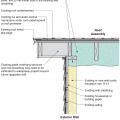
Unvented roof assembly at rake retrofitted with a filler piece and taped top edge of existing house wrap or building paper to seal the top of wall-to-roof transition
Unvented roof assembly at rake retrofitted with spray foam installed along the underside of the roof deck and extended to the rake edge to insulate and air seal the attic