Showing results 251 - 300 of 354
These factory-built walls consist of 9.5-inch I-studs sheathed with coated OSB, faced with OSB, and dense-packed with cellulose; a second interior surface of drywall is added to provide a 1.5-inch cavity for electrical wiring.
This 2x6 wall is advanced framed and filled with dense-packed cellulose insulation.
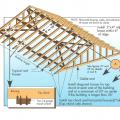
This Habitat for Humanity builder ordered roof trusses with a 2-foot by 2-foot notch next to the center post then lined the cutout with rigid foam to form an insulated central duct chase to bring the heating and cooling ducts within the conditioned space.
This home is framed with post-and-beam construction and 7-inch wall cavities that will be filled with blown-in fiberglass insulation.
This home’s double-wall construction provides a 9-inch wall cavity for insulation.
This home’s double-wall structure consists of two 2x4 walls set two inches apart, then sheathed on the exterior and netted on the interior to create a 9.5-inch wall cavity that is filled with blown fiberglass insulation.
This hot climate zone home uses high quality batt insulation between studs to insulate this connecting garage wall.
This hot climate zone home uses high quality batt insulation to insulate truss-joist headers.
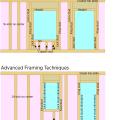
This house is being built with advanced framing techniques including 2x6 24-inch on-center wall framing
This Kalamazoo Habitat for Humanity affiliate installs one layer of foam exterior of the studs and a second layer in between the staggered studs which are set only 2 inches apart to simplify the installation of additional fiberglass batt insulation.
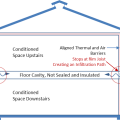
This kneewall has no top plate and the resulting gap provides a wide-open pathway for air and vapor to travel between the living space and the attic
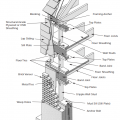
This wood-framed wall is connected with framing anchors, metal strapping and ties, and anchor bolts to secure the roof to the walls and walls to the foundation
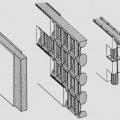
Three common ICF wall systems: the flat wall, the waffle wall, and the post-and-beam wall
To keep chase width to a minimum, use flat sheet metal as opposed to a collar and flex duct for supplies into rooms where the chase is located
Two layers of rigid foam are sandwiched between three layers of lumber to provide a thermal break in the headers above doors and windows.
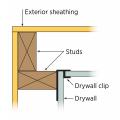
Two-stud corner using drywall clips; detail shows nail placement for exterior trim
Two-stud corners with drywall clips use the least wood and give the best thermal performance
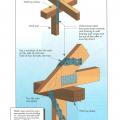
Typical hurricane strap to roof framing detail. Rafter or prefabricated roof truss.
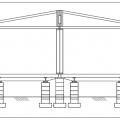
Typical installation of a double section modular home on a pier and ground anchor foundation
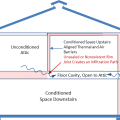
Uninsulated, unsealed, or missing rim joists allow attic air and heat into the floor cavity
Unsealed, uninsulated rim joists allow outside air and heat into the floor cavity
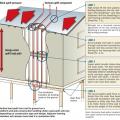
Uplift forces acting on the roof are met with roof-wall connections that distribute the forces down the walls and into the foundation along the continuous load path.
Use a truss joist header assembly as shown here to reduce thermal bridging in hot climate zones.
Utilities are commonly recessed into cutouts in the foam after concrete has been poured
When adding an addition to an existing home, the new construction must meet current code.
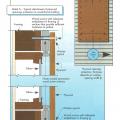
When condensation forms on the interior side of wall sheathing and is not able to dry out, it can lead to mold growth and rotting of wall sheathing and framing
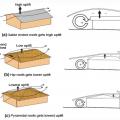
Wind path and uplift force for a gabled roof, a hip roof, and a pyramidal (another variant of a hip) roof design
Window and door rough openings in the ICF wall are surrounded with pressure-treated wood
Windows are installed in new framing in preparation for adding exterior spray foam insulation
Windows are sized and positioned so only one king stud is needed on each side of the window.
Wrong - Board is not properly cut and is split where it is toenailed into top plate.
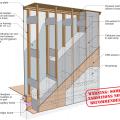
Wrong - Cantilevered floor joist bay cavities are not air sealed with a solid air barrier aligned with the exterior wall.
Wrong - Cantilevered joist bay cavities are not air sealed with a solid air barrier, allowing outside air to flow between floors.