Showing results 151 - 200 of 220
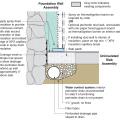
In cold climates, install slab edge insulation when pouring slab on grade foundations.
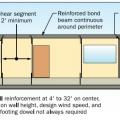
In high wind areas, provide lateral support to masonry end walls to resist high winds.
In high-wind regions, special hardware is used for most framing connections; toe-nailing is not acceptable.
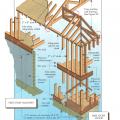
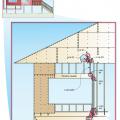
Key connection points for a continuous load path for earthquake and high wind disaster resistance
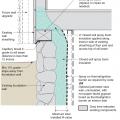
Lower-story wall anchorage to masonry (or concrete) base. Straps properly nailed at wall studs.
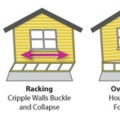
Possible failure scenarios due to house sitting on poorly braced and secured cripple wall
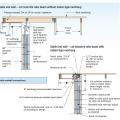
Properly reinforce masonry walls in coastal locations to resist high winds and waves.
Right - A continuous load path connects the roof and wall framing to the foundation.
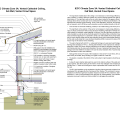
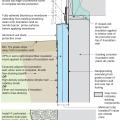
Right - Basement slab with a capillary break of either gravel or a drainage mat.
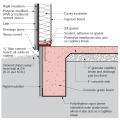
Right - Below-grade concrete has been properly sealed against moisture and is now having insulation installed.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam covers the interior of the foundation wall and wall framing is placed to the inside of the spray foam.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam is used to retrofit an existing rubble basement foundation wall.
Right - Closed-cell spray foam was applied to the interior of a foundation wall.
Right - Permeable rigid mineral wool insulation and appropriate water-management flashing details are integrated with new rigid foam siding to keep water away from the sill beam above the foundation wall
Right - The slab-on-grade foundation is insulated with two layers (R-20) of XPS foam under the-slab and R-10 on the exterior of the stem walls.
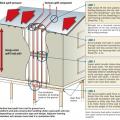
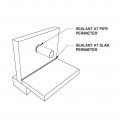
Right – Apply sealant around penetrations through foundation walls and along foundation wall seams
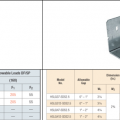
Right – Examples of wall stud to sill plate and foundation and wall rod connectors and brackets.
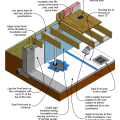
Right – Polyethylene sheeting vapor barrier is installed and sealed to the crawlspace walls with mastic
Right – The insulated concrete forms that are below-grade have a damp-proof coating to prevent moisture seeping into the foundation
Right – The raised-slab, brick-and-block stem wall, above-grade walls, and roof of this house use flood damage-resistant materials, integrated water, vapor, and air control layers, and construction methods which promote good drainage and rapid drying
Right – The raised-slab, CMU block stem wall, above-grade walls, and roof of this house use flood damage-resistant materials, integrated water, vapor, and air control layers, and construction methods which promote good drainage and rapid drying
Right – The raised-slab, poured-concrete stem wall, above-grade walls, and roof of this house use flood damage-resistant materials, integrated water, vapor, and air control layers, and construction methods which promote good drainage and rapid drying
Right – Walls, windows, and wiring are installed in the factory for these modular homes, which are installed at the site on basement foundations made of insulated concrete wall panels.
Rigid insulation and water control layers are installed on the exterior of a flat foundation wall; spray foam insulates the rim joist
Shear Strength Comparison Between a Foundation Stud Anchor (on left) and a Shear Transfer Angle (on right)
Spray foam extends down the inside of the foundation wall to the uninsulated slab; because the wall lacked exterior perimeter drainage, the slab was cut and an interior footing drain was installed.
Structural insulated panels offer a continuous layer of thermal protection and draft resistance around the home and come from the factory precut for fast assembly.
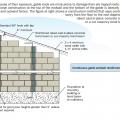
Stucco is installed over rigid insulation, which is installed over a drainage plane consisting of a drainage gap and building wrap layer over the sheathing
The components of a framed wall include from inside to out: gypsum, wood studs, OSB or plywood sheathing, and siding.
The cripple wall hiding the post-and-pier foundation of this wood framed house toppled when the house was shifted partially off its piers by an earthquake
The Habitat affiliate makes its own “ICF” foundation walls with rigid foam held in place with wood spacers.
The sheathing has rotted because there was not a sufficient drainage gap behind the stucco cladding