Showing results 401 - 500 of 578
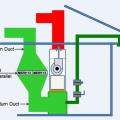
The dehumidifier draws air from a common area in the house, dehumidifies it, and adds it to the supply side of the central air handler for mixing and distribution
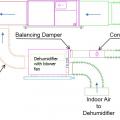
The dehumidifier draws air from both a common area in the house and from outside, dehumidifies it, and adds it to the supply side of the air handler for distribution
The drain pans sit below the cooling coil to catch condensate and direct it to a drain line
The drywall above the dropped ceiling duct chase extends beyond adjoining top plates for a continuous air barrier
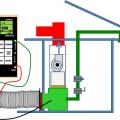
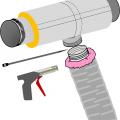
The duct sealing spray injection system application tunnel inflates as the injection system operates
The duct sealing spray injection system includes a blower/heater (background) and the sealant injection unit (foreground)
The ducts are located in conditioned space in open-web joists between the floors and supported to prevent sagging.
The edge of this 1-inch HVAC filter indicates it's dimensions, allowing proper matching of filter to air handler
The ENERGY STAR logo on the manufacturer’s label indicates this is an ENERGY STAR qualifying exhaust fan
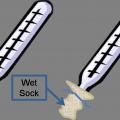
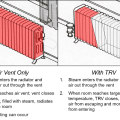
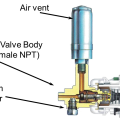
The exposed riser shown here also supplies the radiator. A short pipe runs under the floor to the hand valve.
The gap around this kitchen exhaust duct represents a significant source of air leakage to the unconditioned attic
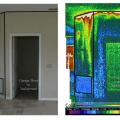
The grille in the photo on the left brings air into a return air plenum under an air handler platform. As shown in the infrared image on the right, the plenum is not air sealed so hot attic air is being pulled into the air handler closet.
The high-efficiency air-to-air heat pump is set in an overflow pan with an emergency shut off sensor in case the condensate tube were to clog and cause condensate to fill up the pan.
The high-efficiency mini-split heat pump provides cooling and heating; a drain pipe carries condensate away to a location that meets local code requirements.
The HVAC equipment's condensate drain pan is equipped with a water-level detection device that will shut off the equipment if the water level pan in the pan gets too high
The individual exhaust systems for each dwelling unit in this multifamily building result in large numbers of penetrations in the exterior façade
The manufacturer’s label found on this exhaust fan housing shows a sone rating of 1.0
The mechanical room in the insulated basement houses the water heating equipment, including the storage tank for the solar thermal system and the wall-hung boiler as well as the air handler for the hydro coil and high-efficiency (16 SEER) air conditioner.
The MERV rating, particle capture efficiencies, and pressure drops are printed on the side of this 1-inch pleated filter
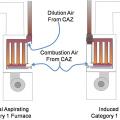
The natural draft and induced draft furnace are both Category I appliances that receive combustion air from the combustion appliance zone
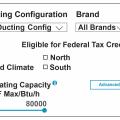
The NEEP Cold Climate Air Source Heat Pump List allows users to search, sort, and filter for cold climate heat pumps by brand, model, product type, and ducting configuration; an advanced search provides helpful resources for sizing to the heating load
The raised hood at the base of the vent stack on this water heater shows that it is an atmospheric vented gas water heater
The tape is covered with mastic to ensure an airtight seal between the duct and the fitting
The trash chute and trash room in a multistory multifamily building are depressurized with exhaust fans to minimize odors.
The ultra-efficient air-to-water heat pump draws heat from the outside air to heat inside room air in winter and domestic hot water year-round.
The ultra-efficient ground source heat pump (COP 4.4) delivers conditioned air throughout the home via ducts; an ERV provides fresh air to the system.
The ventilation controller is next to the thermostat and has a manual override button
The very high efficiency (4.7 COP) ground-source heat pump provides hot water to a tank for radiant floor heat and domestic hot water.
These ducts were installed within the home's conditioned space in a central chaise down the main hallway.
These plots compare sizing approaches in terms of the approximate annual heating load a heat pump might carry throughout the year for a hypothetical home in Minneapolis, MN.
This “high static ducted cassette” heat pump system is similar to a traditional centrally ducted system, serving several areas of a home from one indoor unit
This air handler is located within the homes conditioned space in a closet on the main floor of the home (Source: Tommy Williams Homes).
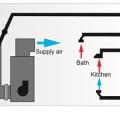
This air handling unit provides outside air at the same rate as the air being exhausted from the bathroom exhaust fan; local kitchen exhaust is provided by a range hood with a dedicated makeup air intake and dehumidification is provided by a separate unit
This bath exhaust fan ventilation control can be set by the HVAC technician for continuous operation, delayed shut off, or a set amount of minutes each hour
This central ventilation system uses an energy recovery ventilator, pre-conditioning unit, and elevator shaft exhaust fan to supply air to dwelling units and corridors and to exhaust air from units and the elevator shaft in a multifamily building
This depiction of a saddle installed window heat pump does not obstruct window use and provides fairly quiet 120 Volt operation
This dropped soffit runs the length of the house providing a convenient place to locate one trunk duct with several very short side ducts that supply heat and cooling to most rooms of the house.
This ducted mini-split heat pump was installed in the unvented, conditioned attic and ducted with short duct runs to several nearby rooms.
This ducted, wall-mounted range hood exhaust fan replaced a recirculating fan that did not adequately remove kitchen contaminants.
This ductless wall-hung indoor unit has supplemental air filters (outlined in red), which only filter a portion of the airflow; most of the air bypasses the supplementary filters and only passes through the standard mesh filters.
This energy recovery ventilator (ERV) provides balanced ventilation to a dwelling unit in a multifamily building
This home’s balanced fresh air system includes a filtered fresh air intake that is wired to the central HVAC system with timer controls while exhaust fans in the kitchen, bathrooms, and laundry room pull stale and moist air from the home.
This home’s domestic hot water is provided by three systems: solar water heating panels, a heat pump water heater, and an air-to-water heat pump, which also provides hot water to a fan coil.
This home’s ultra-efficient ground-source heat pump provides hot water for space heating as well as domestic hot water for the 50-gallon storage tank.
This HRV, installed in a conditioned attic, provides balanced ventilation to the whole home
This is the compact outside unit for an ultra-efficient air-to-water heat pump (COP 4.1) that provides space heating and domestic hot water.
This MSHP operates with 120 volts power, has an EER of 18 Btu/Wh, uses about 800 W at full output, and operates remotely with a smart home control system
This multi-split heat pump system incorporates several indoor units connected to just one outdoor unit; the indoor units include a wall-mounted unit, floor-mounted, ceiling cassette, and mini-air handler.
This plot shows a heat pump’s minimum and maximum cooling capacities overlaid with a home’s cooling load line, allowing a designer to assess how well-suited the equipment is for the specific home.
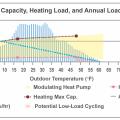
This plot shows a heat pump’s minimum and maximum heating capacities overlaid with a home’s heating load line as well as the annual heating load hours for the home, allowing a designer to assess how well-suited the equipment is for the specific home.
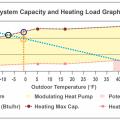
This plot shows a heat pump’s minimum and maximum heating capacities overlaid with a home’s heating load line, allowing a designer to assess how well-suited the equipment is for the specific home.
This plot shows a heat pump’s minimum and maximum heating capacities overlaid with a home’s heating load line, allowing a designer to assess how well-suited the equipment is for the specific home.
This single-zone mini-split ductless heat pump has only one indoor wall-mounted unit and one outdoor unit.
This traditional centrally ducted heat pump heats and cools the entire home through a network of ducts.
This typical dropped ceiling hallway chase shows a complicated air sealing scheme where chase ceiling drywall meets sidewall top plates
This upflow air handler for a traditional heat pump has an electric resistance auxiliary heating element located at the top of the unit (circled in red).
This utility room houses a high-efficiency gas boiler to provide hot water for the radiant floor heating system and faucets. It also has a central air source heat pump and an energy recovery ventilator.
This wall-hung ductless indoor mini-split heat pump contains a fan, filter, and heating/cooling coil just like a traditional central air handler for a ducted heat pump system
To attach the flex duct to a main trunk duct or any other connection, the flex duct is pulled over the connecting collar at least 2 inches past the raised bead, then the insulation is pulled back
To increase surface area and reduce pressure drop for high MERV filters, the return duct can be constructed to permit the installation of two furnace filters side by side
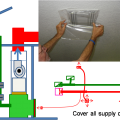
To prepare for a total duct test at final, cover all of the supply outlets and return inlets
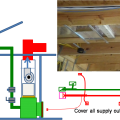
To prepare for a total duct test at rough-in, cover all of the supply outlets and return inlets
Transfer grills and jump ducts provide pathways for air to reach the centrally located HVAC return grille, even when bedroom doors are shut.
Transom returns are installed over interior doors to provide a pathway for return air
Trunk to duct connections are properly insulated and have been sealed with mastic
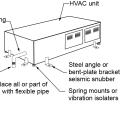
Two L-brackets or seismic snubbers are installed at each corner of the HVAC unit and a vibration isolator or spring mount is installed in each corner to anchor the unit while allowing for slight movement in an earthquake
Two pieces of flex duct are spliced together with a metal sleeve, nylon draw bands, mastic, metal tape, and more mastic
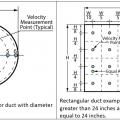
Velocity measurement locations for round and rectangular ducts; velocity measurements should be taken at several locations representative of equal sectional areas across the duct cross-sectional area
Ventilation air comes directly from outdoors, not from adjacent dwelling units, garages, crawlspaces, or attics
Ventilation air inlets ≥ 2 ft. above grade or roof deck in Climate Zones 1-3 or ≥ 4 ft. above grade or roof deck in Climate Zones 4-8 and not obstructed
Ventilation air inlets located ≥10 ft. of stretched-string distance from known contamination sources such as stack, vent, exhaust hood, or vehicle exhaust
Ventilation air inlets provided with rodent / insect screen with ≤ 0.5 inch mesh